Diagraphs Worksheets
All About These 15 Worksheets
This collection of digraph worksheets is much more than a set of activities-they empower students to navigate the rich world of phonics, an integral part of their literacy journey. Designed with both educators and learners in mind, these worksheets offer a structured yet engaging approach to mastering digraphs, which are a key element of phonemic awareness and language development. The worksheets are not just exercises on paper; they are carefully crafted opportunities for students to dive into the world of sounds, letters, and words, fostering not only their understanding of digraphs but also their confidence in reading, writing, and spelling.
Digraphs, combinations of two letters that produce a single sound, play a foundational role in language acquisition. Without a strong grasp of digraphs, students may struggle with reading fluency, comprehension, and spelling accuracy-skills that are critical as they move from decoding individual letters to fluently reading entire words and sentences. These worksheets offer a pathway for students to practice these combinations in a variety of engaging ways, allowing them to internalize this crucial concept through active learning.
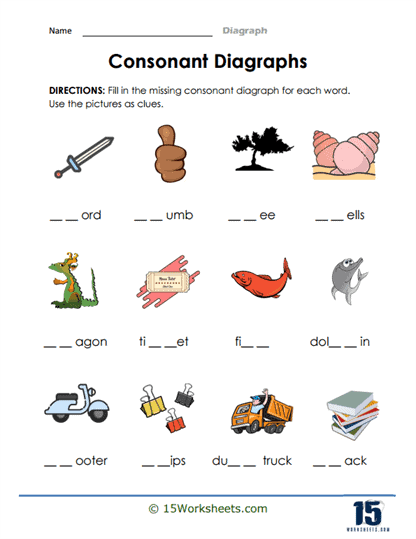
These worksheets are more than just routine drills-they are carefully designed exercises that offer a variety of activities aimed at engaging students of different learning styles and abilities. From matching games to sorting tasks, students are encouraged to explore how letters work together to form new sounds. For example, a worksheet might ask students to identify images of a “whale,” “phone,” or “ship” and match them with their corresponding digraphs: “wh,” “ph,” and “sh.”
By incorporating a mix of visual, auditory, and kinesthetic learning styles, these worksheets cater to a broad spectrum of learners. Visual learners can benefit from seeing the words and pictures, auditory learners can practice by saying the digraphs aloud, and kinesthetic learners can engage through writing or physically moving objects in sorting exercises. This dynamic approach ensures that every student has the opportunity to grasp the concept of digraphs in a way that makes sense to them.
These worksheets are designed to grow with the student. They begin with simpler, more common digraphs like “sh” and “ch,” and progress to more challenging ones, like “ph” and “wh.” This gradual increase in difficulty helps to build confidence and competence, ensuring that students not only learn the material but retain it as well.
While these worksheets are an excellent tool for mastering digraphs, they are just one part of a larger effort to inspire a lifelong love of reading. Learning digraphs is a foundational skill, but it’s the confidence gained through this mastery that carries students forward. When students can decode words effortlessly, they are more likely to engage with reading, find joy in storytelling, and develop curiosity about the written word.
In this way, these worksheets do more than just teach digraphs-they ignite a spark. Students who feel competent in their reading abilities are more likely to pick up a book for fun, dive into new topics, and explore different genres. They become independent learners, capable of tackling more complex texts and advancing in their academic journeys.
What Are Digraphs?
Digraphs are combinations of two letters that represent a single sound (phoneme) in a word. They can be made up of two consonants (consonant digraphs) or a combination of a consonant and a vowel (vowel digraphs). Digraphs are essential to understand as they help children learn the different letter combinations that create specific sounds in English, which in turn improves their reading, writing, and pronunciation skills.
Digraphs in phonics refer to a combination of two letters that make a single sound. They are a common component of many languages, including English. In a digraph, the individual sounds of the two letters are not identifiable – they form a new, unique sound together.
Some common digraph examples include:
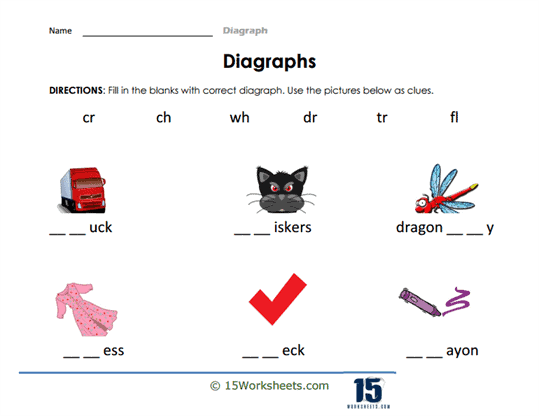
Consonant digraphs:
“sh” as in “ship” (sound: /ʃ/)
“ch” as in “chair” (sound: /tʃ/)
“th” as in “thin” (sound: /θ/) or “then” (sound: /ð/)
“ph” as in “phone” (sound: /f/)
“wh” as in “when” (sound: /w/ or /hw/)
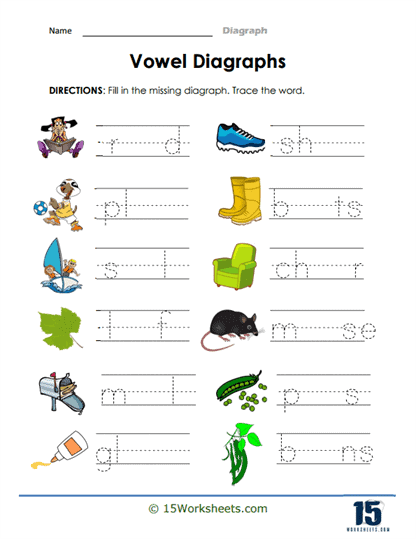
Vowel digraphs:
“ai” as in “rain” (sound: /eɪ/)
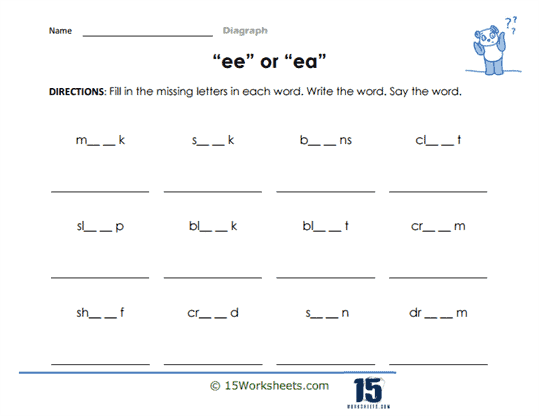
“ee” as in “feet” (sound: /iː/)
“oa” as in “boat” (sound: /oʊ/)
“ue” as in “blue” (sound: /uː/)
“oi” as in “coin” (sound: /ɔɪ/)
How To Teach Digraphs To Kids
Teaching digraphs to children can be a pivotal moment in their literacy journey, as it equips them with essential tools for decoding language. When children begin to encounter words that are not simply sounded out letter by letter, they often need guidance to understand how combinations of letters work together to form unique sounds. These combinations, known as digraphs, play a fundamental role in reading fluency, comprehension, and overall language mastery. But how exactly should we approach teaching them? Let’s explore some strategies that not only simplify this process but make it engaging and effective for young learners.
Engaging Methods for Teaching Digraphs
The process needs to be engaging, multi-sensory, and repetitive to ensure lasting understanding. Here are some effective methods:
1. Interactive Word Hunts
One powerful way to introduce digraphs is through interactive word hunts. As you introduce a specific digraph, such as “sh” or “ch,” encourage children to search for words in their environment that contain that digraph. Whether you’re reading a book together or walking through the classroom, children will become more attuned to the sounds and symbols they are learning. This turns digraph identification into a fun game rather than a daunting task.
2. Sound Sorting Activities
Another effective strategy is to create sound sorting activities. For example, you can have a variety of word cards, some with the digraph you’re focusing on and others without. Ask children to sort the cards into two piles: those that contain the digraph and those that don’t. By physically interacting with the words and sorting them, children engage both their visual and auditory senses, reinforcing their understanding of the sound that the digraph makes.
3. Using Phonetic Games and Apps
In today’s digital age, there are a variety of educational apps and games that focus on phonics and digraphs. Incorporating technology can make learning feel more like play, especially for younger children who may struggle with traditional teaching methods. Apps that provide instant feedback on pronunciation and identification of digraphs can give children the extra practice they need, in a way that feels rewarding.
4. Multisensory Learning: Writing and Drawing
For some children, writing out words that contain digraphs or even drawing pictures associated with those words can make a huge difference in retention. When they draw a picture of a “ship” and label it, they are reinforcing the “sh” sound visually and kinesthetically. This multisensory approach appeals to children who may not learn as effectively through auditory instruction alone.
Repetition and Reinforcement: Keys to Success
It’s important to recognize that learning digraphs, like many other reading skills, takes time and repeated exposure. A single lesson on “ch” or “th” will likely not be enough for most children to fully grasp the concept. Repetition is crucial, but so is variety. The more ways children are exposed to digraphs-in reading, writing, speaking, and listening-the more likely they are to internalize the knowledge.
Consider incorporating digraph practice into daily routines. For example, begin each day with a “digraph of the week” and spend a few minutes brainstorming words that contain that digraph. This not only reinforces their understanding but keeps the learning process light and manageable, avoiding overwhelm.
The Road to Reading Fluency
As children become more comfortable with digraphs, you’ll notice a marked improvement in their reading abilities. They will begin to encounter new words with confidence, knowing that they can decode them using the skills they’ve learned. This boost in confidence is crucial for fostering a love of reading, which is ultimately the goal of phonics instruction.
Fluency is about more than just speed-it’s about reading with understanding and ease. By teaching digraphs effectively, we help children approach reading with a sense of mastery and enjoyment. Once they have the tools to decode words quickly, they can focus on comprehension and meaning, diving deeper into stories, information, and ideas without getting stuck on the mechanics of reading.
The Importance of Digraphs
In the world of early literacy, few building blocks are as fundamental yet as often overlooked as digraphs. These powerful combinations of two letters that create a single sound, such as “ch,” “sh,” or “th,” are pivotal to mastering the English language. While they might seem like simple letter pairs, digraphs are crucial in laying the foundation for reading, writing, and overall language comprehension. Their significance extends far beyond phonetics; they serve as a gateway to unlocking fluency, expanding vocabulary, and fostering a deeper understanding of text.
The Bedrock of Language Mastery
Phonetic awareness is one of the first steps in a child’s journey toward becoming a proficient reader. It’s the ability to hear, identify, and manipulate sounds in spoken language. Digraphs, by their very nature, challenge students to recognize that two letters can work together to form a single sound. This concept may seem basic to adult readers, but for young learners, it’s a monumental leap in their understanding of how language functions.
By mastering digraphs, students sharpen their phonemic awareness-the ability to break down and manipulate sounds in words. When a child realizes that the letters “s” and “h” create the distinct “sh” sound, they begin to see patterns in the language, which helps them tackle unfamiliar words with more confidence. This growing awareness is not just about recognizing letters; it’s about developing the mental agility to manipulate those sounds, an essential skill for reading and spelling fluently.
Word Decoding
Decoding is the process of translating written words into sounds. For new readers, the ability to decode words accurately is a fundamental skill that directly influences their reading fluency. Digraphs play a pivotal role in this process. Without a firm grasp of digraphs, students may stumble when encountering words that contain these sound combinations, slowing down their reading and leading to frustration.
However, when a child is proficient in recognizing digraphs, they can decode words quickly and efficiently. This proficiency allows them to focus less on individual sounds and more on the meaning of the text. For example, once they’ve mastered the digraph “ch,” they can easily read words like “chair” or “chicken” without having to labor over the sounds. This increased fluency not only builds confidence but also frees up cognitive energy to focus on higher-order reading skills, such as comprehension and inference.
Bridging the Gap Between Sound and Sight
Spelling and reading are two sides of the same coin, and a strong understanding of digraphs is essential to becoming a proficient speller. When students learn how digraphs represent specific sounds, they can apply this knowledge to spell words accurately. Instead of relying on memorization alone, they begin to understand the logic behind spelling patterns, which makes spelling far more manageable.
Take the word “bath,” for example. Knowing that “th” forms a single sound helps students remember how to spell it correctly. Without this knowledge, students might spell the word phonetically, using just “t” or “f,” leading to errors. Understanding digraphs provides students with a set of rules they can apply across many words, reducing their reliance on guesswork and improving their overall spelling accuracy.
Vocabulary Expansion
Vocabulary development is another area where digraph mastery plays a crucial role. The more familiar students are with the sounds and letter combinations that make up words, the more capable they become of understanding and learning new vocabulary. This is particularly important as students encounter words with more complex phonetic patterns, many of which contain digraphs. By mastering digraphs, students are better equipped to recognize and make sense of unfamiliar words they encounter in their reading, which in turn broadens their understanding of language and expands their vocabulary. As they continue to learn and apply new words, their ability to express themselves grows, enriching their communication skills and opening doors to more advanced learning opportunities. The more words a student knows, the better they can comprehend texts, engage in conversations, and express their ideas creatively and accurately.
The Power of Efficient Word Recognition
Reading comprehension, the ability to understand and interpret the meaning of text, is the ultimate goal of learning to read. Recognizing digraphs plays a critical role in this process because it allows students to decode words quickly and accurately. When students can recognize common digraphs without hesitation, they free up cognitive resources to focus on the meaning of the text rather than getting bogged down by trying to sound out each word. This fluency in word recognition leads to smoother, more natural reading, which enhances comprehension. For example, if a student reads the sentence “The child chased the cat,” their ability to recognize the digraph “ch” in both child and chased allows them to focus on the story itself, rather than struggling with individual sounds. As a result, they can better grasp the plot, themes, and details of what they are reading, which is essential for academic achievement and lifelong learning.
The importance of digraphs in early literacy cannot be overstated. From enhancing phonetic awareness to boosting reading comprehension, mastering digraphs lays the groundwork for a lifetime of reading and writing success. Digraphs help students decode words with greater ease, spell more accurately, expand their vocabulary, and comprehend texts more fully. For educators and parents, focusing on digraphs is a powerful way to support children’s literacy development and set them on a path toward academic success. As students become more proficient in recognizing and using digraphs, they gain confidence and independence as readers and writers, ready to explore the vast world of language with curiosity and skill. The mastery of digraphs is not just a milestone in literacy; it is the foundation upon which all future learning is built.
This collection of Digraphs worksheets is an invaluable resource that equips educators to guide their students toward phonetic mastery. By engaging with these worksheets, students not only develop a strong foundation in digraphs but also enhance their reading, spelling, and overall language proficiency. This collection empowers educators to nurture young learners on their journey to becoming confident and proficient readers and communicators, capable of navigating the complexities of the English language with ease.