Emotional Intelligence Worksheets
All About These 15 Worksheets
Emotional intelligence (EI) worksheets help students, teachers, homeschoolers, and tutors enhance emotional awareness, empathy, and self-regulation skills. They serve as educational resources that focus on developing an individual’s ability to recognize, understand, and manage their emotions, as well as to relate empathetically to the emotions of others. Emotional intelligence is a critical skill not just for personal well-being but also for building strong interpersonal relationships, academic success, and effective conflict resolution.
The worksheets in this collection provide a structured way to engage with emotional learning through various exercises that focus on self-awareness, emotional regulation, empathy, and social skills. These activities are particularly useful in classroom settings, homeschool curriculums, and individual tutoring sessions, as they encourage reflective thinking and help students of all ages better understand their emotional responses.
A Look At The Worksheets
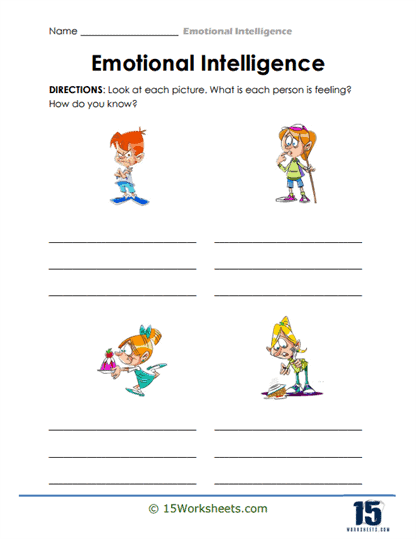
Students working through the Emotional Intelligence worksheet series are essentially becoming emotional superheroes – capes optional, but encouraged. These worksheets aren’t just paper and ink; they’re emotional gyms, each one targeting a different muscle of the mind and heart. The journey kicks off with Feelings Detectives, Emotion Explorer, and Emotion Observer, where students hone their emotional magnifying glasses to recognize, name, and better understand their feelings. These worksheets are like emotional safari maps – no lions or tigers, but definitely some wild outbursts and teary mysteries to decode. By learning to tell frustration from fear or excitement from panic, students begin to master the fine art of not shouting at their siblings over the last cookie.
Then there’s a shift toward real-world reflection with Trigger Tracker, Strong Reactions, and Pause & Reflect. This is where students dig deep into the emotional volcanoes inside them: what makes them blow, what kind of lava comes out, and how not to scorch the village every time. Trigger Tracker is like an emotional detective journal: “Hmm, I noticed I scream into a pillow every time my little brother touches my stuff. Interesting.” With Pause & Reflect, students learn that there’s actually a space between a feeling and an action, and you can live there for a second before turning into a human tornado. It’s emotional Jedi training.
Next up, we enter the philosophical dojo with worksheets like Challenge Reflections, Conflict Insights, and Situation Analyzer. These sheets teach students that emotions aren’t just pesky mood gremlins but actually valuable signals during challenging moments. These activities ask students to look at sticky social situations and dissect them like a moral frog in science class: “What happened? Why did I freak out? Could I have maybe not body-slammed my way out of that conversation?” Students gain insight into how conflicts start, how they escalate, and most importantly, how to de-escalate without yelling “YOU NEVER LISTEN TO ME!” at maximum volume.
The self-improvement squad of worksheets – Emotion IQ Quiz, Emotion Analyzer, and Strengths & Gaps – let students play emotional scientist on themselves. These ask them to rate their own emotional awareness, self-regulation, and ninja-level empathy skills. Emotion IQ Quiz is like a BuzzFeed quiz, but instead of “Which Avenger Are You?”, it’s “Are You About to Cry or Just Hungry?” With Strengths & Gaps, students realize that maybe they’re excellent at calming down but struggle to say “I’m sorry” without swallowing a small piece of their pride. It’s personal growth – with pencil marks.
The creative corner: Emotion Journal, Emotion Solutions, and Feel & Act are where students get to put all their learning into practice and sketch out real emotional game plans. These are the strategy guides for becoming a compassionate, well-adjusted human being. With Feel & Act, students figure out how feelings drive behavior, and how maybe next time, instead of turning into a walking thundercloud, they could use their words – revolutionary! These sheets invite kids to take ownership of their inner world, one doodle, sentence, or self-aware facepalm at a time. By the end of this worksheet gauntlet, students are more than just emotionally intelligent – they’re emotionally wise, which is basically the same thing, but with a beard and a sense of calm.
What is Emotional Intelligence?
Emotional Intelligence (EI), often referred to as emotional quotient (EQ), is the ability to recognize, understand, manage, and influence one’s own emotions as well as those of others. Unlike the traditional notion of intelligence, which is often measured through cognitive abilities such as logical reasoning and problem-solving (IQ), emotional intelligence focuses on one’s emotional awareness and interpersonal skills. The concept gained widespread popularity following the work of psychologist Daniel Goleman, who identified EI as a critical factor in personal and professional success. Essentially, emotional intelligence is about being smart with feelings.
One of the key components of emotional intelligence is self-awareness. This refers to the ability to accurately perceive your emotions and be aware of them as they happen. Individuals with high self-awareness are conscious of their emotional states, and they understand how their emotions affect their thoughts and behavior. This skill is essential in identifying emotional triggers and managing reactions to various situations. By being self-aware, a person can more effectively navigate complex emotional landscapes, avoiding impulsive actions that could lead to negative consequences.
Another critical aspect of EI is self-regulation, which involves the ability to manage and control one’s emotions in healthy and constructive ways. Self-regulation prevents emotional outbursts, rash decisions, and behavior that may lead to regret. It also allows individuals to remain calm under pressure and adapt to changing circumstances. Self-regulation is not about suppressing emotions but rather about finding appropriate outlets and responses. This skill is especially valuable in leadership and team settings, where maintaining emotional stability can foster a positive and productive environment.
Empathy is another cornerstone of emotional intelligence, referring to the capacity to understand and share the feelings of others. Empathy involves active listening, recognizing the emotional cues of others, and responding to them in a way that shows genuine concern. It helps individuals connect more deeply in both personal and professional relationships. High levels of empathy can improve collaboration, teamwork, and conflict resolution, as individuals who are empathetic are more likely to consider others’ perspectives and foster inclusive environments.
Social skills, which encompass communication, relationship management, and conflict resolution, form a significant part of emotional intelligence. Individuals with strong social skills can build rapport easily, manage disputes effectively, and lead with influence rather than authority. These skills are crucial in environments that require teamwork and collaboration. Emotional intelligence, in this context, becomes a valuable asset for both personal well-being and career advancement. It helps individuals navigate social complexities and establish meaningful connections, ultimately enhancing their overall success in various life domains.