Irregular Verbs Worksheets
All About These 15 Worksheets
This collection of worksheets are designed to help students practice and understand the unique forms of irregular verbs in the English language. These worksheets include exercises and activities that require students to identify and use irregular verbs in sentences.
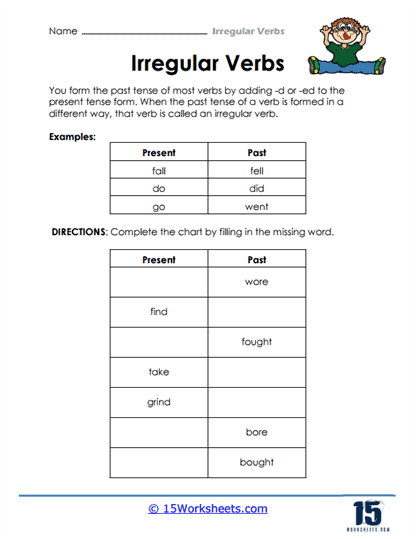
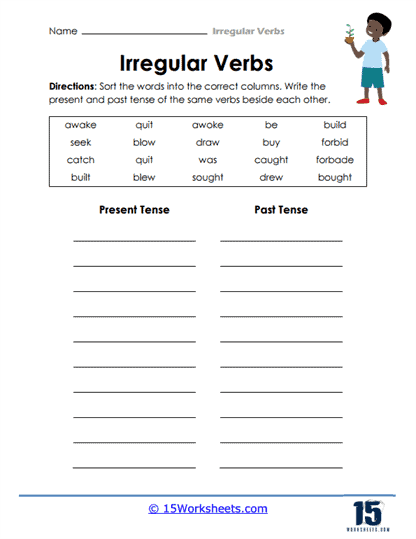
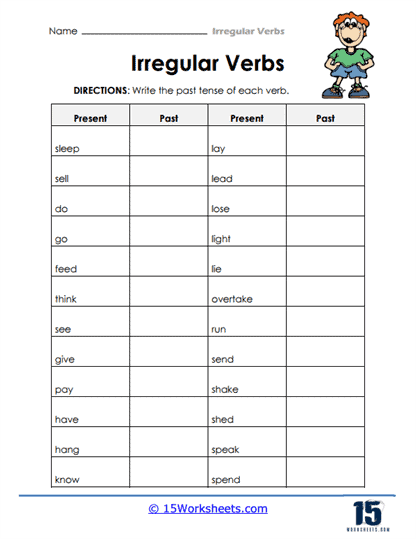
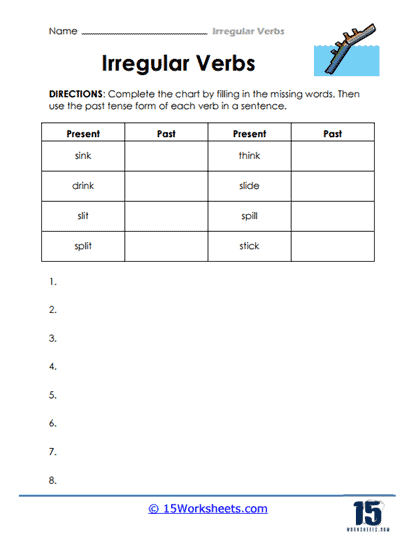
These worksheets provide students with lists of common irregular verbs and their past tense and past participle forms to help them memorize and internalize the irregular verb forms. Some worksheets may also include visual aids to help students expand their vocabulary while getting a better understanding of the patterns and variations of irregular verb forms. Through these worksheets, students will:
- Be familiar with the past and participle forms of irregular verbs;
- Rewrite sentences to change the tenses of their irregular verbs;
- And construct their own sentences using irregular verbs correctly.
By completing these worksheets on irregular verbs, teachers can help their students improve their understanding and use of these important verbs in spoken and written communication. Consistent practice with irregular verbs can help learners build their vocabulary, increase their fluency, and ultimately become more confident and effective communicators in the English language.
What are irregular verbs?
Irregular verbs are verbs in the English language that do not follow the regular conjugation pattern in the past tense or past participle form. Unlike regular verbs, which form their past tense by adding -ed to the base form of the verb (e.g. “walked,” “talked”), irregular verbs have their own unique forms in the past tense and past participle.
Examples of irregular verbs include “go” (went, gone), “eat” (ate, eaten), “write” (wrote, written), and “break” (broke, broken). It is important to learn these irregular verb forms as they do not follow a predictable pattern and must be memorized. With this, here are some tips on how to transform irregular verbs into their past and past participle forms:
- Memorize the irregular verbs – Since irregular verbs do not follow a consistent pattern, the best way to learn them is by memorizing them. There are many irregular verb lists available online, or you can make your own list and practice them regularly.
- Use context clues – Sometimes, the context of the sentence can give you a clue about the past or present form of an irregular verb. For example, if the sentence is in the past tense and the subject is singular, the past tense form of the verb will usually end in “-ed.”
- Use regular verb patterns as a guide – Although irregular verbs do not follow the regular verb pattern, you can use the regular verb pattern as a guide to help you remember the past tense and past participle forms. For example, the past tense of “think” is “thought,” which follows the pattern of adding “-t” to the base form of the verb.
- Practice, practice, practice – The more one practices using irregular verbs in context, the easier it will be to remember their past and present forms. By using irregular verbs in daily conversation or writing, or accomplishing this set of worksheets, mastery on irregular verbs will come naturally.
Remember, mastering irregular verbs takes time and practice, but with dedication and effort, students can become more comfortable using them in both verbal and written communication.