Imperatives Worksheets
All About These 15 Worksheets
These Imperatives worksheets are a useful tool for teachers to help their students learn about imperatives in English. The first worksheet in this collection begins with an introduction to imperatives and their basic form and function. This will include an explanation of how imperatives are used to give commands, make requests, or offer suggestions, such as “share the swing” or “play with me.” By completing these worksheets, students will:
- Transform various sentences into imperatives;
- Answer various writing prompts by providing the appropriate imperatives;
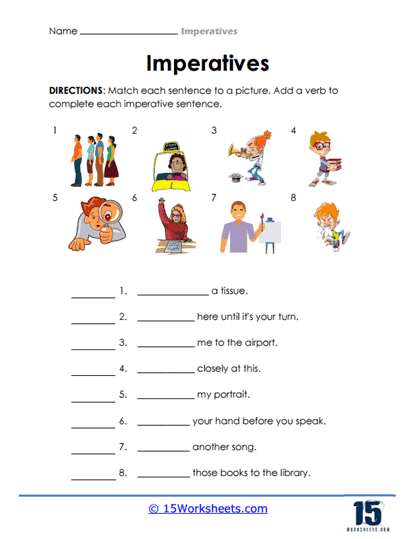
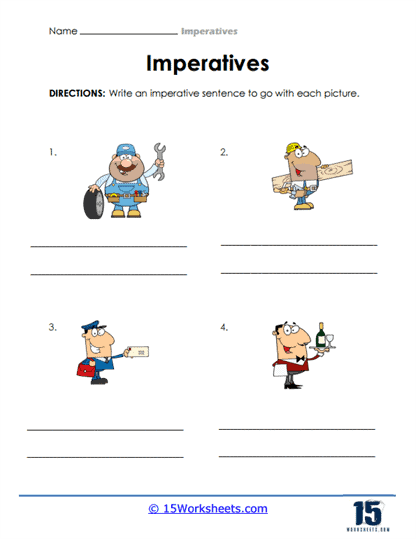
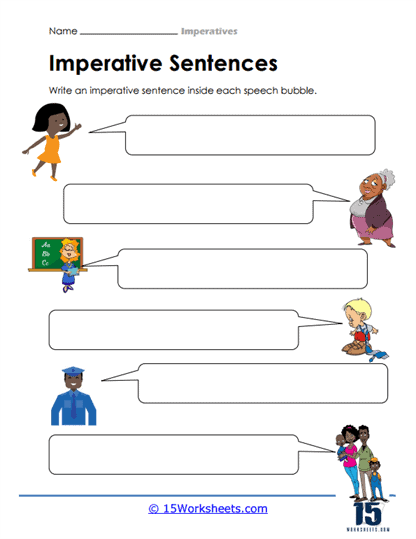
- Create their own imperative sentences that correspond to the given pictures;
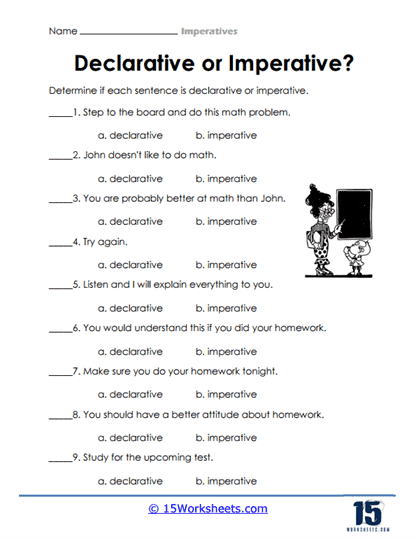
- Distinguish imperatives from interrogatives and declaratives;
- And come up with entirely new sentences that correctly follow the form of imperatives.
Overall, these worksheets are a comprehensive and engaging resource that help students understand and master the use of imperatives in English.
What are Imperatives and why do they matter?
An imperative sentence is a type of sentence that is used to give a command or make a request. It is a sentence that is structured in such a way as to give an order or direction to someone. Imperative sentences are a type of declarative sentence, which means that they make a statement, but the statement is in the form of a command or request.
Imperative sentences are formed by using the base form of a verb without a subject. The subject of the sentence is usually implied, and the sentence is addressed directly to the person being commanded or requested to do something. For example:
- “Open the window.” (command)
- “Please pass me the salt.” (request)
- “Don’t forget to call me.” (command/negative)
In the above examples, the verb “open,” “pass,” and “forget” are used in their base form without a subject. The first sentence is a command, while the second is a request. The third sentence is a negative command, which is formed by adding “do not” or “don’t” before the base form of the verb.
Imperative sentences can be structured differently depending on the context or the tone of the sentence. For example, a polite imperative sentence might include the word “please” before the verb, while a more forceful imperative sentence might use stronger language or include an exclamation point. For example:
- “Please be quiet.” (polite request)
- “Stop talking!” (forceful command)
In summary, an imperative sentence is a type of sentence that is used to give a command or make a request. It is formed by using the base form of a verb without a subject, and can be structured differently depending on the context or tone of the sentence. Imperative sentences are an essential component of English grammar and are used in a wide variety of contexts.
How to distinguish Imperatives from Declaratives and Interrogatives
Imperative sentences, declarative sentences, and interrogative sentences are three different types of sentences in English. Here are some ways to distinguish between them:
- Imperative sentences are sentences that give commands or make requests. They are formed using the base form of a verb without a subject. The subject of the sentence is often implied. Imperative sentences are often structured in such a way as to give an order or direction to someone.
Example: “Close the door.”
- Declarative sentences are sentences that make statements or express facts or opinions. They are formed using a subject followed by a verb and often end with a period. Declarative sentences can be positive or negative.
Example: “The sun is shining.”
- Interrogative sentences are sentences that ask questions. They are formed by inverting the subject and verb, adding a question word (such as who, what, where, when, why, or how), and often ending with a question mark.
Example: “Where is the library?”
In summary, the main way to distinguish between these three types of sentences is by their function. Imperative sentences give commands or make requests, declarative sentences make statements or express facts/opinions, and interrogative sentences ask questions. The structure and word order of each type of sentence also differs, which can help to identify them.