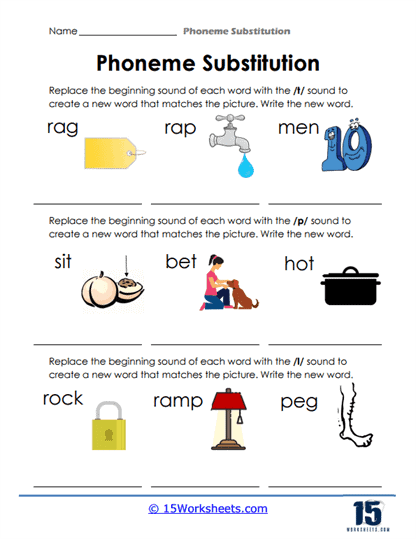
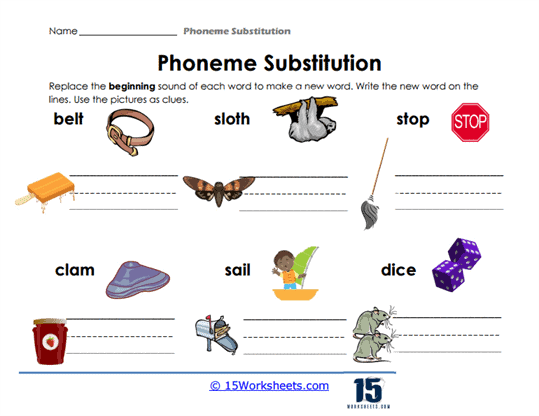
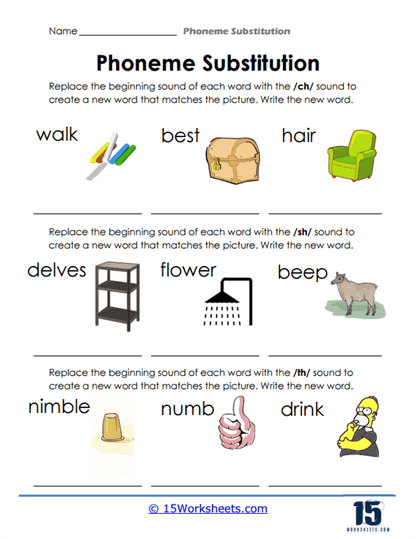
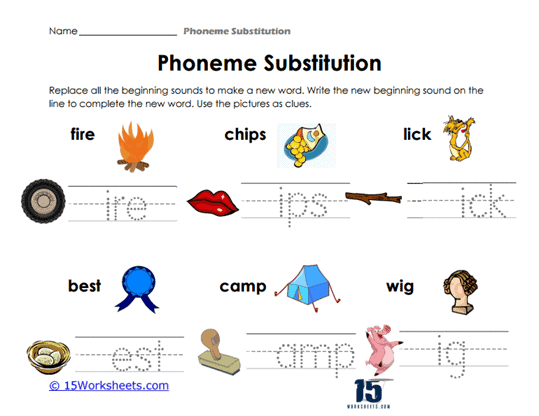
Phoneme Substitution Worksheets
All About These 15 Worksheets
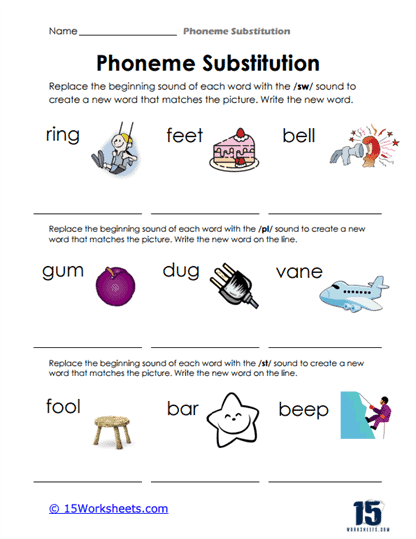
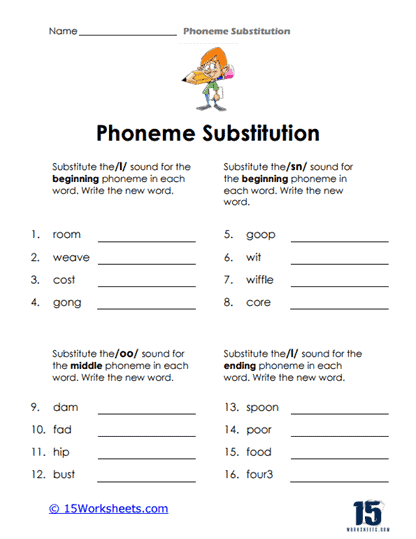
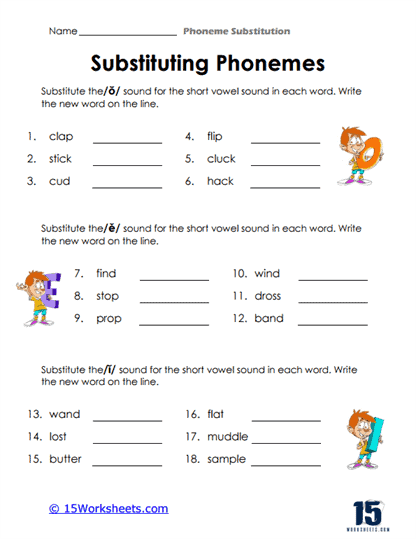
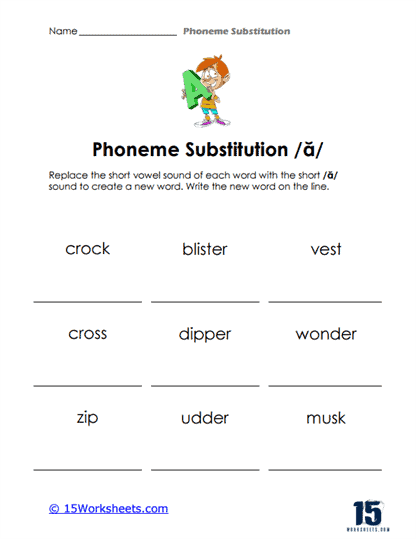
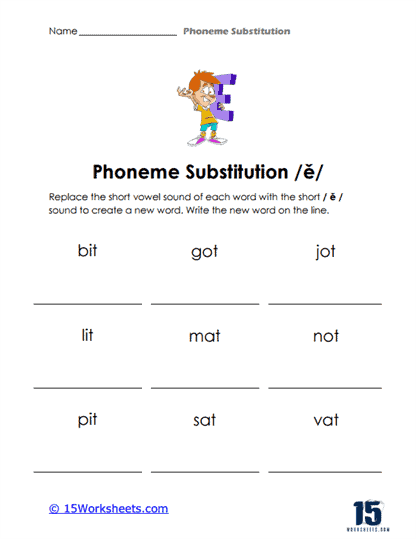
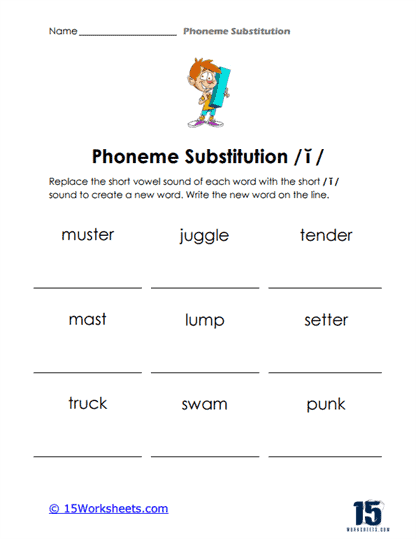
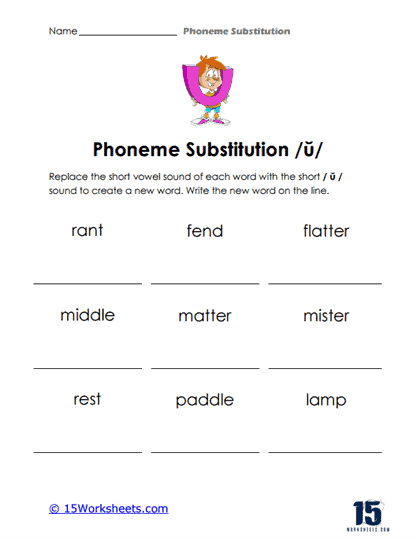
Phoneme substitution is a vital phonemic awareness skill that significantly contributes to a student’s literacy and language development. This skill involves the ability to replace one phoneme (the smallest unit of sound in language) in a word with another phoneme to create a new word.
To support students in mastering this essential skill, we present a collection of Phoneme Substitution worksheets. These worksheets have been thoughtfully designed to provide students with structured and engaging opportunities to practice and refine their phoneme substitution skills.
What are Phoneme Substitution Worksheets?
Phoneme Substitution Worksheets are educational resources designed to help students practice and learn phoneme substitution, which is the ability to replace one sound or phoneme in a word with a different sound or phoneme to create a new word. These worksheets often include various activities, such as matching, sorting, or writing exercises, that focus on the sounds of the letters of the alphabet and how they combine to form words.
What Is Phoneme Substitution?
Phoneme substitution is the process of replacing one phoneme (speech sound) in a word with another phoneme to create a new word. It is an essential skill in phonemic awareness, which is the understanding that words are made up of distinct sounds that can be manipulated and combined to create meaning. Phoneme substitution involves changing the initial (beginning), medial (middle), or final (ending) sound in a word and recognizing how the new sound alters the word’s meaning.
How To Teach Phoneme Substitution To Students
To teach phoneme substitution effectively, educators should:
- Introduce individual phonemes and their corresponding letters or letter combinations, focusing on the most common sounds in English.
- Model phoneme substitution by demonstrating how to replace the initial, medial, or final sound in a spoken word to create a new word.
- Provide ample opportunities for students to practice phoneme substitution with various words, starting with simple CVC (consonant-vowel-consonant) words and gradually progressing to more complex words.
- Use multisensory techniques to engage learners, such as using letter tiles, magnetic letters, or asking students to physically represent the new sound as they replace it.
- Create engaging activities and games that focus on phoneme substitution, such as word ladders, where students change one word into another by altering one sound at a time.
By teaching phoneme substitution and providing consistent practice, educators can help students develop strong phonemic awareness skills that will serve as a foundation for successful reading and writing development.
The Importance of Phoneme Substitution
Understanding and practicing phoneme substitution is of paramount importance for several reasons:
- Reading Proficiency: Phoneme substitution is a foundational skill for reading. It helps students manipulate sounds in words, enhancing their ability to decode words and read fluently.
- Spelling Competence: Proficiency in phoneme substitution enhances spelling skills. When students can substitute phonemes, they gain a deeper understanding of the sound-symbol correspondence in words.
- Phonemic Awareness: Phoneme substitution fosters phonemic awareness, which is the ability to recognize and manipulate individual phonemes. This skill is essential for literacy development, reading comprehension, and spelling.
- Language Skills: Understanding phoneme substitution contributes to improved overall language skills, including speaking and listening, as students become more aware of sound changes in words.
This collection of Phoneme Substitution worksheets is a valuable resource for educators and parents committed to supporting their students’ phonemic awareness and literacy development. Proficiency in phoneme substitution is not just an academic exercise; it’s a fundamental skill that opens the doors to reading fluency, comprehension, effective communication, and spelling accuracy.
By using these engaging worksheets, students will strengthen their ability to substitute phonemes with confidence, ultimately improving their overall language proficiency and literacy skills. This collection is an investment in their future success, ensuring they have a solid foundation in phoneme substitution and language skills.