Conflict Resolution Worksheets
All About These 15 Worksheets
Conflict is an inevitable part of life, and learning how to resolve conflicts effectively is a skill that students will carry with them well beyond the classroom. Whether dealing with disagreements in friendships, family dynamics, or future workplace challenges, conflict resolution is key to building and maintaining healthy relationships. The series of 15 conflict resolution worksheets is designed to give students the tools and strategies they need to address conflicts constructively. Through a range of practical exercises, students will learn how to handle disagreements with empathy, assertiveness, and a clear focus on problem-solving. These worksheets are an invaluable resource for anyone looking to improve their communication and relationship-building skills.
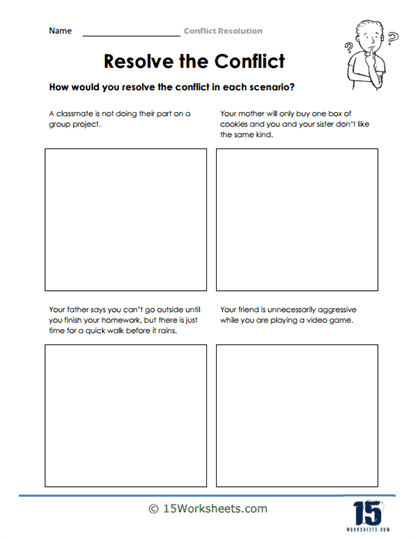
One of the foundational aspects these worksheets address is helping students understand the nature of conflict itself. By exploring the different forms and levels of conflict, students will develop a nuanced understanding of how conflicts arise and escalate. For example, a worksheet might guide students through a scenario in which a minor disagreement over group project responsibilities turns into a larger issue due to miscommunication and frustration. By analyzing the dynamics of this conflict, students can pinpoint the moments where better communication or early intervention might have prevented escalation. This ability to recognize early warning signs is a critical first step in becoming a more effective conflict resolver.
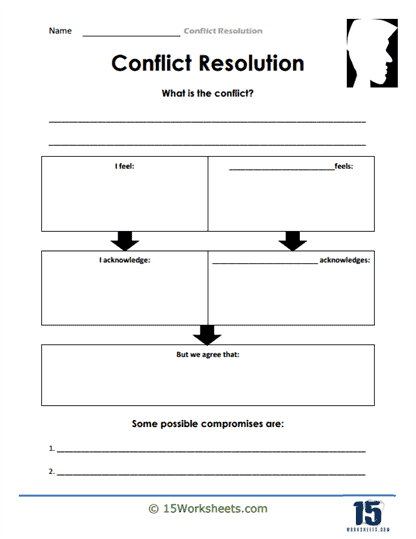
Empathy plays a central role in resolving conflicts peacefully, and these worksheets emphasize the importance of putting oneself in another person’s shoes. Students will learn how to listen actively to others’ perspectives and validate their emotions, which can de-escalate tension and foster mutual understanding. For example, one exercise may ask students to role-play a situation where two friends are arguing, with one student practicing active listening and reflecting the other person’s feelings. This simple act of acknowledging someone’s emotions can be incredibly powerful in diffusing conflict. By practicing empathy in these guided scenarios, students become more adept at understanding different viewpoints, which is crucial for resolving real-world conflicts.
Assertive communication is another key focus of the worksheets. Many conflicts arise because people either avoid expressing their needs or do so in an aggressive manner. These worksheets teach students how to communicate their needs and boundaries clearly while maintaining respect for others. For instance, a worksheet might present a situation where a student feels overwhelmed by the demands of a group project and needs to ask their peers for more support. Students will practice framing their requests assertively—using “I” statements and focusing on solutions rather than blame. This kind of communication fosters respect on both sides and helps prevent misunderstandings from turning into larger conflicts.
In addition to communication, these worksheets guide students through the process of problem-solving, helping them identify the root causes of conflicts and brainstorm solutions. Conflict resolution is not just about airing grievances—it’s about finding workable compromises that benefit everyone involved. The worksheets may present a scenario, such as a scheduling conflict in a group project, and ask students to list potential solutions, evaluate the pros and cons of each option, and work towards a decision that satisfies all parties. By practicing this structured approach to problem-solving, students learn how to navigate conflicts in a logical and cooperative manner, which is a valuable skill in both personal and professional contexts.
Negotiation is another critical element of conflict resolution that these worksheets address. In many situations, reaching a resolution requires give-and-take from all parties involved. Students will learn how to engage in constructive negotiation, aiming for solutions that are fair and beneficial for everyone. For example, in a conflict over shared responsibilities, students might practice proposing compromises that acknowledge the needs of both sides. This process teaches students the art of finding middle ground without feeling like they are “losing” in the situation. Learning to negotiate effectively helps students develop the confidence to advocate for their own needs while still working collaboratively with others.
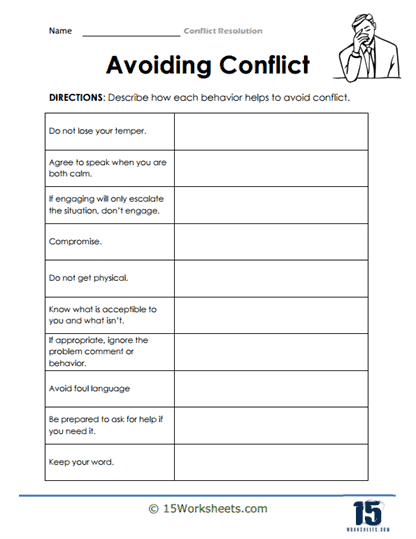
Managing emotions is also a crucial component of conflict resolution, and these worksheets provide strategies for staying calm in heated situations. Many conflicts are exacerbated by uncontrolled anger or frustration, so learning how to manage these emotions is key to resolving disagreements peacefully. One worksheet might focus on mindfulness or breathing techniques that students can use when they feel themselves getting upset during a confrontation. These exercises equip students with the tools to maintain their composure, which allows for more rational and productive conversations. By practicing emotional regulation, students become better equipped to handle conflict without letting their feelings take control.
Self-reflection is an integral part of the learning process in these worksheets. After practicing various conflict resolution strategies, students are encouraged to assess their own strengths and areas for improvement. For instance, after a role-play exercise, students might reflect on whether they were able to stay calm, listen effectively, or propose fair solutions. This self-assessment fosters personal growth and helps students understand the lessons they’ve learned through the worksheets. By analyzing their performance in conflict situations, students gain self-awareness and can continue to refine their conflict resolution skills over time.
How to Help Students Learn Conflict Resolution Skills
Learning how to handle conflicts and disagreements is an integral part of growth. Children learn a number of social skills like self-control, empathy and cooperation in the early years of their life. That isn’t all. The key ingredient to lifelong success resides in learning adequate conflict resolution skills in the early years of growth. Here’s how to help them learn the right skills to stir their intellectual development right from the classroom.
Incorporate Games and Activities
Children learn best through activities aimed at developing their social-emotional skills. One great strategy to incorporate in a lesson is role play, especially in groups. This way, they’re able to understand different perspectives and have fun at the same time. They also get a taste of other people’s point of views.
Encourage Dialogue
The practice of engaging in a dialogue isn’t something everyone is familiar with, even as an adult. It’s something people learn through their environments. This is why a classroom is the best place to start from.
Younger students who have grown enough to be able to engage in a conversation with each other can be encouraged to have a discussion right after a role play. This way, they will be reminded that they were playing different characters.
Encourage Drawing Pictures
Whenever children are faced with a conflict at hand, encourage them to draw a picture or write about what happened. This way, they’ll have a considerable amount of time to cool-off and they will also be able to reflect on what happened and it caused them to feel.
As a teacher, one can also prompt them with questions like:
- “How did it make you feel?”
- “Could you have done something differently?”
- “What would you have done differently?”
No two scenarios are alike. However, these general strategies can do wonders in creating a constructive and peaceful classroom for students of any age.
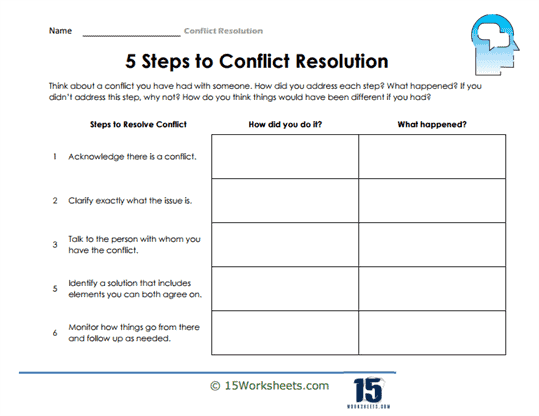
Steps to Practice Conflict Resolution
Step 1: Encourage them to cool off
Allow your students to calm down and do not aim to rush past this Step. If you see them struggling with it, intervene and encourage them to take a few deep breaths.
Step 2: Encourage them to listen and comprehend
This can be a pretty challenging one to go through especially if children haven’t been exposed to similar situations in the past. This is where a teacher’s support is required the most. Help them listen and understand the other student’s perspective so they can engage
in a dialogue with them.
Step 3: Allow them to take responsibility
Once a student has shared their side of the story, they must be taught to take responsibility for their actions. This is because, in most if not all cases, they may have some part of the responsibility even if it isn’t equal. It’s important to urge them to think if they could’ve done something differently.
Step 4: Have them come up with solutions
Once they’ve moved past listening and acknowledging, have them come up with a solution to the problem at hand. You can kick start the process by pouring in some suggestions.
Step 5: Forgive, affirm and thank
Not every situation demands an apology. Therefore, students can be encouraged to acknowledge where they went wrong, affirm that they would be mindful and forgive the other party.