Anger Management Worksheets
About These 15 Worksheets
This worksheet collection is an essential resource designed to help students, teachers, and homeschoolers understand and manage emotions effectively. These worksheets offer a variety of engaging activities that guide users through the process of identifying triggers, recognizing their feelings, and implementing practical strategies to control anger. The collection is user-friendly, available in PDF format, and is perfect for viewing, downloading, and printing, making it accessible to everyone involved in the educational process.
This collection includes worksheets that focus on the basics of anger management. For instance, some activities prompt students to determine whether certain behaviors, such as yelling or remaining calm, are helpful or harmful when angry. These exercises are vital for helping young learners distinguish between positive and negative responses to frustration, reinforcing healthy habits that they can practice daily. Other worksheets encourage students to engage in positive self-talk by identifying and coloring statements that promote calmness and rational thinking. These activities emphasize the importance of internal dialogue in controlling emotions and offer practical tools for redirecting negative thoughts.
In addition to these exercises, the collection also includes worksheets that challenge students to assess the outcomes of their anger. Through true-or-false questions, students critically evaluate common misconceptions about anger, such as whether acting out makes them feel better or whether revenge solves problems. These thought-provoking activities aim to debunk myths and provide a clearer understanding of the consequences of unchecked anger. Similarly, another worksheet prompts students to reflect on socially acceptable ways of expressing anger, encouraging them to choose and visualize healthier ways of dealing with frustration in different scenarios.
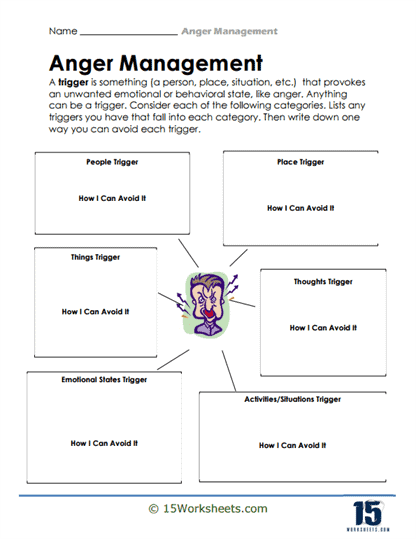
To complement these activities, the collection offers worksheets that guide students in identifying their personal anger triggers. By drawing or writing about situations that provoke their anger, students become more aware of their emotional responses and can start to take control. This self-awareness is further enhanced by activities that ask students to rate their anger triggers on a scale, helping them recognize the intensity of their feelings and prioritize areas that need the most attention.
This series provides reflection-based worksheets where students analyze the strategies they’ve used to manage their anger in the past. These activities encourage users to evaluate the effectiveness of these strategies both in the short and long term, prompting them to consider whether these methods have improved their lives and how they might adjust their approach in the future. This kind of reflective practice is essential for long-term emotional growth and helps students develop a deeper understanding of how to manage their emotions constructively.
In addition to these core activities, the collection could also include worksheets that focus on building new behavior patterns. These might prompt students to identify small steps they can take to change their reactions to anger and consider how these changes can be reinforced over time. Activities like these are crucial for helping students internalize healthier behavior and see tangible improvements in how they handle anger.
This set also includes creative exercises, such as drawing or writing about what they feel when they’re angry and how they can transform those emotions into something positive. These creative outlets are vital for helping students process their emotions in a non-threatening way and can be particularly beneficial for those who struggle with verbal expression.
What is Anger Management?
Anger management is a therapeutic approach that helps individuals recognize the signs of anger and develop strategies to deal with it in a healthy and constructive manner. For young people, learning to manage anger is particularly important as it is a crucial part of their emotional development. During childhood and adolescence, emotions can often feel overwhelming and difficult to control, leading to outbursts, frustration, or even aggression. Anger management teaches young people how to recognize the early signs of anger, understand what triggers it, and take steps to calm themselves before their emotions escalate.
One of the key components of anger management is self-awareness. Young people learn to identify the physical and emotional cues that signal rising anger, such as a racing heartbeat, clenched fists, or feelings of irritation. By becoming more aware of these signs, they can intervene earlier in the anger process, which helps prevent outbursts or aggressive behavior. This self-awareness is the foundation for all other anger management strategies, as it enables young people to catch their anger before it spirals out of control.
Another essential aspect of anger management is teaching young people how to express their emotions in a healthy way. Often, anger stems from underlying emotions such as frustration, hurt, or fear. Through anger management, young people learn to articulate these feelings rather than letting them fester and turn into anger. For example, instead of lashing out when they feel frustrated, they might learn to say, “I feel frustrated because I don’t understand this assignment.” This kind of communication not only helps to defuse anger but also encourages problem-solving and builds stronger relationships with others.
Anger management also emphasizes the importance of coping strategies. These strategies can range from deep breathing exercises to taking a break and engaging in a calming activity, such as listening to music or going for a walk. By practicing these techniques, young people can learn to calm themselves in the moment, preventing their anger from escalating. Over time, these coping strategies become habits, enabling young people to handle anger more effectively whenever it arises.
In addition to these immediate strategies, anger management also involves long-term changes in behavior and thinking. For instance, young people might learn to challenge negative thought patterns that contribute to their anger, such as assuming that others are intentionally trying to hurt them. By adopting a more balanced and realistic perspective, they can reduce the frequency and intensity of their anger. Moreover, anger management often includes goal-setting, where young people work towards specific objectives, such as improving their communication skills or reducing the number of angry outbursts they have each week.
The benefits of anger management for young people extend beyond just controlling their temper. Learning to manage anger effectively helps them build emotional resilience, improves their relationships with peers and family members, and enhances their overall mental health. It also equips them with important life skills, such as problem-solving, emotional regulation, and assertive communication, which will serve them well into adulthood. When young people can handle their anger constructively, they are more likely to succeed academically, socially, and later in their professional lives.