Plurals Worksheets
All About These 15 Worksheets
This collection of plurals worksheets are designed to help students learn and practice the rules of forming plurals in English grammar. These worksheets provide a variety of exercises that require students to identify and use plurals correctly in sentences.
These worksheets include fill-in-the-blank exercises, identification and matching activities, rewriting tasks, and short writing prompts. They cover a range of pluralization rules, including adding “-s” or “-es” to the end of a word, changing “-y” to “-ies,” using irregular plural forms, and identifying uncountable nouns that do not have a plural form. By accomplishing these worksheets, students will:
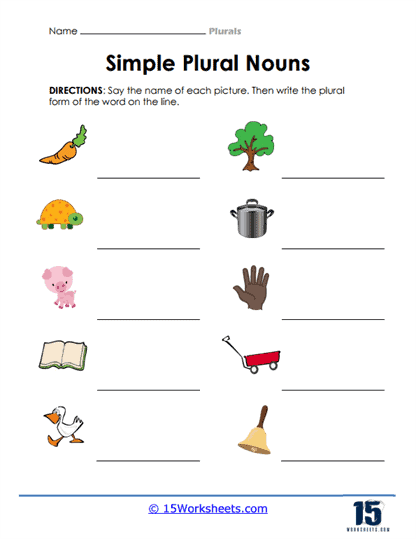
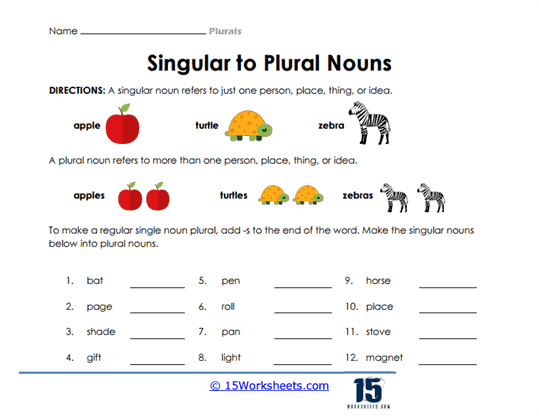
- Determine the plural form of words through visual cues;
- Be familiar with all the pluralization rules and exceptions;
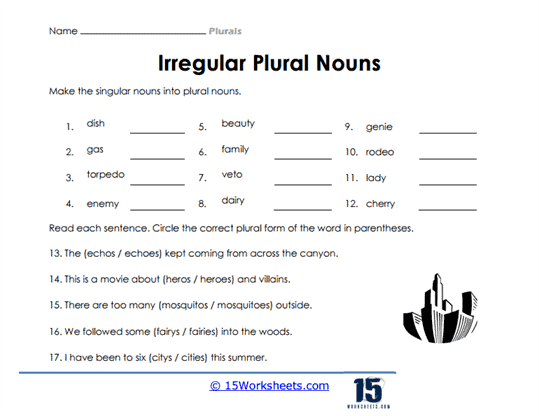
- Expand their vocabulary with irregular plurals;
- Identify non-count nouns;
- Use the plural forms of words correctly in their own sentences;
- And spot errors in sentences that have incorrect usage of plural forms of words and correct them.
Overall, these worksheets are a helpful tool for helping students improve their grammar skills and develop accuracy in their writing. By completing the exercises, students can gain a better understanding of the rules of forming plurals and practice applying them correctly in their writing. They are also useful for reinforcing grammar concepts taught in the classroom and helping students build confidence in their language abilities.
Pluralization and why it matters
Plurals are a type of noun that refer to two or more persons, places, things, or ideas. They are used when referring to multiple entities, as opposed to a single entity. In English grammar, there are several rules for forming plurals.
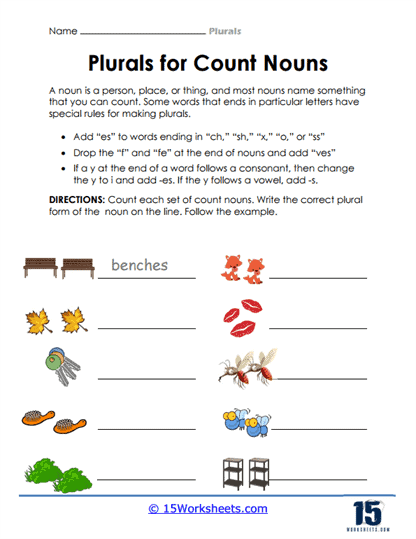
- Count nouns refer to things that can be counted, such as books, dogs, or trees. To form the plural of count nouns, you typically add “-s” to the end of the word. For example:
- Book → Books
- Dog → Dogs
- Tree → Trees
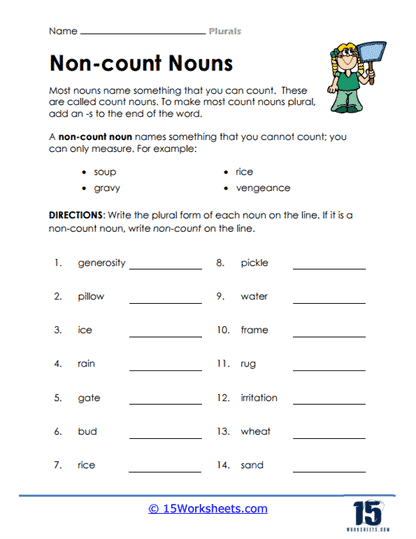
- Non-count nouns refer to things that cannot be counted or quantified, such as water, sand, or air. These nouns do not have a plural form and are considered singular. For example:
- Water (singular, non-count)
- Sand (singular, non-count)
- Air (singular, non-count)
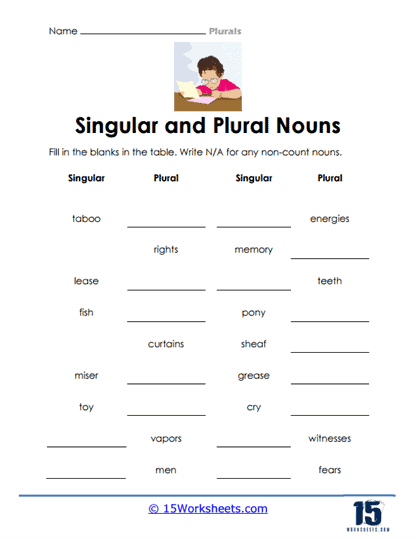
- Some nouns have irregular plural forms that do not follow the typical rules of adding “-s” or “-es” to the end of the word. For example:
- Mouse → Mice
- Goose → Geese
- Child → Children
It’s important to use the correct form of a noun in a sentence to ensure that the subject-verb agreement is correct. For example, the verb form changes depending on whether the subject is singular or plural. For example, we say “the dog barks” (singular) but “the dogs bark” (plural).
In summary, plurals are a type of noun that refer to two or more persons, places, things, or ideas. Count nouns typically add “-s” to the end of the word to form the plural, while non-count nouns are considered singular and do not have a plural form. Irregular plural forms do not follow typical pluralization rules and must be learned individually.