Social Skills Worksheets
All About These Worksheets
This series of worksheets will help individuals, particularly students, develop and refine the interpersonal skills necessary for positive and successful interactions with others. These worksheets cover a wide range of social skills, including communication, empathy, active listening, conflict resolution, and emotional regulation. Social skills are vital for building and maintaining healthy relationships, whether in a school setting, workplace, or within personal relationships. By working through structured activities and reflective exercises, individuals can become more aware of their behavior, better understand how their actions impact others, and learn how to navigate social situations more effectively.
One of the primary benefits of social skills worksheets is that they help individuals become more self-aware. Self-awareness is a key component of emotional intelligence, which is critical for fostering healthy interactions. These worksheets often include exercises that encourage people to reflect on their own behaviors, feelings, and how they respond to different social situations. For instance, a worksheet might ask an individual to think about a recent disagreement they had and identify how their emotions influenced their behavior. This kind of reflection allows individuals to gain insight into their social strengths and areas where they may need improvement. By fostering self-awareness, these worksheets help people understand how they come across in social settings and how they can modify their behavior to communicate more effectively and build stronger relationships.
In addition to self-awareness, social skills worksheets are instrumental in teaching communication techniques. Many people struggle with expressing themselves clearly, listening actively, or managing difficult conversations, and these worksheets offer structured guidance on how to improve these skills. For example, a worksheet might focus on teaching assertive communication—showing individuals how to express their thoughts and needs confidently while remaining respectful of others. This could include practicing the use of “I” statements, which help prevent accusations and defensiveness in conversations (e.g., “I feel upset when…” rather than “You always…”). Another common exercise might involve practicing active listening, where individuals are encouraged to repeat back what someone has said to ensure understanding before responding. Developing these communication skills is critical for daily interactions, whether resolving conflicts with peers, collaborating on group projects, or maintaining close friendships and family relationships.
There are also powerful and valuable lessons in empathy and emotional regulation, which are essential for building strong, trusting relationships. Many worksheets include exercises designed to help individuals practice putting themselves in others’ shoes, fostering a greater sense of empathy. For instance, a worksheet might present a scenario where two people are in conflict and ask the student to consider each person’s perspective, identifying what they might be feeling and why. By practicing empathy, individuals become better equipped to navigate social situations with sensitivity and compassion, which helps them form deeper, more meaningful connections with others. Additionally, these worksheets often provide strategies for managing emotions, such as anger or frustration, which can prevent conflicts from escalating. Exercises like deep breathing, identifying emotional triggers, and practicing calming techniques enable individuals to regulate their emotional responses and engage in healthier, more constructive conversations.
Another important function of social skills worksheets is helping individuals improve their problem-solving and conflict resolution skills. Conflicts are an inevitable part of life, and knowing how to handle them effectively is essential for maintaining positive relationships. These worksheets often present various conflict scenarios and guide individuals through the process of resolving disagreements peacefully. For example, a worksheet might ask individuals to identify the root cause of a conflict, brainstorm possible solutions, and evaluate the potential outcomes of each approach. This type of structured problem-solving exercise teaches individuals how to address issues directly and constructively rather than avoiding them or reacting impulsively. By learning how to resolve conflicts calmly and collaboratively, individuals can reduce tension in their relationships and work toward solutions that benefit everyone involved.
The work also emphasizes the importance of cooperation and teamwork. Many social situations, whether in school, at work, or in personal relationships, require individuals to work well with others. Worksheets focused on teamwork help individuals understand the importance of listening to others’ ideas, compromising when necessary, and contributing positively to group dynamics. For example, an exercise might involve a team-based scenario where each person has a role to play, and the worksheet guides the individual through how to balance their contributions while respecting the roles of others. These activities are particularly useful for students who frequently work on group projects, as they help reinforce the idea that success often comes from collaboration and mutual respect rather than competition.
This collection of worksheets focuses on developing resilience and coping strategies for social challenges. Social interactions can be stressful or intimidating for many people, especially in new or unfamiliar settings. Worksheets that address social anxiety or fear of rejection can help individuals manage their discomfort and build confidence in their social abilities. For instance, a worksheet might include exercises on role-playing difficult conversations, or provide tips on how to start conversations in new social settings. These types of activities encourage individuals to practice social interactions in a safe, structured environment, which helps reduce anxiety and increases their confidence when they encounter real-life situations. Over time, this builds resilience, making it easier to bounce back from difficult interactions or social setbacks.
Types of Exercises on These Worksheets
Active Listening – To enhance listening skills and ensure understanding. Students may be given scenarios where they have to identify key points or emotions from a narrative. Alternatively, they could role-play conversations. Active listening teaches students to pay close attention, not just to words, but also to non-verbal cues, thus improving understanding and empathy.
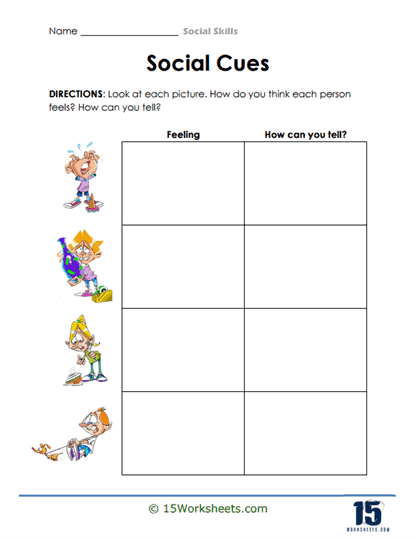
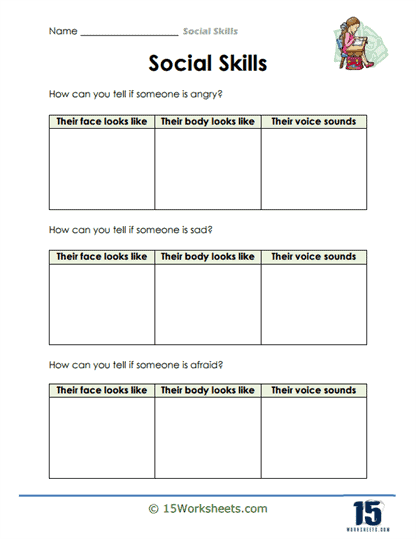
Emotional Recognition – To identify and understand emotions in oneself and others. Students might view pictures of facial expressions or read scenarios and then determine the emotions being expressed. Recognizing emotions is foundational for empathy and effective communication.
Assertiveness Training – To communicate one’s needs or boundaries without being aggressive. Role-playing various scenarios where students practice expressing their needs or setting boundaries. Assertiveness allows individuals to stand up for themselves while respecting others.
Conflict Resolution – To navigate disagreements or misunderstandings effectively. Students are given conflict scenarios and are asked to find a resolution using discussion and compromise. Disagreements are natural, but resolving them amicably strengthens relationships.
Turn-Taking – To teach patience and fairness in interactions. Group activities or games that require participants to wait their turn. Turn-taking is a fundamental social skill, especially in group settings, promoting fairness and patience.
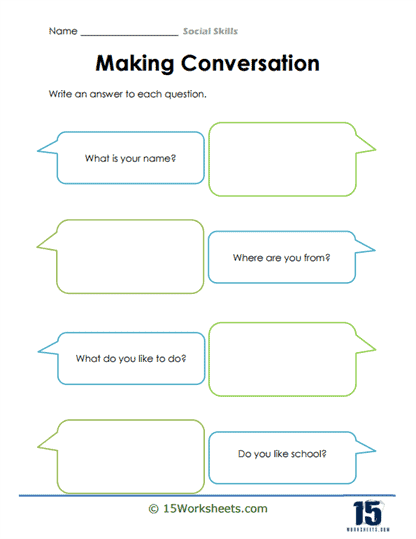
Starting and Ending Conversations – To initiate and conclude interactions gracefully. Role-playing different scenarios, such as meeting someone new or ending a phone call. This skill is vital for building and maintaining relationships.
Reading Social Cues – To understand non-verbal communication. Students watch videos or analyze pictures to identify non-verbal cues like body language, facial expressions, or tone. Much of human communication is non-verbal; understanding these cues can prevent misunderstandings.
Problem Solving – To collaboratively find solutions to challenges. Group activities where students face a challenge and must work together to solve it. Collaboration and collective brainstorming often lead to more effective solutions.
Giving and Receiving Feedback – To offer constructive criticism and accept feedback. Role-playing sessions where students practice giving praise, constructive feedback, and then receiving the same. Constructive feedback is essential for growth, and knowing how to give and receive it fosters trust.
Empathy Practice – To cultivate understanding and compassion for others. Discussing scenarios where someone is facing a challenge and students share how that person might feel. Empathy builds strong, supportive relationships.
What Are Social Skills?
Social skills are the tools and behaviors we use to interact with others effectively and harmoniously in various social settings. They are essential for building relationships, navigating social situations, and functioning successfully in society. These skills help us communicate our thoughts and feelings, understand others’ perspectives, work collaboratively, and resolve conflicts. Social skills encompass a wide range of behaviors, each contributing to the overall ability to interact positively with others.
Key Components of Social Skills
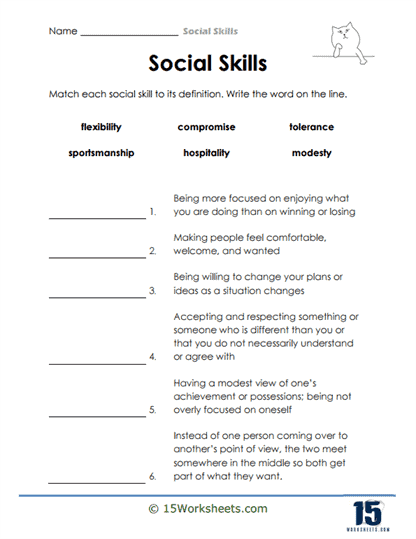
Social skills are comprised of several key components, each playing a vital role in how we interact with others and navigate various social situations. One of the foundational elements of social skills is communication. Verbal communication is the most direct form, involving the use of words to express our thoughts, ideas, and feelings. Effective verbal communication hinges on clarity, the appropriate use of tone, and an understanding of the audience. It is not just about speaking clearly and confidently but also about ensuring that the message is tailored to the listener, taking into account their background, knowledge, and perspective. Equally important is the skill of listening, which allows us to fully engage with and understand the speaker, making communication a two-way process that builds stronger connections and mutual understanding.
In addition to verbal communication, non-verbal communication plays a crucial role in how we convey and interpret messages. These are the unspoken elements, such as facial expressions, body language, gestures, eye contact, and posture. Non-verbal cues often speak louder than words, revealing a person’s true feelings and intentions. For instance, a person might say they are fine, but their slouched posture and lack of eye contact may indicate otherwise. Understanding and effectively using non-verbal communication can greatly enhance our ability to connect with others and respond to their needs.
Active listening is another critical component of communication, and it involves more than just hearing the words that are spoken. It requires fully concentrating on what the other person is saying, understanding their message, responding thoughtfully, and remembering the information shared. Active listening fosters better relationships by making the speaker feel valued and understood, which can lead to more meaningful and productive conversations.
Empathy is another cornerstone of social skills, deeply intertwined with effective communication. At its core, empathy involves the ability to recognize and understand the emotions of others. This requires not only sensitivity to emotional cues but also a genuine interest in how others feel. Understanding emotions goes beyond merely identifying what someone is feeling; it involves delving into why they feel that way, which is essential for forming deep, compassionate connections.
Perspective-taking is a vital aspect of empathy. It involves stepping into someone else’s shoes to see the world from their viewpoint. This ability helps us understand the motivations behind others’ actions and behaviors, fostering compassion and reducing judgment. When we take the time to consider someone else’s perspective, we can respond to them in a more understanding and supportive manner.
Responding with care is the practical application of empathy in social interactions. It means acknowledging others’ feelings and providing the necessary support or comfort. Whether it’s offering a listening ear, giving advice, or simply being present, responding with empathy strengthens relationships and builds trust.
Cooperation is another essential social skill that enables individuals to work together effectively to achieve common goals. Teamwork, a key element of cooperation, involves sharing responsibilities, being open to others’ ideas, and contributing fairly to group efforts. Successful teamwork requires individuals to balance their own needs and perspectives with those of the group, working together harmoniously to accomplish tasks.
Respect for others is fundamental to effective cooperation. It involves acknowledging and valuing different viewpoints, even when they differ from our own. Cooperation thrives in environments where individuals are considerate, flexible, and willing to compromise. This respect helps maintain a positive and productive group dynamic, allowing everyone to contribute their best.
Conflict resolution is an inevitable part of cooperation, as disagreements and differing opinions are natural in any group setting. Effective conflict resolution begins with identifying the problem and understanding the needs of all parties involved. Clear communication and active listening are essential in this process, ensuring that everyone feels heard and understood.
Negotiation is often necessary to find a solution that satisfies everyone involved. This requires patience, understanding, and a willingness to compromise. It’s important to approach negotiation with a mindset focused on finding a mutually beneficial resolution rather than winning the argument.
Managing emotions during conflicts is crucial to preventing situations from escalating. Emotional regulation allows individuals to remain calm and rational, facilitating more productive discussions and leading to fairer outcomes. By keeping emotions in check, individuals can engage in conflict resolution that not only solves the immediate issue but also preserves and even strengthens the relationships involved.
The Importance of Social Skills in Life
Building Relationships – Whether it’s friendships, familial ties, or romantic relationships, effective social skills foster stronger, more meaningful connections.
Professional Success – In the workplace, collaboration, communication, and teamwork are indispensable. Social skills facilitate these interactions, often influencing career progression.
Academic Achievements – Group projects, presentations, and classroom discussions all require social skills. Students with well-developed interpersonal abilities often find these tasks more manageable and rewarding.
Mental Well-being – Positive social interactions and the ability to navigate complex social scenarios can significantly boost self-esteem and reduce feelings of loneliness or isolation.
Conflict Avoidance – Many conflicts arise from misunderstandings or ineffective communication. Proficient social skills can prevent these conflicts or resolve them more amicably.
Community Engagement – Active participation in community or group activities requires a certain degree of social adeptness. These skills ensure smoother interactions and more fruitful engagements.
Overall Life Satisfaction – Humans are inherently social beings. Meaningful interactions and connections often lead to increased happiness and contentment in life.