Modal Auxiliaries Worksheets
All About These 15 Worksheets
These Modal Auxiliaries worksheets are educational resources for teachers that seek to help their students understand and practice the use of modal auxiliary verbs in English. Modal auxiliary verbs are a type of auxiliary verb that express various degrees of ability, possibility, permission, obligation, and necessity.
These worksheets include various exercises and activities, such as fill-in-the-blank questions, sentence completion activities, multiple-choice questions, writing exercises, and more, which all allow students to practice using modal auxiliary verbs correctly. The first few worksheets in this collection also provide examples and explanations of different types of modal auxiliary verbs, such as can, could, may, might, must, should, and would. This helps teachers in introducing the topic to students to build their basic knowledge for this lesson first.
Through these worksheets, students can improve their ability to recognize and use modal auxiliary verbs correctly, which is essential for effective communication in English. Modal auxiliary verbs are used in a variety of sentence structures, and they are commonly found in both spoken and written English. By completing these worksheets, students will:
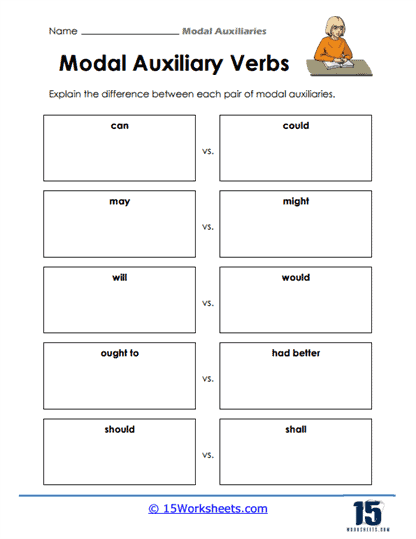
- Understand the function and usage of different modal auxiliary verbs such as: can and could, may and might, will and would, should and shall, ought to and had better, must and have to;
- Identify the the correct modal auxiliaries that need to be added to incomplete sentences;
- Explain in their own words the differences between each pair of modal auxiliaries;
- And construct their own sentences using modal auxiliaries.
In summary, these worksheets on Modal Auxiliaries provide opportunities for students to develop their critical thinking and decision-making skills. By understanding the meaning and usage of different modal auxiliary verbs, students can make informed choices about what actions to take in different situations.
What are Modal Auxiliaries and why do they matter?
Modal auxiliaries are a type of auxiliary verb that express various degrees of ability, possibility, permission, obligation, and necessity. They are used to modify the main verb in a sentence and indicate the speaker’s attitude towards the action being described.
The following are some common pairs of modal auxiliaries, along with their definitions and examples:
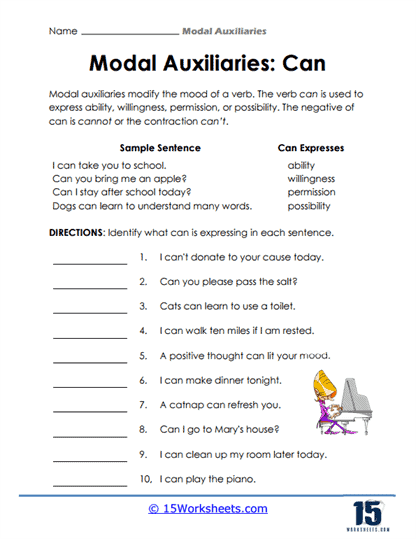
- Can and Could – “Can” expresses ability, while “could” expresses past ability or possibility. Example: “I can swim in the pool,” and “When I was younger, I could swim faster.”
- May and Might – “May” expresses possibility, while “might” expresses a more remote or uncertain possibility. Example: “It may rain tomorrow,” and “If I study hard, I might get an A on the test.”
- Will and Would – “Will” expresses future certainty or determination, while “would” expresses a hypothetical situation or willingness. Example: “I will meet you at the park tomorrow,” and “If I had the time, I would go to the concert.”
- Should and Shall – “Should” expresses advice or obligation, while “shall” expresses future intention or obligation. Example: “You should study for the exam,” and “I shall attend the meeting tomorrow.”
- Ought to and Had Better – “Ought to” expresses moral obligation, while “had better” expresses strong advice or warning. Example: “You ought to apologize for your mistake,” and “You had better be careful when crossing the street.”
- Must and Have to – “Must” expresses strong obligation or necessity, while “have to” expresses external obligation or necessity. Example: “I must finish this report by tomorrow,” and “I have to go to work every day.”
Overall, understanding and using modal auxiliaries correctly is crucial for effective communication in English, as they are used frequently in both spoken and written language.