Letters and Sounds Worksheets
All About These 15 Worksheets
The journey of literacy begins with mastering the fundamentals of letters and their corresponding sounds. This foundation in phonics is essential for young learners as it forms the basis for reading, writing, and effective communication. This collection of Letters and Sounds worksheets aims to help students develop a strong understanding of letters and their associated sounds. These worksheets provide a structured and engaging way for students to explore this critical aspect of language learning.
What are Letters and Sounds Worksheets?
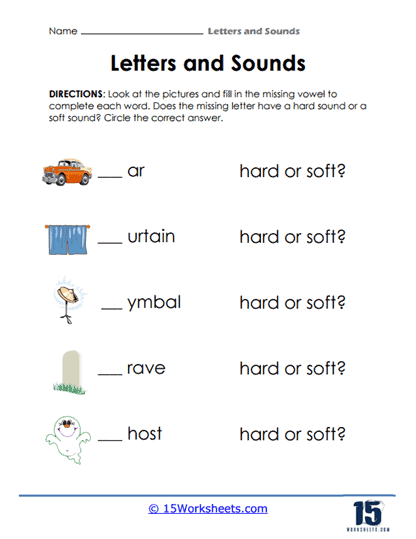
Letters and Sounds Worksheets are educational resources designed to help students practice and learn about the sounds and letters of the alphabet. These worksheets often include various activities, such as matching, sorting, or writing exercises, that focus on the sounds of the letters of the alphabet and how they combine to form words.
Letters and sounds relate through a system called phonics, which is the relationship between the symbols (letters or combinations of letters) and the sounds they represent in spoken language. In alphabetic languages like English, letters or groups of letters correspond to specific speech sounds or phonemes.
Here are some key points about how letters and sounds relate:
Alphabetic Principle – The foundation of phonics, the alphabetic principle, states that written words are composed of letters that represent the sounds of spoken words.
Phonemes – Phonemes are the smallest units of sound in a language. In English, there are about 44 phonemes, which can be represented by a single letter or a combination of letters.
Graphemes – Graphemes are the written symbols (letters or combinations of letters) that represent a specific phoneme. For example, the phoneme /b/ is represented by the grapheme “b” in the word “bat.”
Consonants and Vowels – In English, there are 21 consonant letters (e.g., b, c, d, f, etc.) and 5 vowel letters (a, e, i, o, and u). Consonants typically represent more distinct sounds, while vowels can represent various sounds depending on the context and word structure.
Letter Combinations – Some phonemes are represented by combinations of letters, such as “th” representing the /θ/ sound in “thin” or the /ð/ sound in “this.” Another example is “sh,” which represents the /ʃ/ sound in “ship.”
Digraphs and Trigraphs – A digraph is a combination of two letters representing one sound, such as “ch” for the /tʃ/ sound in “chair” or “ea” for the /iː/ sound in “beach.” A trigraph is a combination of three letters representing one sound, like “igh” for the /aɪ/ sound in “light.”
Spelling Patterns – In English, certain spelling patterns can help predict the pronunciation of a word. For instance, a “silent e” at the end of a word often indicates that the preceding vowel is long, as in “cake” or “ride.”
Irregularities – English has many irregularities and exceptions due to its complex history and borrowing of words from other languages. Some words have unusual spellings or do not follow typical phonics rules, like “one” or “eight.”
Understanding the relationship between letters and sounds is crucial for learning to read, write, and spell in an alphabetic language like English. Phonics instruction helps learners to decode words by recognizing and blending the individual sounds represented by the letters.
How to Teach Letters and Sounds
Teaching letters and sounds effectively involves a systematic and explicit approach to phonics instruction. Here are some strategies and tips for teaching letters and sounds:
Introduce Letters and Their Corresponding Sounds – Start by teaching the most common sound that each letter represents. Use visual aids like alphabet cards, posters, or magnetic letters to reinforce learning.
Teach Letter Formation – Teach children how to write both uppercase and lowercase letters, emphasizing correct letter formation and pencil grip. Use tracing exercises and provide ample opportunities for practice.
Begin with Simple CVC Words – Once students have learned a few consonant and vowel sounds, introduce simple Consonant-Vowel-Consonant (CVC) words, like “cat,” “dog,” or “hat.” This helps students learn to blend sounds together to form words.
Teach Blending – Teach students how to blend individual sounds together to read words. Start with simple CVC words and gradually progress to more complex words.
Teach Segmenting – Help students learn to break words down into individual sounds, an essential skill for spelling and reading. Start with simple CVC words and gradually progress to more complex words.
Introduce Digraphs and Trigraphs – Teach common letter combinations, like “sh,” “ch,” “th,” and “igh,” that represent single sounds. Provide examples of words containing these combinations and have students practice reading and spelling them.
Teach Phonics Rules – Introduce and practice rules that govern the relationship between letters and sounds, like the silent “e” rule or the “double consonant” rule. Be sure to also discuss exceptions to these rules.
Use Decodable Texts – Encourage students to practice reading with decodable texts, which are specifically designed to include words that can be decoded using the phonics skills they’ve learned.
Incorporate Multisensory Techniques – Use a variety of teaching methods that engage multiple senses, such as visual, auditory, and kinesthetic, to reinforce learning. Techniques might include using letter tiles or magnetic letters, tracing letters in sand or shaving cream, or using songs and chants to teach letter sounds.
Provide Ample Practice – Provide plenty of opportunities for students to practice reading, writing, and spelling words using the letters and sounds they’ve learned. Use games, worksheets, and activities to keep students engaged and motivated.
Review and Assess – Regularly review and assess students’ progress to identify areas that may need additional instruction or practice. Provide targeted support and intervention when needed.
Encourage Reading – Foster a love of reading by sharing engaging stories and books with students. Encourage them to practice their phonics skills by reading independently or with a partner.
Remember that every student learns at a different pace, so it’s essential to be patient and provide individualized support as needed. By using these strategies and tips, you can help your students build a strong foundation in phonics, which will support their development as proficient readers and writers.
The Importance of Letters and Sounds
Understanding letters and their corresponding sounds is of paramount importance for several reasons:
- Reading Proficiency: The ability to recognize and associate letters with their sounds is the cornerstone of reading. This knowledge allows students to decode words, enabling them to read fluently and comprehend text effectively.
- Spelling Competence: Mastering letter-sound correspondence is essential for spelling words accurately. It empowers students to write confidently and express their thoughts clearly.
- Vocabulary Development: Building a strong foundation in letters and sounds expands a student’s vocabulary. A rich vocabulary enhances their ability to understand and use words in a variety of contexts.
- Enhanced Communication: Proficiency in letters and sounds equips students with the skills needed for effective verbal and written communication. This skill is invaluable in both academic and real-world situations.
This collection of Letters and Sounds worksheets is a valuable resource for educators and parents committed to supporting their students’ literacy development. A solid grasp of letters and their corresponding sounds is the foundation upon which a student’s reading and writing skills are built.
By using these engaging worksheets, students will strengthen their ability to read, write, and understand language with confidence. This collection equips them with essential skills for a lifetime of effective communication and academic success, giving them a significant advantage in their educational journey.