Rhyming Worksheets
What are Rhyming Worksheets?
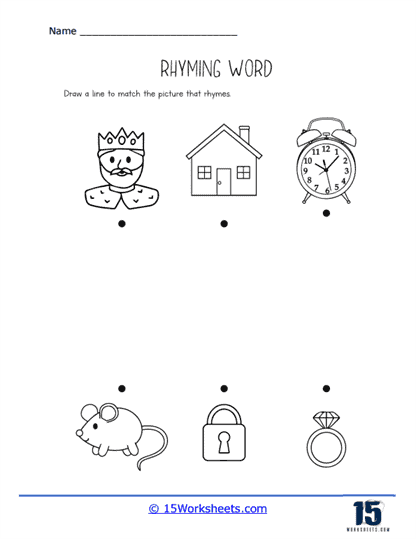
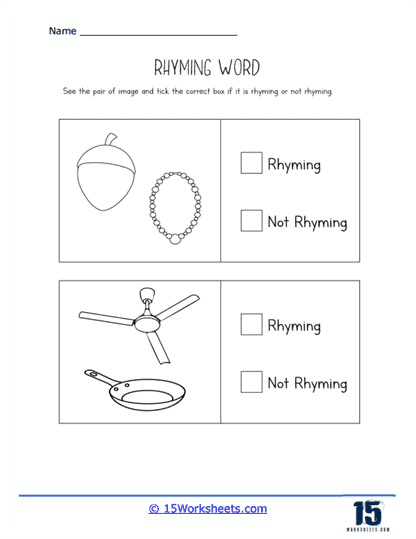
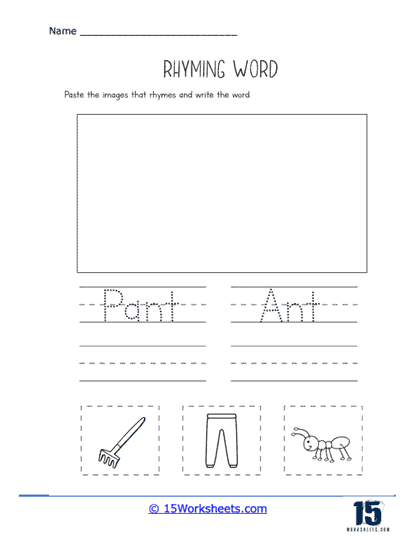
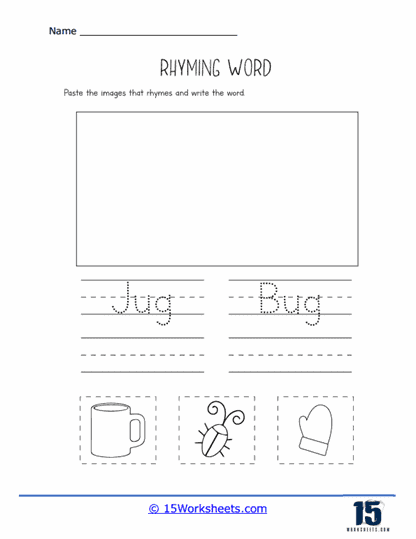
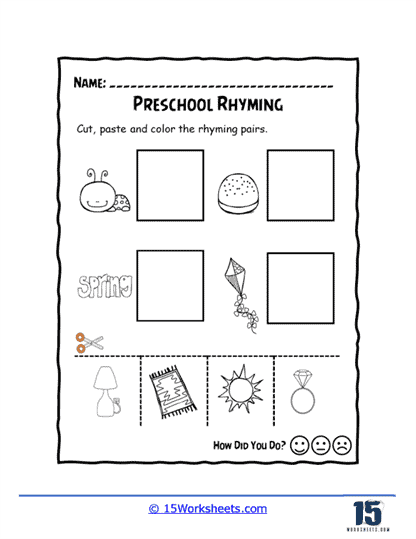
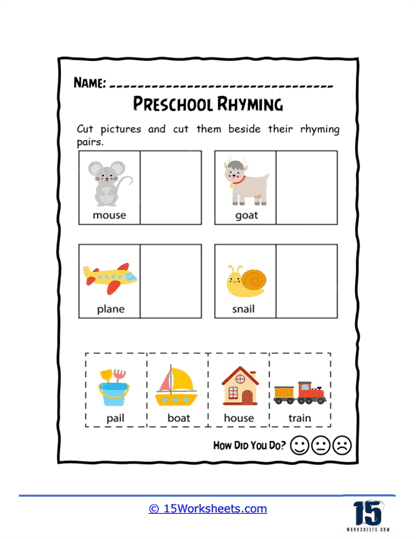
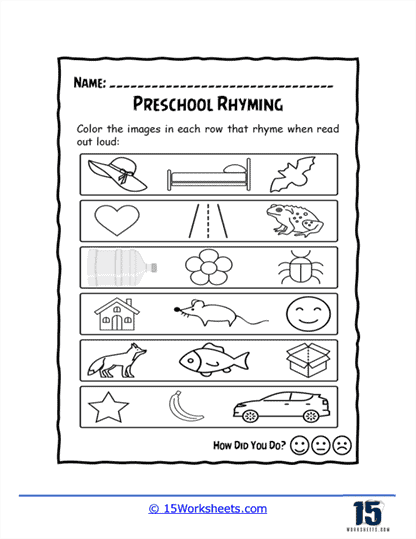
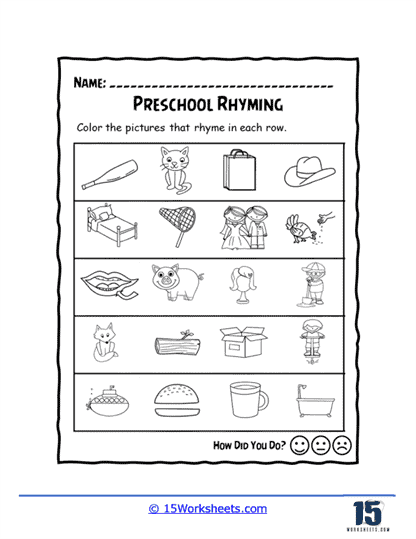
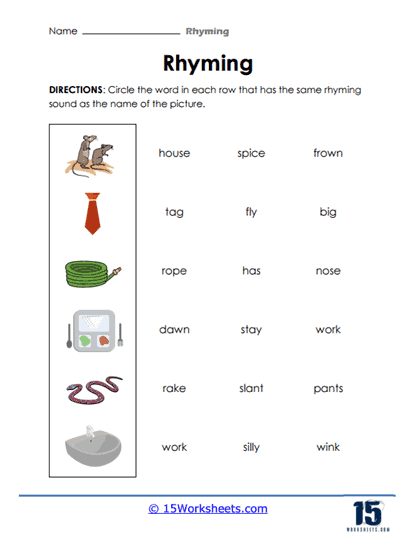
Our series of rhyming worksheets will help young children develop their phonics skills and enhance their understanding of language through the recognition and use of rhyming words. These worksheets include a variety of activities aimed at encouraging children to identify words that sound alike, match rhyming pairs, and create their own rhymes. Rhyming is a fundamental phonological awareness skill, and mastering it is essential for early literacy development. By focusing on the sounds within words rather than their meanings, rhyming worksheets provide children with a playful and engaging way to explore language, which in turn strengthens their reading and writing abilities.
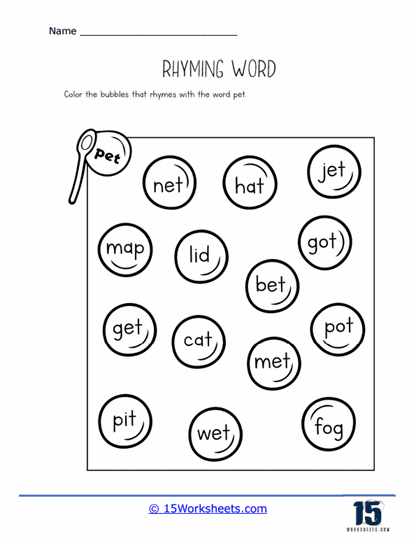
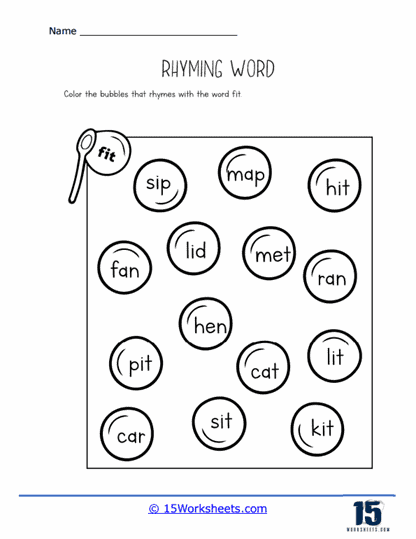
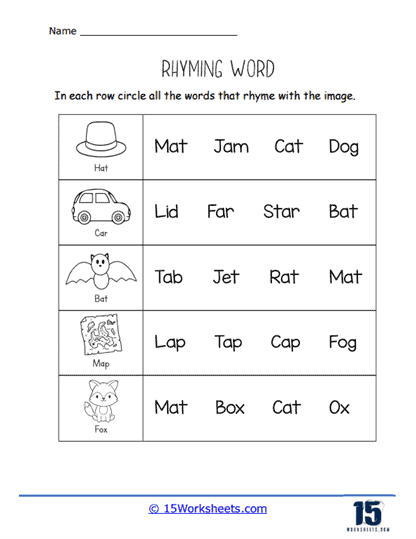
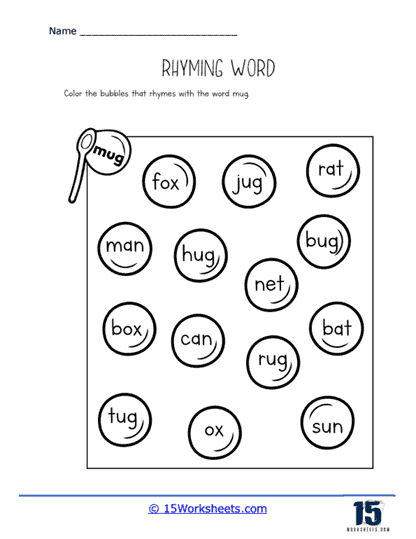
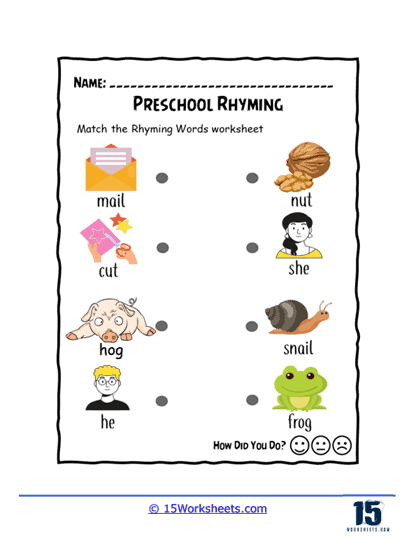
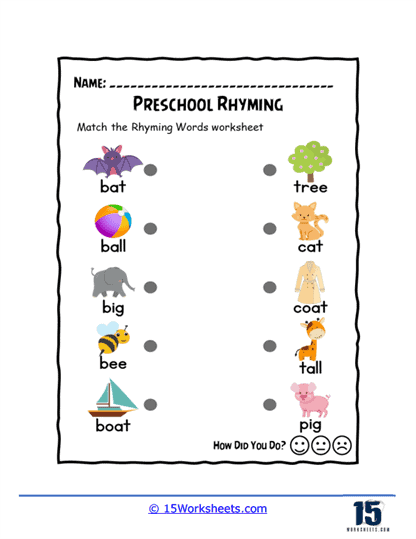
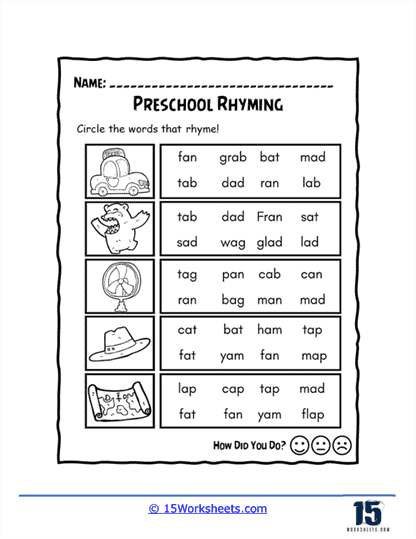
One key function of our rhyming worksheets is to help children recognize sound patterns in words. This recognition of phonemes, or individual units of sound, is a crucial part of phonics, the system by which written language is connected to spoken language. Rhyming exercises often involve identifying words that have the same ending sounds, such as “cat” and “hat” or “dog” and “frog.” By repeating these exercises, children become more attuned to the structure of words and the relationships between different sounds. This not only aids in phonological awareness but also enhances their decoding skills when they eventually encounter new words in reading.
These worksheets also offer opportunities for children to expand their vocabulary and improve their language comprehension. When children are asked to think of rhyming words or match words with their rhyming counterparts, they are exposed to a broader range of vocabulary. For example, a worksheet that asks children to find rhymes for the word “tree” might introduce them to words like “bee,” “free,” and “key.” As they learn new words and their meanings, they build a richer linguistic foundation, which can improve both their spoken and written language skills. This vocabulary development is an important aspect of literacy, as it enables children to communicate more effectively and understand more complex texts.
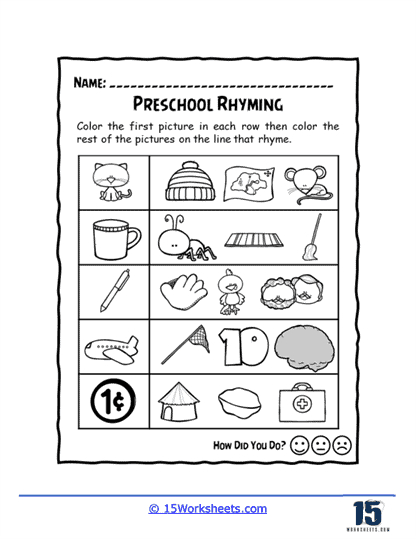
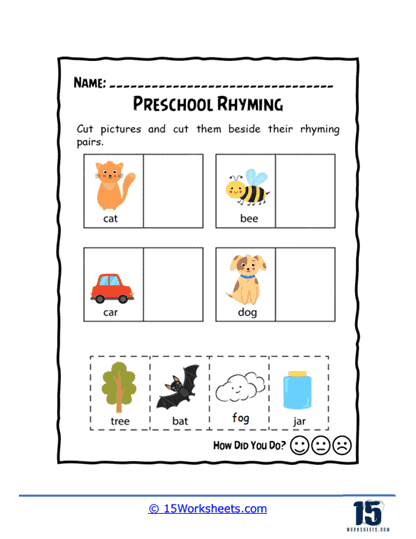
We hope that these worksheets make learning enjoyable and engaging, which is critical for maintaining young children’s interest in early literacy activities. Many worksheets incorporate fun elements like coloring, drawing, or interactive games, which make the process of learning to rhyme feel more like play than work. For example, children might be asked to color pictures of objects that rhyme or connect rhyming words with lines or arrows. These visual and hands-on activities appeal to different learning styles and help to keep children motivated. When children enjoy the learning process, they are more likely to retain the information and develop a positive attitude toward reading and writing.
How Rhyming Improves You Language Skills
Rhyming plays a significant role in developing language arts skills, as it helps learners recognize patterns, build phonemic awareness, and enhance various aspects of language acquisition. Here are some reasons why rhyming is beneficial for language arts skills:
Phonemic Awareness – Rhyming helps build phonemic awareness, as it requires learners to identify and manipulate the individual sounds within words. Recognizing the similarities and differences between words with the same ending sounds (e.g., cat, bat, mat) helps learners develop their ability to distinguish and work with phonemes.
Listening Skills – Rhyming activities often involve listening to and identifying words that rhyme, which helps improve learners’ auditory processing and listening skills. These skills are essential for successful language acquisition and comprehension.
Vocabulary Development – Rhyming introduces learners to new words and their meanings, expanding their vocabulary. As they encounter and recognize patterns in rhyming words, they can more easily guess the meaning of unfamiliar words based on their context and structure.
Reading and Spelling – Rhyming helps develop reading and spelling skills by familiarizing learners with common letter patterns and combinations. This familiarity enables them to decode and spell new words more effectively.
Memory and Retention – Rhyming can aid memory and retention by organizing information into easily recognizable patterns. This is particularly useful when learning new vocabulary, as it can help learners remember words and their meanings more effectively.
Creative Expression – Rhyming plays a key role in creative expression, particularly in poetry and songwriting. Engaging with rhyming helps learners develop an appreciation for the aesthetic and rhythmic aspects of language, which can inspire their own creative writing and expression.
Fluency and Prosody – Rhyming helps learners develop fluency and prosody in their speech by exposing them to the natural rhythm and intonation patterns of language. This can improve their overall language skills and make them more confident speakers.
Motivation and Engagement – Rhyming activities are often fun and engaging, which can motivate learners to participate and stay focused on their language arts lessons.
Incorporating rhyming activities and exercises into language arts instruction can help learners develop various skills, including phonemic awareness, listening, vocabulary, reading, spelling, creative expression, and fluency. By engaging with rhyming, learners can improve their overall language abilities and gain a deeper appreciation for the beauty and versatility of language.