Phoneme Segmenting Worksheets
All About These 15 Worksheets
This phoneme segmenting worksheets collection is super helpful for developing early reading skills by focusing on phonemic awareness, a cornerstone in literacy education. Phonemic awareness-the ability to recognize and manipulate individual sounds in words-plays a critical role in a child’s ability to decode written language and form a strong foundation for reading and writing. This set of worksheets has been carefully designed to address and nurture this key aspect of literacy development, offering a wide range of exercises that progressively challenge students while ensuring engagement and understanding. By examining how these worksheets operate, we can better appreciate the strategies employed to foster students’ phonemic awareness and their overall literacy progress.
Building Phonemic Awareness Through Sound Segmentation
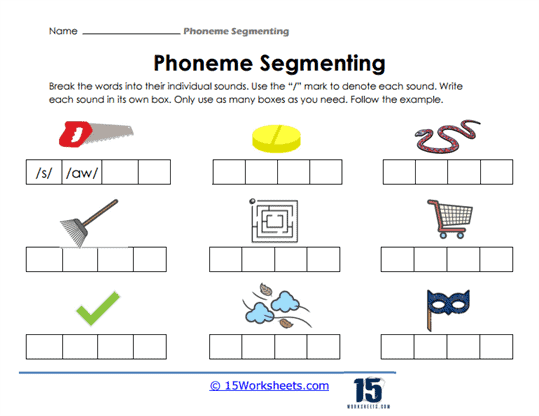
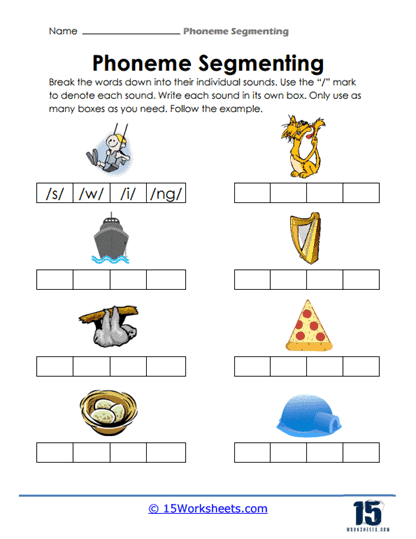
At the heart of these worksheets is the skill of sound segmentation, which allows students to break down words into their smallest sound components, known as phonemes. This is an essential step in learning to decode words—a fundamental task in early literacy. Each worksheet presents a word visually, often accompanied by a picture, allowing students to connect the spoken word with its segmented phonemes. For example, when a student is asked to say the word “dog” and then break it into its constituent sounds /d/, /o/, and /g/, they are practicing the ability to hear each distinct phoneme. This activity promotes phonemic awareness by drawing attention to the individual sounds in a word, something that is not immediately obvious in normal speech.
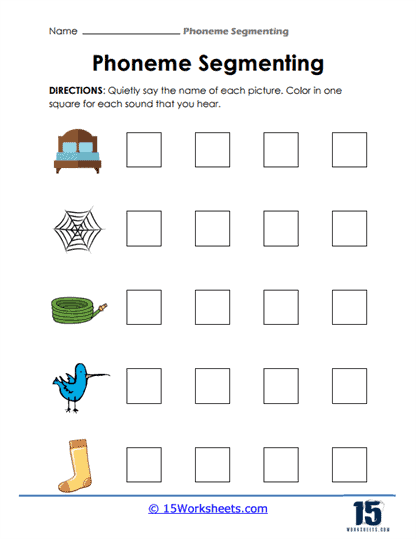
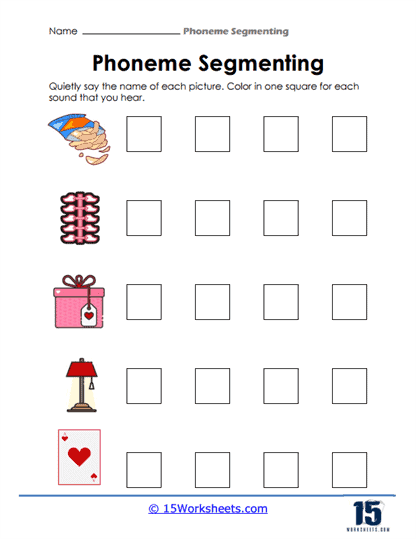
By encouraging students to color or fill in shapes, such as squares or circles, that represent each sound they hear in a word, these worksheets provide a tactile and visual element to the learning process. The act of physically marking the number of sounds helps solidify the connection between auditory input (hearing the sounds) and motor output (physically identifying each phoneme). This multisensory approach is critical for early learners, particularly those who benefit from visual and kinesthetic reinforcement, ensuring they remain engaged while mastering the skill of sound segmentation.
Differentiating Sounds and Counting Phonemes
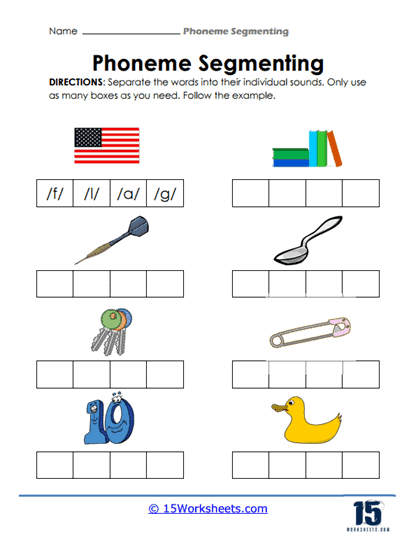
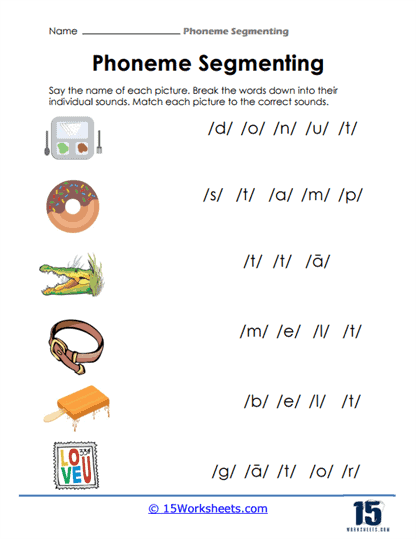
Another key feature of these worksheets is the emphasis on phoneme differentiation and counting. Worksheets that include activities where students must associate specific pictures with the correct number of phonemes offer a direct, hands-on way for children to understand the structure of words. For instance, a worksheet might show a picture of a flag, prompting students to break the word down into its component sounds: /f/, /l/, /a/, /g/. This kind of activity not only reinforces the concept of phonemic segmentation but also allows students to begin distinguishing between different types of sounds, such as consonants and vowels.
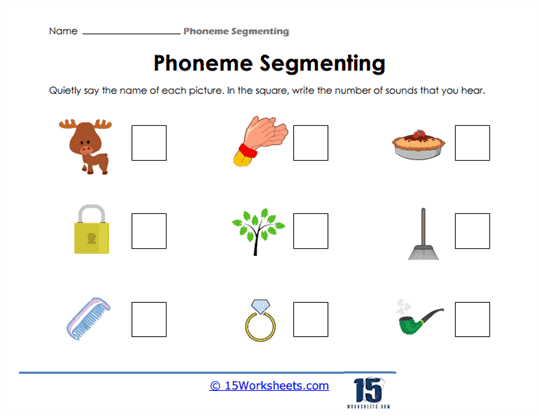
Phoneme counting goes beyond simply recognizing individual sounds—it helps children grasp the concept that words are composed of multiple phonemes that can be isolated and then blended back together. This skill is vital as students move from recognizing sounds to reading words fluently. The more they practice identifying and counting phonemes, the better they become at decoding unfamiliar words, an essential step in becoming proficient readers and writers.
Visual Cues and Engagement with Patterns
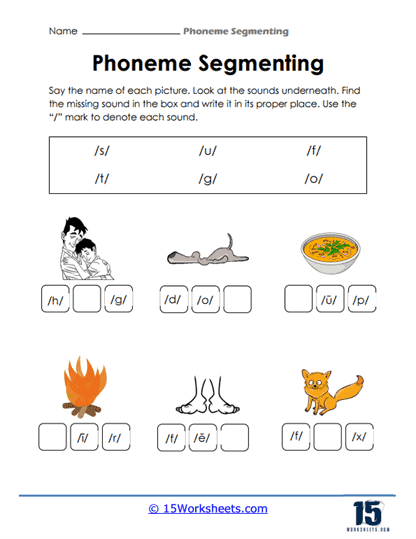
The inclusion of visual elements, such as pictures and diagrams, adds an engaging dimension to the worksheets, making the learning process more approachable for young students. Visual cues serve to anchor phonemic awareness in a familiar context, allowing students to associate abstract sounds with concrete images. For example, a worksheet featuring a picture of a cat might ask students to fill in the missing /t/ sound. This exercise not only reinforces the phonemes they already know but also encourages them to listen carefully for missing sounds, developing their auditory discrimination skills.
By focusing on identifying missing sounds in familiar words, these worksheets train students to listen more carefully, heightening their ability to detect subtle sound patterns in spoken language. These visual and auditory connections ensure that students stay actively engaged, turning what might otherwise be a rote exercise into a dynamic learning experience that appeals to different learning styles.
Gradually Developing Phonemic Skills
As students progress through the collection, the tasks grow in complexity, ensuring that their phonemic awareness evolves along with their overall literacy skills. Early worksheets focus on simple phoneme segmentation and recognition, but later worksheets introduce more challenging exercises that involve filling in missing phonemes or matching specific phonemes to corresponding pictures. This gradual increase in difficulty ensures that students are not only recognizing individual sounds but also learning how to manipulate them-a critical aspect of advanced phonemic awareness.
For example, some worksheets may require students to substitute one sound for another, helping them understand how phoneme manipulation changes the meaning of a word. This skill is pivotal as students move toward more advanced reading skills, such as phoneme substitution and deletion, which are essential for fluent reading and word comprehension. By guiding students through this process, the worksheets prepare them to tackle more sophisticated literacy tasks and set them on a path toward independent reading.
Scaffolding and Versatility
One of the standout features of this collection is its built-in scaffolding, which ensures that students at different stages of their literacy journey can benefit from the exercises. The worksheets are designed to build upon one another, starting with simple sound recognition and moving toward more complex phonemic tasks. This scaffolding is particularly helpful for educators, as it allows them to tailor the difficulty level of the exercises to meet the specific needs of their students. Whether a child is just beginning to segment sounds or is ready to engage in phoneme manipulation, there are worksheets within the collection that can address their unique learning requirements.
The versatility of these worksheets makes them ideal for differentiated instruction. Teachers can easily modify the activities to suit the needs of individual students, whether by focusing on phoneme counting for beginners or challenging more advanced learners with tasks that involve sound manipulation and substitution. This flexibility ensures that the worksheets remain a valuable resource throughout the various stages of phonemic awareness development.
What Is Phoneme Segmenting?
Phoneme segmenting is a foundational skill in the journey toward reading and writing proficiency. At its core, phoneme segmenting involves breaking down a spoken word into its individual sounds, or phonemes. These phonemes are the smallest units of sound that make up language, and the ability to identify them is critical for effective communication. By mastering phoneme segmenting, learners gain a deeper understanding of how language is constructed, which sets the stage for success in reading, spelling, and writing.
Phoneme segmenting goes hand-in-hand with phonemic awareness-the recognition that words are made up of distinct sounds that can be manipulated and combined to convey meaning. This skill allows students to hear a word like “cat,” for example, and break it down into the separate sounds /k/, /a/, and /t/. By doing so, they begin to grasp the sound-symbol relationships that are central to reading. This ability to deconstruct language into smaller parts empowers students to understand not only how to pronounce words but also how to decode and encode them.
The Role in Reading Development
For young readers, phoneme segmenting is a crucial step toward understanding the sound structure of words. It directly contributes to their ability to decode new or unfamiliar words, which is essential for reading fluency. When a child can break a word into its phonemes, they can more easily match those sounds to corresponding letters or letter patterns. This decoding skill is vital for students as they encounter new vocabulary in their reading journey.
By building strong phonemic awareness through phoneme segmenting, students also become more adept at encoding-spelling words correctly by mapping sounds to their written forms. This process of segmenting phonemes enhances the learner’s ability to read and write with confidence, as they can independently figure out how to tackle unfamiliar words without relying solely on memorization.
The Building Block for Literacy
Phoneme segmenting is one of the key contributors to phonemic awareness, a skill that enables learners to manipulate and play with sounds. Phonemic awareness is the foundation of reading readiness. Children who develop this skill early on are better equipped to understand how individual sounds combine to form words. Phoneme segmenting encourages learners to recognize that sounds can be rearranged, substituted, or omitted to create entirely new words. This flexibility with language forms the basis of many phonics strategies used in classrooms to teach reading.
Beyond simply identifying sounds, phonemic awareness allows students to experiment with language. They learn to swap phonemes to form new words, helping them develop a deeper, more intuitive sense of how language works. This skill fosters creativity with language and opens up pathways for learners to become more engaged and confident readers.
How To Teach Phoneme Segmenting To Students
Teaching phoneme segmenting is a critical component of early literacy, as it helps students break down words into individual sounds, a foundational skill for reading and spelling. To do this effectively, educators need a structured approach that balances direct instruction, practice, and engaging activities. By introducing phoneme segmenting in an interactive and systematic way, teachers can ensure that students develop the skills they need for future success in reading.
The first step in teaching phoneme segmenting is introducing individual phonemes and their corresponding letters or letter combinations. Since English is built on a complex system of sounds and spellings, it’s crucial to start with the most common sounds that students will frequently encounter. For instance, educators can focus on the basic consonants and short vowels found in simple CVC (consonant-vowel-consonant) words such as “cat” or “dog.” Breaking these sounds down one by one helps students grasp the concept of phonemes and how they are represented in writing. When educators provide clear, direct instruction on these sounds, students begin to understand the relationships between spoken language and written symbols, which is the cornerstone of phoneme segmenting.
Once students are familiar with individual phonemes, it’s essential to model how to segment sounds in words. Educators should frequently demonstrate how to break down spoken words into their component sounds, making sure to emphasize how each sound corresponds to a written letter or combination of letters. For example, when segmenting the word “bat,” the teacher can explicitly say the word aloud, isolate each sound (/b/ /a/ /t/), and show how those sounds map to the letters “b,” “a,” and “t.” Modeling this process repeatedly helps students internalize how spoken language is translated into written form, an important step in phoneme awareness and spelling skills.
Providing students with ample opportunities to practice phoneme segmenting is equally important. As with any new skill, practice is key to mastery. Starting with simple CVC words gives students the chance to focus on three sounds at a time, making the task manageable and less overwhelming. As students become more confident, teachers can gradually introduce more complex words, adding consonant blends, digraphs, and vowel combinations. By progressing from easier to more difficult words, students are more likely to experience success and build confidence in their abilities.
This collection of Phoneme Segmenting worksheets is a valuable resource for educators and parents committed to supporting their students’ phonemic awareness and literacy development. Proficiency in phoneme segmenting is not just an academic exercise; it’s a fundamental skill that opens the doors to reading fluency, comprehension, and effective communication.
By using these engaging worksheets, students will strengthen their ability to segment phonemes with confidence, ultimately improving their overall language proficiency and literacy skills. This collection is an investment in their future success, ensuring they have a solid foundation in phoneme segmenting and language skills.