Possessive Pronouns Worksheets
All About These 15 Worksheets
Possessive pronouns are an essential component of grammar, serving to indicate ownership or association with a noun. Mastering their use is crucial for clear, concise communication in both writing and speaking. To facilitate this learning process, these possessive pronouns worksheets offer an invaluable tool for both teachers and students. Designed to teach and reinforce the correct use of possessive pronouns, these worksheets not only present the foundational rules but also provide ample opportunities for practice, ensuring that students grasp the concept fully.
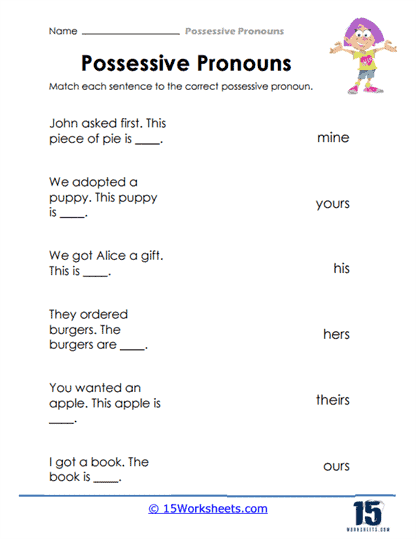
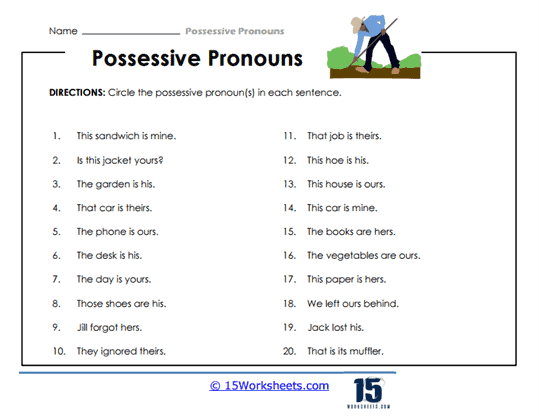
Each worksheet includes a variety of examples and exercises aimed at helping students recognize possessive pronouns within sentences and apply them in the proper context. The activities range from simple fill-in-the-blank exercises, where students insert the appropriate possessive pronoun, to more complex tasks like rewriting sentences to incorporate possessive pronouns. Additionally, matching exercises challenge students to pair pronouns with the corresponding nouns, deepening their understanding of ownership relationships in sentences. By offering this range of activities, the worksheets cater to different learning styles and ensure that students of varying skill levels can benefit from them.
Through consistent practice, students will develop the ability to accurately identify possessive pronouns and associate them with the nouns they modify. This not only enhances their grammatical knowledge but also helps them recognize the differences between possessive pronouns and other types of pronouns, such as subject and object pronouns. Furthermore, students will be encouraged to demonstrate their understanding by completing short writing prompts, where they must use possessive pronouns in their own sentences. This element of personal expression within the exercises reinforces their ability to apply the rules in real-world communication scenarios, making the learning process both interactive and practical.
Beyond simply recognizing and using possessive pronouns in structured exercises, students will also be able to show a deeper understanding of how these pronouns function in different sentence structures. By working through these worksheets, they gain confidence in using possessive pronouns correctly in both written and spoken language. Such proficiency is vital for effective communication, as the ability to express ownership clearly can prevent misunderstandings and enhance the overall clarity of one’s message.
For educators, these worksheets are more than just a teaching resource; they also serve as an effective assessment tool. By reviewing students’ responses, teachers can gauge each student’s comprehension of possessive pronouns and identify areas where additional instruction might be needed. This targeted feedback allows teachers to tailor their lessons more effectively, ensuring that each student can improve their usage of possessive pronouns over time. Whether used as part of a daily grammar lesson or as a review activity, these worksheets are a flexible, practical resource that can significantly aid in the development of students’ linguistic abilities.
What Are Possessive Pronouns?
Possessive pronouns are a type of pronoun that show ownership or possession of a noun or pronoun. They are used to indicate that something belongs to someone or something else.
Here are some examples of possessive pronouns:
- My, mine – “This is my book.” “The red pen is mine.”
- Your, yours – “Is this your coat?” “Those shoes are yours.”
- His – “That is his car.”
- Her, hers – “The bag is hers.”
- Its – “The bird flapped its wings.”
- Our, ours – “Our house is on the corner.” “These seats are ours.”
- Their, theirs – “The dogs are theirs.” “The pencils belong to them, they’re theirs.”
Notice how possessive pronouns can either stand alone or modify a noun. When they stand alone, they often come at the end of a sentence. For example, “The book is mine.”
Common Errors To Avoid
Possessive pronouns can be tricky, and many students frequently make avoidable mistakes when using them in writing or speaking. Teachers can play a crucial role in helping students recognize these common errors, which will significantly improve their grasp of grammar and communication skills. Understanding these errors is the first step to correcting them, and by breaking down the most prevalent mistakes, educators can equip students with the tools they need to avoid these pitfalls in the future.
One of the most common mistakes students make is using the wrong possessive pronoun, which happens when the pronoun chosen does not agree with the subject of the sentence. Possessive pronouns, such as “his,” “her,” “their,” and “its,” must match the number and gender of the person or thing they are referring to. For example, using “their” to refer to a single person, when “his” or “her” is more appropriate, can create confusion and weaken the clarity of the sentence. While there has been a growing acceptance of “they” as a singular pronoun in gender-neutral contexts, formal writing often still requires precise agreement. Educators should emphasize the importance of matching the possessive pronoun to the subject to ensure students use language that is both grammatically correct and clear.
Another frequent error involves the misuse of apostrophes with possessive pronouns. It’s essential to remember that possessive pronouns, unlike possessive nouns, do not require apostrophes. This can be a source of confusion because possessive nouns, such as “John’s” or “the cat’s,” require an apostrophe to show ownership. On the other hand, possessive pronouns such as “its,” “hers,” and “theirs” do not. A common example of this confusion is mixing up “its” (the possessive form) with “it’s” (a contraction of “it is”). Students may mistakenly believe that adding an apostrophe to “its” makes it possessive, when in fact it changes the meaning entirely. By reinforcing this rule, teachers can help students avoid this common misstep and write more clearly.
Students also often confuse possessive adjectives with possessive pronouns. While the two may seem similar, they serve different grammatical purposes. Possessive adjectives, such as “my,” “your,” “his,” and “their,” modify a noun directly by indicating ownership. For example, in the sentence “This is my book,” “my” is a possessive adjective that describes the noun “book.” In contrast, possessive pronouns stand alone, replacing both the noun and the possessive adjective, as seen in the sentence “This book is mine.” Here, “mine” is a possessive pronoun that takes the place of “my book.” Understanding this distinction is vital for students, as it helps them avoid awkward or unclear constructions in their writing. Teachers should encourage students to carefully consider whether they need to modify a noun or replace it entirely when choosing between possessive adjectives and pronouns.
Another area where students commonly struggle is using possessive pronouns with gerunds. A gerund, which is a verb ending in “-ing” that functions as a noun, often appears in sentences where a possessive pronoun is necessary. When a possessive pronoun precedes a gerund, the pronoun should be in its possessive form. For instance, the correct phrase would be “I appreciate your helping me” rather than “I appreciate you helping me.” The latter sentence incorrectly uses “you” instead of “your,” which can make the meaning ambiguous or less grammatically precise. By guiding students to use possessive pronouns with gerunds correctly, teachers can help them write more polished and sophisticated sentences.
Students sometimes misplace possessive pronouns within a sentence, leading to awkward phrasing. In English, possessive pronouns should be placed directly before the noun they are modifying. For example, the phrase “his car” is grammatically correct because “his” directly modifies “car.” However, students may mistakenly use constructions like “the car of his,” which, while understandable, sounds awkward and unnecessarily convoluted. By teaching students the correct positioning of possessive pronouns, educators can help them develop a more natural and fluid writing style.