Consonant Digraphs Worksheets
All About These 15 Worksheets
This series of worksheets will introduce students to the concept of consonant digraphs, an essential aspect of early literacy that focuses on phonetic understanding. Consonant digraphs occur when two consonant letters are combined to produce a single, distinct sound. This concept is fundamental for young learners as they develop the skills needed to decode words effectively, laying the groundwork for fluent reading and accurate spelling.
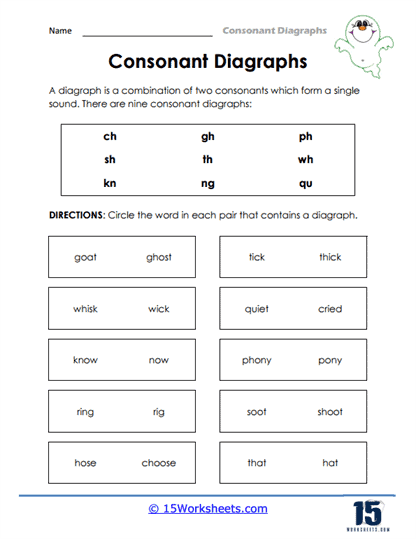
Consonant digraphs are commonly found at various positions within words-at the beginning, middle, or end-and they significantly affect the pronunciation of the word. For instance, consider the digraph “ch,” which appears at the beginning of words like “chair” and “chocolate” and creates a sound distinct from either of its individual letters. Similarly, “sh” forms a unique sound in words like “ship” or “wash,” and the digraph “th” appears in words like “thing” and “bath,” contributing to the uniqueness of English sounds. Another example is “ph,” which represents the sound of “f,” as seen in words like “phone” or “elephant.”
A Look at the Worksheets In This Collection
Learning consonant digraphs might sound like a dusty old phonics lesson, but not when you’re armed with the worksheets from this collection! Students begin their phonetic quest with Spotting Special Sounds, a delightful safari where “sh,” “ch,” “th,” and “wh” leap from the bush like startled lemurs. Say And Write gently encourages kids to open their mouths, sound out these duos of sound magic, and then trap them on paper like spelling wizards in training. Think of it as Hogwarts for phonics – only the wand is a pencil, and the magic spell is “cheese.”
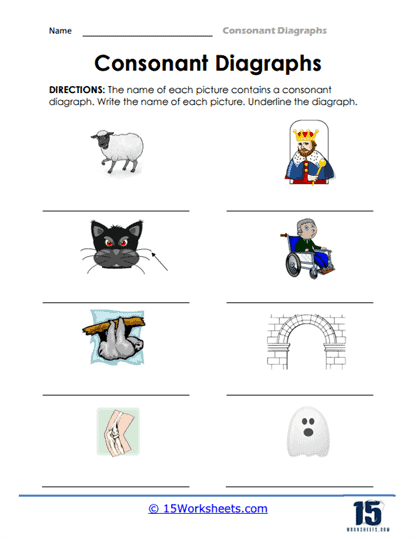
In Detect And Underline, students don trench coats and become mini Sherlocks of sound, sniffing out sneaky digraphs hiding in plain sight. Take Your Pick tempts them with phonetic multiple-choice mayhem – choose wisely, for only one digraph can save the word from meaninglessness. Then there’s Complete The Word, where the poor, helpless words show up missing limbs, and it’s up to our heroic students to graft on the right “ck,” “sh,” or “th” to restore them to full literacy health. It’s like orthopedic surgery for the English language.
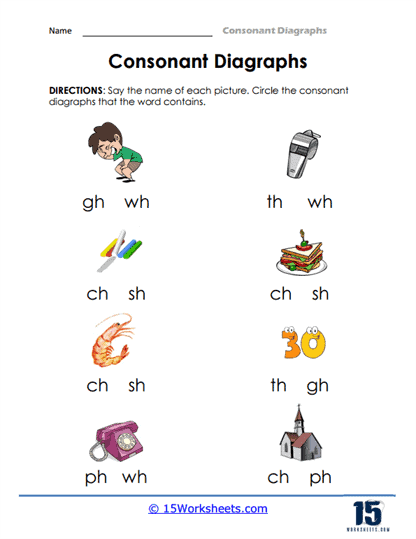
Spell It Out is where spelling meets creativity. Kids don’t just regurgitate digraphs – they build them, Frankenstein-style, letter by letter. Picture Clues ups the ante with a guessing game: What’s this image? A ship? A chair? Only by summoning the correct digraph can the puzzle be solved. Then in Digraph Discovery, students become Indiana Jones of phonics, unearthing ancient consonant relics buried in everyday words. There’s no snake pit, but there is a quiz at the end.
Sound Secrets adds a mysterious flair – almost espionage-level phonics. Words hide behind silent letters, and only a student with a good ear (and maybe a decoder ring) can crack the code. Then comes Categorize And Conquer, the worksheet equivalent of sorting your laundry – but with digraphs. Organize those sounds like a true phoneme professional. Consonant Digraph Sleuths gives students a magnifying glass and an attitude: find those digraphs like you’re solving a murder, because a mispronounced “ch” is basically a crime in reading class.
We wrap up with the grand finale: Listen And Learn trains the ears to become sonar-level digraph detectors. Fill Them In is a puzzle where consonant duos race to complete the gaps – like phonics speed dating. A Triple Challenge dares kids to tackle three tasks in one worksheet – they’ve climbed the digraph mountain and now face the boss level. And finally, Five For Each is a lightning round of digraph mastery. By the time students finish these, they won’t just know digraphs – they’ll dream in them. These worksheets may start with scribbles, but they end with sound-based enlightenment. Or at the very least, a well-earned snack and a triumphant fist-pump.
What Are Consonant Digraphs?
Consonant digraphs are an essential concept in early literacy that helps young readers break through common language barriers. These pairs of consonants work together to form a single sound, or phoneme, that differs from the sounds the individual letters would typically make on their own. Unlike consonant blends, where both letters retain their unique sounds, consonant digraphs combine to create a distinct sound that is crucial for decoding words. For example, in the word ship, the letters “s” and “h” do not produce their separate sounds but merge into the unique /ʃ/ sound. Understanding these combinations is critical for young readers as they begin to make sense of written language.
For children learning to read, consonant digraphs can pose a challenge. The fact that two letters can make one sound is not always intuitive. This is where consonant digraph worksheets play a pivotal role. These worksheets introduce and reinforce the digraphs in a structured way, allowing children to recognize patterns in language. For instance, when a child encounters the digraph “ch” in words like chair, cheese, and school, they begin to associate that combination of letters with the /tʃ/ sound. Over time, this consistent practice helps children quickly recognize and pronounce words containing these digraphs, which in turn improves their reading fluency and confidence.
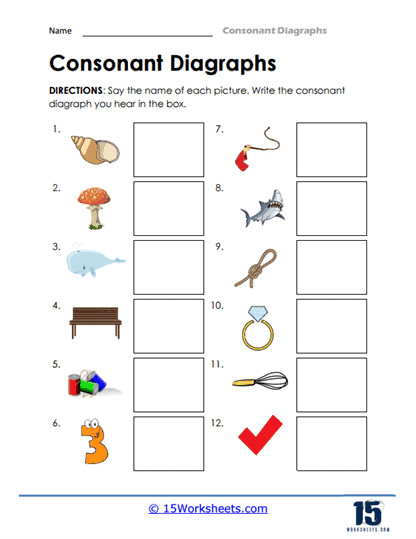
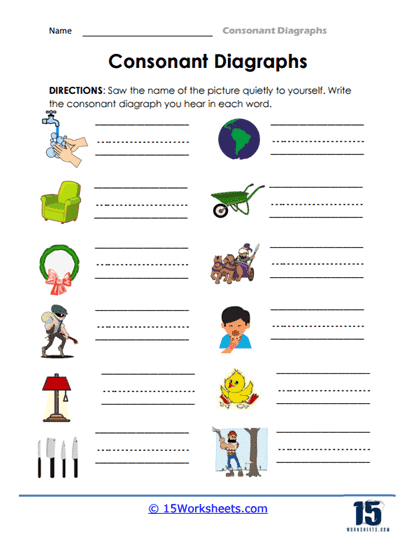
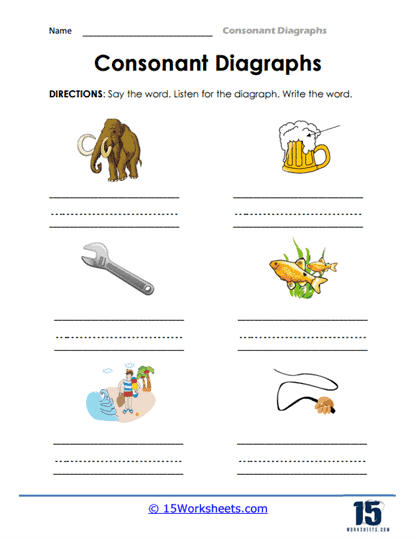
The use of consonant digraph worksheets is particularly beneficial for children who are just beginning to master phonics. Phonics is the relationship between sounds and their written representations, and understanding digraphs is a critical aspect of this skill. Worksheets might begin with simple matching activities where children connect a picture (such as a fish) with the corresponding word that contains the digraph “sh.” This kind of visual reinforcement helps children solidify their understanding of how the digraphs function in everyday words.
As children progress, the worksheets can become more complex, including fill-in-the-blank exercises where students are asked to choose the correct word with a digraph to complete a sentence. For example, a sentence might read, “I saw a _______ in the ocean,” and the student would choose between words like fish and wish. This type of activity reinforces not only the sound of the digraph but also its meaning and context within a sentence, helping to build both phonetic understanding and comprehension skills simultaneously.
One of the key benefits of focusing on consonant digraphs through worksheets is that it improves reading fluency. Reading fluency is the ability to read with speed, accuracy, and proper expression. When children struggle to decode digraphs, it can slow down their reading, making the process frustrating and disjointed. However, when children practice digraphs through repetition on worksheets, they begin to recognize these combinations quickly, leading to smoother and more automatic reading. For instance, a child who repeatedly encounters the digraph “th” in words like thin, bath, or the will start to recognize it more quickly, boosting their overall fluency.
Consonant digraph worksheets also help with pronunciation, which is crucial for young readers who are still mastering spoken language. Some digraphs, like “th,” can be tricky because they come in both voiced and voiceless forms. The word thin has a voiceless “th” (/Θ/), while the word this uses a voiced “th” (/ð/). By using worksheets that highlight these subtle differences, children can practice both reading and speaking the words correctly. For example, a worksheet might include a list of words for students to read aloud, paying special attention to whether the “th” is voiced or voiceless. This kind of activity strengthens both reading and speaking skills, making the child a more effective communicator.
In addition to improving reading fluency and pronunciation, consonant digraph worksheets are instrumental in expanding a child’s vocabulary. As students become familiar with different digraphs, they also encounter new words that contain these letter combinations. For example, when learning the digraph “ph” in words like phone, graph, and dolphin, students are not only mastering the /f/ sound but are also expanding their vocabulary with terms they might not encounter in everyday speech. These worksheets introduce new, age-appropriate words that children can incorporate into both their spoken and written language, thereby enhancing their overall language skills.
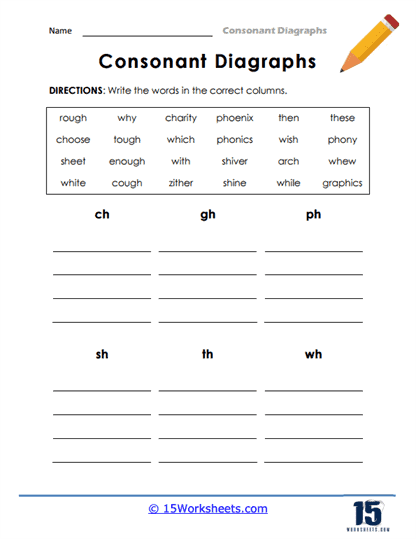
Another effective exercise often found in consonant digraph worksheets is word sorting. In these activities, children are presented with a list of words and asked to sort them based on the digraphs they contain. For instance, they might be given words like whale, when, whisker, chip, ship, and thin, and asked to sort them into categories based on whether they contain “wh,” “ch,” “sh,” or “th.” This task helps students to focus on the specific sound each digraph makes and reinforces their understanding through comparison.
Reading comprehension passages that incorporate consonant digraphs are another useful tool. These worksheets might include a short story filled with words containing digraphs, followed by questions that test a student’s understanding of the text. For example, a passage might describe a boy going fishing (highlighting the digraph “sh”) or a family going on a whale-watching trip (reinforcing the digraph “wh”). These stories not only provide context for the digraphs but also help children practice reading fluidly while improving their comprehension skills.
Why Are Consonant Digraphs An Important Part of Phonics?
Phonics is a fundamental building block of literacy, enabling children to connect letters with their corresponding sounds and decode words effectively. One of the most critical elements of phonics instruction involves understanding consonant digraphs, which play a key role in expanding vocabulary, improving reading fluency, enhancing spelling skills, and simplifying the complexity of English phonemes. These digraphs, formed when two consonants combine to make a single sound, are essential for helping students unlock a greater understanding of how language works. The mastery of consonant digraphs can pave the way for a smoother, more confident reading experience.
Vocabulary Expansion Through Digraphs
One of the most immediate benefits of learning consonant digraphs is the expansion of vocabulary. By understanding digraphs, children can access a wider variety of words and phrases, many of which would be difficult to pronounce or understand if tackled letter by letter. Consonant digraphs like “th,” “sh,” “ch,” and “ph” create sounds that do not exist within individual consonants, making them critical for reading and pronunciation. For example, without the digraph “th,” words like “the” or “this” would be mispronounced and misunderstood. Similarly, the “sh” sound in words like “ship” or “shoe” allows children to differentiate between words that otherwise could be confusing.
Imagine a young learner encountering the word “phone” for the first time. Without understanding that the letters “ph” together make the sound of an “f,” the child might try to pronounce each letter separately, saying something like “puh-hone.” Mastering consonant digraphs equips them with the knowledge that certain combinations create a specific sound, allowing for a much more accurate and smoother reading process.
Improving Reading Fluency and Comprehension
Consonant digraphs also play a pivotal role in reading fluency. When students first start reading, they often attempt to sound out words by breaking them into individual letters, which can slow down their reading and make it more difficult to grasp the meaning of sentences. However, by understanding that certain letter pairs form unique sounds, children can begin to read words as complete units rather than individual letters. This allows them to read faster and more accurately, improving not only their speed but also their comprehension.
Take, for instance, a child trying to read the sentence, “The cat sat on the chair.” If they are unfamiliar with consonant digraphs, they might struggle with “th” in “the” or “ch” in “chair,” leading to a choppy reading experience where each sound is isolated. This breaks the flow of the sentence, making it harder for the child to understand the story as a whole. On the other hand, a student who has been taught consonant digraphs will recognize these sound combinations immediately, allowing them to glide through the sentence with ease, maintaining the context and meaning.
As a result, worksheets focused on consonant digraphs can be immensely valuable for improving fluency. These worksheets often provide students with practice opportunities to encounter digraphs in various words and sentences, helping them develop the automaticity needed for fluent reading. For example, a worksheet might have students match pictures to words that contain digraphs, reinforcing the sound and meaning connection in a fun, engaging way.
Enhancing Spelling Skills
In addition to improving reading skills, consonant digraphs are incredibly helpful for spelling. English spelling is often unpredictable, with many words defying typical phonetic rules. However, understanding digraphs can provide a helpful framework for students as they learn to predict and recognize the correct spelling of words. When children understand that “ch” makes a specific sound in words like “cheese” or “chair,” they are more likely to remember the spelling of these words, as they are no longer guessing which letters to use.
For instance, consider the word “graph.” If a child understands that “ph” can make the sound of “f,” they are less likely to misspell the word. Worksheets that focus on spelling with consonant digraphs can be instrumental here. These worksheets often involve activities like fill-in-the-blank exercises, where students must choose the correct digraph to complete a word, or spelling lists where they practice writing words that contain digraphs. Such practice can solidify the connection between sound and spelling, making it easier for children to tackle more complex words.
Simplifying the Complexity of English Phonemes
The English language is unique in that it contains more phonemes than there are individual letters to represent them. Phonemes are the distinct sounds that make up words, and in English, many of these sounds are represented by combinations of letters rather than single letters alone. This is where consonant digraphs come into play. Without digraphs, it would be impossible to accurately represent all the sounds needed to form the words we use daily.
English is also a language that has borrowed many words from other languages, such as Greek, Latin, and French. As a result, certain sounds and letter combinations from these languages have been adopted into English, making it even more crucial for students to understand how digraphs work. Words like “phone” (from Greek) or “champagne” (from French) would be far more challenging to pronounce and spell without knowledge of digraphs like “ph” and “ch.”
Through the use of consonant digraph worksheets, students are exposed to a variety of words that illustrate the complexity of English phonemes in an accessible way. These worksheets provide practice in both pronunciation and spelling, reinforcing the concept that certain letter combinations are essential to the proper use of the English language.