Communication Worksheets
All About These 15 Worksheets
Effective communication is one of the most important life skills students can develop. It affects nearly every aspect of their lives, from personal relationships to academic success and future professional growth. In today’s fast-paced world, the ability to clearly convey thoughts, listen attentively, and interpret nonverbal cues is crucial. This series of 15 worksheets is specifically designed to help students improve their communication abilities by exploring both verbal and nonverbal aspects of communication. Through a variety of targeted exercises, students will not only learn about the theory behind effective communication but also gain practical skills that they can apply in their everyday interactions.
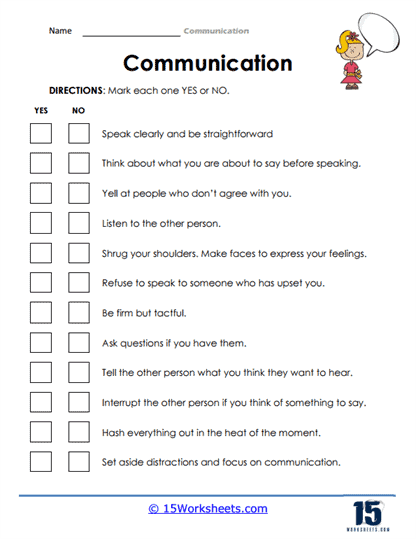
One of the core focuses of these worksheets is helping students understand the fundamental dos and don’ts of communication. Students are often unaware of how small communication missteps-such as interrupting, using a dismissive tone, or failing to actively listen-can significantly impact their conversations and relationships. These worksheets guide students through common communication pitfalls and teach strategies to avoid them. For example, one exercise may ask students to reflect on a recent conversation and identify moments where they could have been better listeners or more respectful in their responses. By recognizing these areas for improvement, students can consciously work on enhancing their verbal interactions, whether in a classroom discussion, a group project, or even at home with family members.
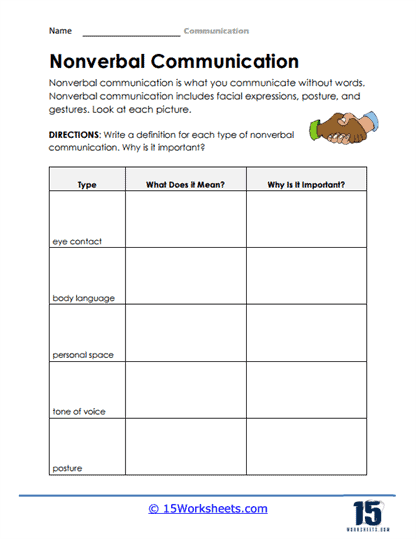
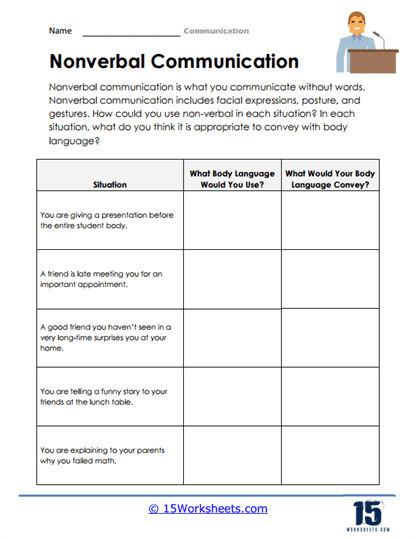
Another crucial element explored in these worksheets is the power of nonverbal communication. Body language, facial expressions, gestures, and even posture play a significant role in how messages are received and interpreted. For example, a student may say all the right words during a presentation, but if their arms are crossed or they avoid eye contact, the audience may perceive them as uninterested or disengaged. The worksheets provide practical scenarios where students must analyze nonverbal cues and reflect on how they align with verbal communication. Activities like role-playing or observing conversations without sound help students understand how nonverbal signals can either support or contradict the spoken message. This insight is invaluable not just for personal conversations but also for professional settings, where body language often speaks louder than words.
These worksheets also offer opportunities for self-assessment, encouraging students to take an honest look at their communication styles. Many people are unaware of how they come across to others, and these activities prompt students to reflect on their habits, such as whether they dominate conversations, speak too quietly, or struggle with maintaining eye contact. By using real-life examples and tailored feedback, the worksheets help students pinpoint areas where they can grow. For instance, one exercise might involve keeping a communication journal for a week, noting specific instances where communication broke down and why. This process fosters self-awareness, allowing students to identify and address their weaknesses, thus fostering healthier and more productive relationships.
In addition to examining individual communication styles, the worksheets delve into the influence of cultural norms and situational context on nonverbal communication. Different cultures interpret gestures, eye contact, and personal space in various ways, and understanding these differences is key to effective communication in diverse environments. For example, a student may learn that while maintaining direct eye contact is seen as a sign of confidence in some cultures, it may be considered rude or confrontational in others. The worksheets provide exercises that simulate cross-cultural interactions, teaching students how to adapt their communication to different audiences, contexts, and cultural backgrounds. This skill is particularly valuable in today’s globalized world, where students will frequently interact with individuals from various cultural backgrounds in both personal and professional settings.
Conflict resolution is another important theme in these communication worksheets. Many conflicts arise due to misunderstandings, poor listening, or ineffective expression of thoughts and emotions. The worksheets guide students through strategies for resolving disagreements calmly and respectfully, such as using “I” statements, avoiding accusatory language, and seeking to understand the other person’s perspective before responding. For example, an activity might involve analyzing a fictional scenario where a disagreement occurs, and students must identify what went wrong and how it could be handled differently. Through these exercises, students develop skills in negotiation, empathy, and problem-solving, which are essential for resolving conflicts in a constructive manner.
One of the most valuable aspects of these worksheets is the focus on active listening. In many conversations, people tend to focus on what they are going to say next, rather than fully absorbing what the other person is saying. Active listening is a skill that requires full attention, empathy, and the ability to respond thoughtfully. The worksheets include exercises where students practice summarizing what they’ve heard, asking clarifying questions, and providing feedback that shows they’ve understood the speaker’s message. These tasks are designed to sharpen their ability to listen effectively, which in turn improves the quality of their responses and strengthens their relationships.
These worksheets emphasize the importance of tailoring communication to different audiences and contexts. Whether speaking to a peer, a teacher, or a potential employer, students need to adjust their tone, language, and message to suit the situation. For instance, a casual conversation with a friend will have a different style and vocabulary than a formal email to a professor. One exercise might involve rewriting the same message for different audiences-such as turning an informal text into a formal letter-helping students learn how to adapt their communication style appropriately. This skill is crucial for professional growth, as clear, tailored communication is a key element in making a positive impression in the workplace.
What is Communication?
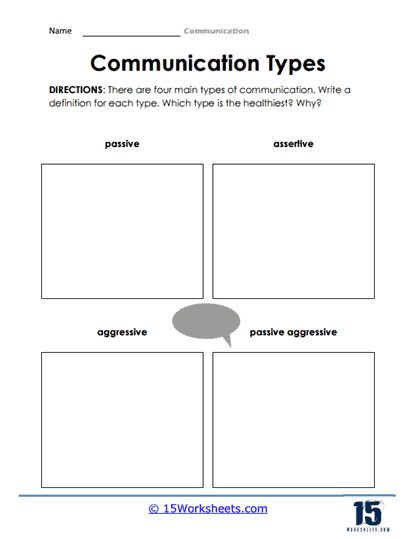
Communication is the process of exchanging information, ideas, thoughts, feelings, and emotions between individuals or groups. There are several different forms of communication, which can be broadly categorized as follows:
- Verbal – The use of spoken or written words to convey messages, thoughts, or ideas. This includes face-to-face conversations, telephone calls, letters, emails, text messages, and various forms of digital communication.
- Nonverbal – The exchange of information without using words, often through body language, facial expressions, gestures, eye contact, and other physical cues. Examples include smiling, waving, or crossing one’s arms.
- Visual – The use of visual elements, such as images, graphics, colors, and symbols, to communicate ideas or information. Examples include photographs, videos, illustrations, infographics, logos, and signage.
- Written – Expressing thoughts and ideas through written words, which can be either printed or digital. Examples include books, newspapers, magazines, blog posts, and social media updates.
- Aural – The use of sound to convey messages or emotions, such as through music, tone of voice, or sound effects.
- Electronic – Communication that takes place through electronic devices and media, such as email, instant messaging, social media platforms, video conferencing, and more.
- Sign Language – A visual language that uses hand gestures, facial expressions, and body movements to communicate, specifically designed for individuals with hearing impairments.
- Tactile – The use of touch to convey messages or emotions, such as through hugs, handshakes, or patting someone on the back.
- Pictorial – The use of pictures, drawings, or other visual representations to communicate ideas or information, such as cave paintings, maps, or diagrams.
These forms of communication can be used individually or in combination, depending on the context and the intended message. Effective communication often involves the use of multiple forms to ensure that the message is clearly understood by the receiver.
How to Improve Your Ability to Communicate
Effective communication is the core of any relationship. Whether you communicate with your friends, family, colleagues, or professional delegates, your ability to establish a fruitful conversation requires your focus on a few significant factors. If you want to know how to communicate effectively, we have covered a few essential tips for you to begin with.
Effective communication is a combination of several ingredients. You must add the appropriate amount of each to construct your arguments. Let’s dive into these factors to learn more.
Listen More, Speak Less
One of the common mistakes most people make is overlooking the importance of listening. When you engage in a group conversation, your audience likes to be heard. You may have all the solutions to their problems, but not hearing them out would make your argument ineffective. To ensure others listen to you while you speak, you must listen to them first.
Understanding the problem is half the solution. When you hear your peers and others out, you can understand them better. Effective listening leads to effective communication.
Non-Verbal Communication Helps A Lot
A common misconception among many is that communication refers to verbal speech. While it is valid to some extent, a significant part comes from non-verbal cues. When engaged in an (individual or group) conversation, your body language speaks more than you do. You may want to focus on your facial expressions and body movements while listening or talking to others.
Some important non-verbal cues include maintaining eye contact, avoiding unnecessary hand gestures, sitting attentively, and avoiding unnecessary movements.
Organize Your Speech First
Preparing yourself to communicate is an integral part of the effective communication process. It helps you create a positive impression, become more confident, and address all the pointers effectively. This practice comes in handy when you communicate in a professional environment. You may not want to call your manager again to address the missing pointers of the meeting.
A good tip for speech organization is to note down cues on a piece of paper before engaging in a conversation. You can also try other ways to follow an organized speech pattern.
Know Who You Are Talking To
Opting for the same speech protocol for everyone may not be wise. It is vital to know your audience before you speak. The way you communicate varies for casual and professional settings. For instance, it may be inappropriate to ask your manager, “What’s up?”. However, asking a friend the same question may be an excellent start to your conversation.
If you are familiar with the person you are speaking to, you can better understand how to initiate an effective conversation.
Overcommunication May Be a Bad Idea
Many speakers overcommunicate to explain the message effectively. While it may work occasionally, overcommunication can confuse and frustrate people. When speaking professionally, you may want to stick to your point. Speech organization helps in cutting the unnecessary clutter from your everyday conversations.
You may use minimum words to express an idea to improve your context development skills and avoid overcommunication.
A Smile Would Hurt Nobody
Many effective communicators fail to impress their audiences due to poor speaking attitudes. Enriching your communication practices with a smile every once can appeal to your listeners. They feel humbled and pay more attention to the speaker in a pleasant environment. While this is true, you may not want to overdo it. Knowing when not to smile is equally important.
To improve your speech attitude, you may practice communicating while looking in a mirror and trying different ways to impart a humble impression on others.
Helping Students Improve Their Communication Skills
Helping students improve their communication skills can be both engaging and enjoyable by incorporating interactive and creative activities. One effective approach is through games that challenge students to use language in dynamic ways. For instance, a popular game like “Charades” allows students to practice nonverbal communication by acting out words or phrases while others guess what they are trying to convey. This not only hones their body language skills but also encourages teamwork and collaboration. Another fun activity is “Two Truths and a Lie,” where students take turns sharing two true statements and one false one, and their peers must guess the lie. This game fosters both verbal communication and active listening, as students must listen carefully to discern the truth from deception.
Another enjoyable way to enhance communication skills is through group projects that involve creative storytelling or role-playing. Students can be tasked with working together to create a skit, video, or even a podcast, where they must collaborate and communicate effectively to produce a finished product. Role-playing scenarios can focus on real-world situations like job interviews, debates, or conflict resolution, allowing students to practice adjusting their tone, vocabulary, and body language depending on the context. For example, having students role-play a negotiation between a customer and a store manager teaches them how to resolve disagreements through clear, respectful dialogue. By incorporating these creative elements, students can build communication skills in a fun, low-pressure environment.
Using technology and social media can also make communication skill-building more exciting. Students can create digital presentations, run a mock social media campaign, or engage in virtual debates. For example, students can be given a topic and challenged to create a series of persuasive social media posts, practicing how to convey messages clearly and effectively in short formats. Alternatively, using video platforms like Flipgrid or Zoom allows students to practice public speaking in a modern and interactive way, recording their presentations or discussions for peer feedback. These activities not only improve communication but also introduce students to the digital tools they will likely encounter in future educational or professional settings. By making communication lessons more interactive and relevant to their interests, students are more likely to engage fully and develop these essential skills.