Letter Reversal Worksheets
All About These 15 Worksheets
These worksheets will help young students, especially those in the early stages of reading and writing, recognize and distinguish commonly confused letters, such as “b” and “d” or “p” and “q.” These letter pairs are frequently reversed by children due to their similar shapes, which can lead to difficulties in both reading comprehension and writing fluency. The worksheets aim to reduce confusion by offering targeted practice in recognizing, identifying, and writing these letters in different contexts.
Teachers, parents, and tutors can use them as supplementary activities to reinforce letter recognition, improve handwriting skills, and build reading confidence in children. Additionally, children with learning challenges such as dyslexia, who may struggle with letter reversals more frequently, can particularly benefit from these types of exercises.
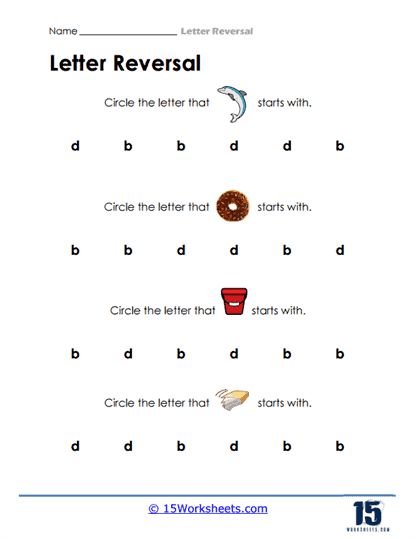
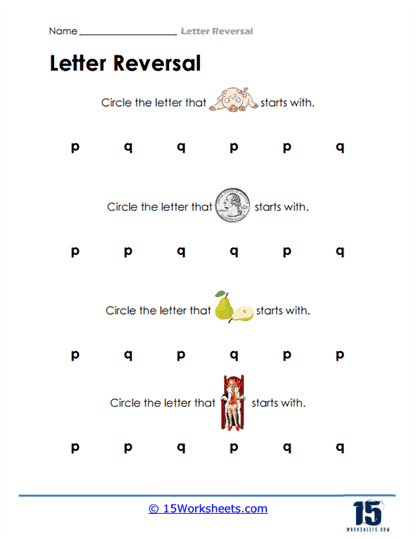
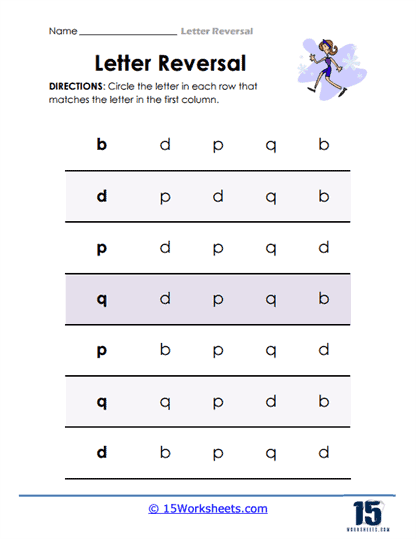
Letter Identification with Visual Cues – A prevalent activity involves providing a visual cue, such as a picture of an object or animal, and asking students to identify the correct starting letter from a set of options. For example, students might be shown a picture of a dolphin and asked to circle the letter “d” from a list that includes both “b” and “d.” This type of activity helps associate specific letters with familiar sounds and images, reinforcing the correct identification of letters. By creating a clear mental link between the image and its sound, students can better retain and retrieve this knowledge when reading or writing.
Bow Tie Matching for Letter Recognition – Some worksheets ask students to circle or color images (such as bow ties) next to the correct letter. For instance, a student might be asked to circle all the bow ties next to the letter “b” and avoid those next to “d.” This simple yet engaging activity encourages close attention to detail, ensuring that children develop a sharper ability to differentiate between similar-looking letters. The repetitive nature of the task builds a stronger recognition of letter forms, promoting accuracy and confidence in reading.
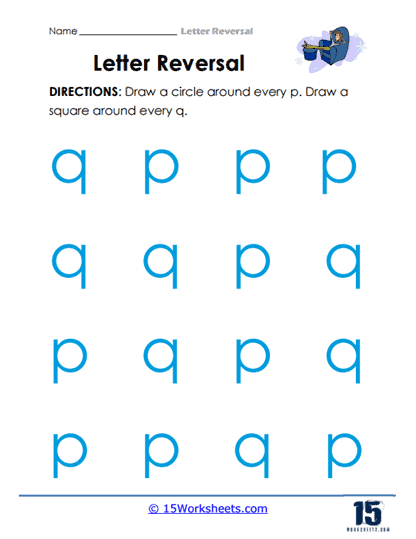
Shape-Based Sorting (Circles and Squares) – Another effective exercise involves students sorting letters into categories based on their shape. They are asked to draw a circle around all instances of the letter “b” and a square around every “d.” This tactile and visual exercise reinforces the differences between the letters and provides practice in letter discrimination. The physical action of drawing different shapes deepens their cognitive engagement, as the students associate the act of sorting with recognizing letter characteristics.
Letter Mazes – In some worksheets, children are tasked with navigating through a maze by following a specific letter, such as coloring every “b” to form a path from the start to the finish. This activity makes letter recognition fun and interactive, while also requiring focus as students work their way through the puzzle. It also helps in identifying letters in various orientations, reinforcing the visual memory of each. The challenge of completing a maze boosts perseverance, rewarding the child with a sense of achievement while they strengthen letter recognition skills.
Letter-Specific Coloring – In coloring-based exercises, students are given two colors and asked to color one letter in one color (e.g., “b” in purple) and the other in a different color (e.g., “d” in orange). This type of activity engages children visually and cognitively, requiring them to pay attention to the specific characteristics of each letter while making the task more enjoyable with the use of colors. The visual differentiation through coloring enhances memory retention, making the contrasting forms of letters stand out more clearly in their minds.
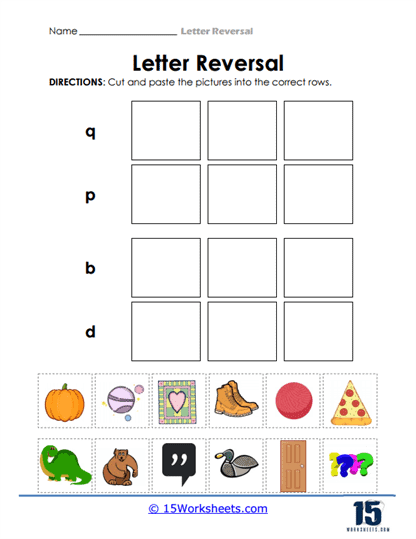
Matching Letters with Objects – Some worksheets ask students to match letters with corresponding pictures that begin with that letter. For example, children might see pictures of a pear, door, or bat, and must place each picture in the correct column under the letters “p,” “d,” or “b.” This not only reinforces letter recognition but also builds early phonics skills as students associate the initial sounds of words with their respective letters. Such activities bridge the gap between visual identification and auditory comprehension, fostering early literacy in a multi-sensory way.
Letter Sorting – In cut-and-paste activities, children are provided with a set of letters and asked to cut them out and sort them into correct categories. For instance, students may need to cut out a mixture of “b” and “d” letters and paste them into columns labeled “b” or “d.” These hands-on activities promote fine motor skills while reinforcing visual distinctions between confusing letters. The active nature of sorting creates a kinesthetic learning experience, deepening their understanding of letter forms through movement and interaction.
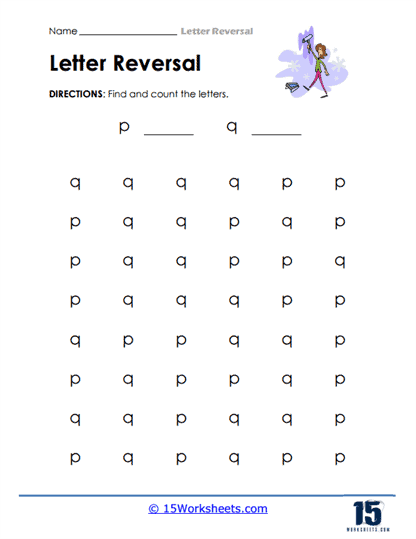
Coloring by Letter Type – Another version of sorting activities involves coloring. Students are instructed to color different letters with assigned colors, such as coloring all the “p”s in one color and all the “q”s in another. This encourages careful observation and helps children internalize the unique aspects of each letter, as they need to differentiate between letters that are visually similar. The task sharpens their visual attention, fostering the ability to spot small differences in letters with ease.
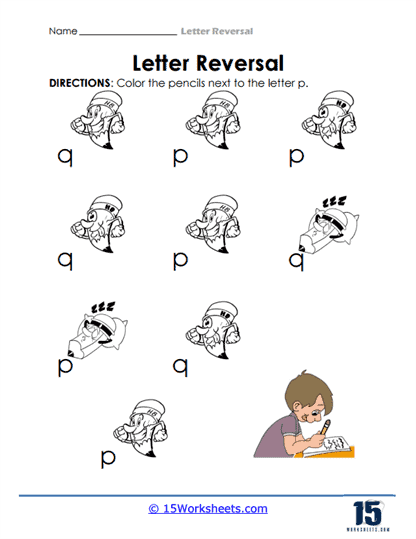
Letter Path Mazes with Different Letters – Similar to the letter-specific maze, children may be given exercises where they follow different letters, such as navigating a path by only selecting the letter “p” while avoiding the reversed “q.” This helps further enhance their ability to discern between mirrored or rotated letters. The complexity of distinguishing between similar forms under pressure strengthens their cognitive flexibility and prepares them for more advanced literacy challenges.
This collection of worksheets includes a wide variety of these exercises. For example, one image features a dolphin, donut, and other objects, where students must circle the starting letter of the object’s name. Another shows a maze where children need to color all the “b”s to create a path, providing a fun and engaging way to practice letter recognition.
The worksheets use vibrant and playful designs, such as green bow ties, sleeping characters, and even gingerbread figures to maintain the child’s interest. Activities that involve cutting and pasting pictures or coloring specific letters are also present, which adds a multi-sensory approach to learning, catering to visual and kinesthetic learners alike.