Persuasive Writing Worksheets
All About These 15 Worksheets
This series of 15 worksheets is an innovative and dynamic resource designed to engage students in persuasive writing through the exploration of multiple genres. These worksheets provide students with a platform to express their ideas, opinions, and arguments in a creative and versatile manner, enhancing their persuasive writing skills while fostering critical thinking and imagination.
The exercises challenge students to go beyond traditional persuasive essays and explore a range of genres, such as letters, speeches, infographics, advertisements, scripts, and more. This series encourages students to think outside the box and adapt their persuasive techniques to various formats, ensuring a well-rounded and adaptable approach to persuasion. Through these worksheets, students will:
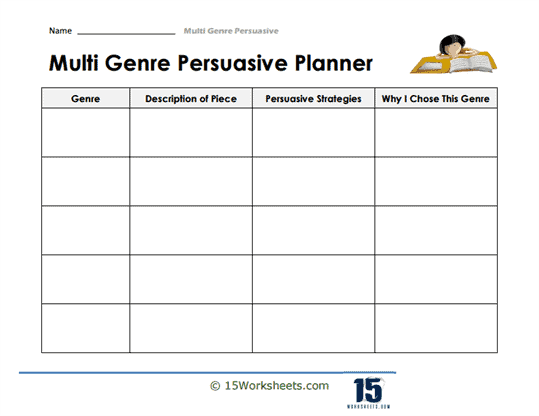
- Understand what a multi genre project is and begin by writing their own persuasive essay;
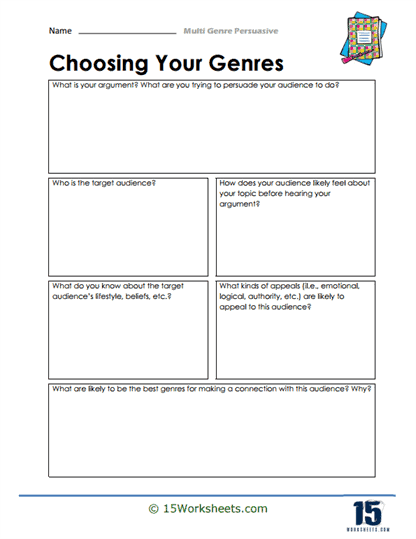
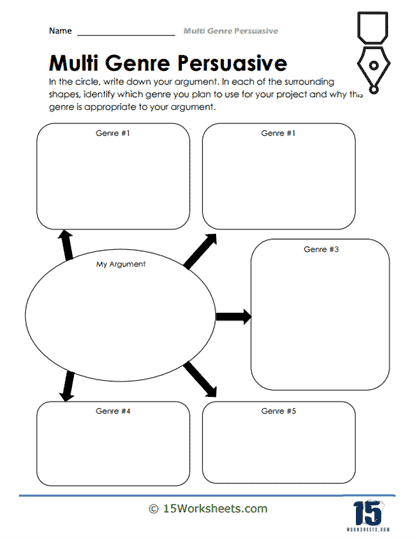
- Brainstorm their own genres;
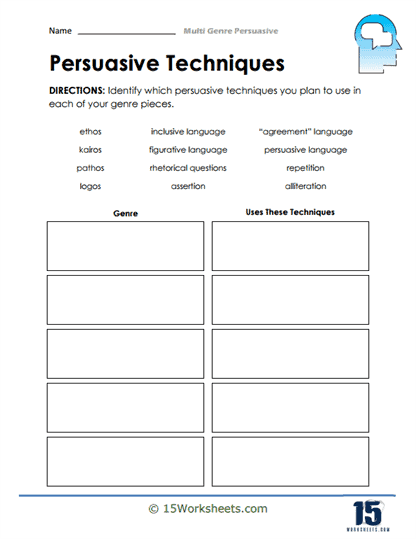
- Match various genres with persuasive strategies that work;
- Master constructing their thesis statements that are backed with supporting details and evidence;
- Develop an understanding of how to effectively adapt their arguments to suit different genres and target audiences;
- And evaluate the effectiveness of different persuasive strategies, revise their arguments for clarity and coherence, and consider alternative approaches to their chosen genre.
This series is suitable for students across different grade levels and can be used in language arts classes, writing workshops, or independent study settings. By using these worksheets, teachers empower their students to develop versatile persuasive writing skills, expand their creative repertoire, and approach persuasion from a multi-dimensional perspective.
In summary, students not only enhance their persuasive writing abilities but also develop critical thinking skills, adaptability, and creativity. These worksheets encourage students to think innovatively, adapt their arguments to different contexts, and effectively persuade their audiences across various genres. This series fosters a deeper understanding of persuasion as a flexible and versatile tool for effective communication.
How to Improve You Persuasive Writing Ability
Improving your persuasive writing ability involves developing skills to present a compelling argument, engage your audience, and convince them of your perspective. Here are some strategies to enhance your persuasive writing skills:
1. Understand Your Audience – Know your target audience’s values, beliefs, and preferences. Tailoring your writing to resonate with your readers will increase the effectiveness of your persuasive efforts.
2. Establish a Clear Position – Clearly state your stance on the topic at the beginning of your writing. This provides a foundation for your argument and helps readers understand your perspective.
3. Research and Gather Evidence – Use reputable sources to gather data, facts, and expert opinions to support your argument. Strong evidence adds credibility to your writing and makes your case more convincing.
4. Use Logical Reasoning – Present your argument in a logical, organized manner. Clearly explain how your evidence supports your position, and address any potential counterarguments or opposing viewpoints.
5. Appeal to Emotions – Use anecdotes, stories, or examples that evoke emotions in your readers. Emotional appeals can enhance the impact of your argument and create a stronger connection with your audience.
6. Use Persuasive Language Techniques – Employ rhetorical devices, such as repetition, analogy, and rhetorical questions, to emphasize key points and engage your readers. Choose words that convey confidence, authority, and enthusiasm.
7. Establish Credibility – Demonstrate your knowledge and expertise on the topic. This may involve citing reputable sources, sharing personal experiences, or referring to the opinions of experts in the field.
8. Maintain a Consistent Tone and Style – Adopt a tone and writing style that appeals to your target audience and is consistent throughout your text. This helps maintain reader engagement and reinforces your message.
9. Use Clear and Concise Language – Ensure your writing is easy to understand and avoids unnecessary jargon or complex language. Clear, concise language helps readers follow your argument and focus on your key points.
10. Edit and Revise – Carefully review your writing for clarity, coherence, and organization. Address any gaps in your argument, and proofread for grammar, punctuation, and spelling errors.
By incorporating these strategies into your writing process, you can improve your persuasive writing ability and create compelling arguments that engage and convince your audience. Practice and feedback from others will also help you refine your skills over time.