Continents Worksheets
All About These 15 Worksheets
These worksheets help facilitate the learning and understanding of geography, cultures, and societies across the globe. These worksheets offer a diverse range of exercises and activities tailored to engage students in immersive and interactive learning experiences. By incorporating various types of exercises, continent worksheets effectively contribute to the comprehensive exploration of different continents, fostering geographical knowledge, cultural appreciation, and critical thinking skills among students.
Through a diverse range of exercises and activities, these worksheets engage students in immersive learning experiences that promote geographical literacy, cultural awareness, critical thinking skills, spatial reasoning, research abilities, global perspective, and multidisciplinary learning. By practicing with continent worksheets, students not only expand their knowledge of the world but also develop the skills and attitudes necessary to navigate an increasingly interconnected and complex global landscape.
Types of Exercises
Map Identification – Map identification exercises are fundamental components of continent worksheets. Students are presented with maps of different continents, and they are tasked with identifying countries, cities, landmarks, and geographical features. These exercises enhance students’ spatial awareness and help them develop map-reading skills essential for understanding global geography.
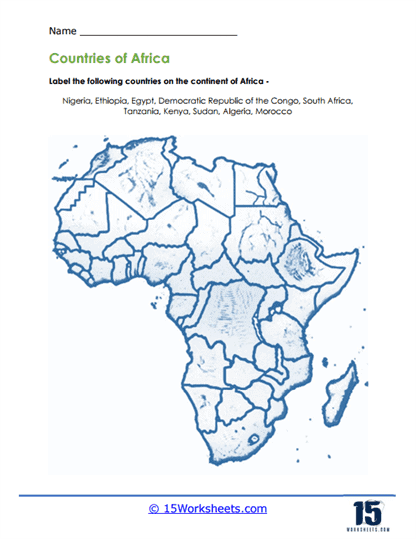
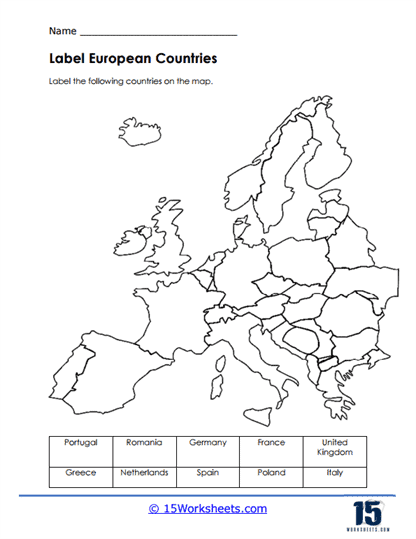
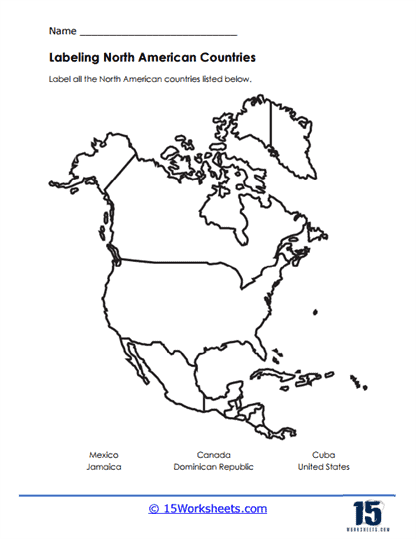
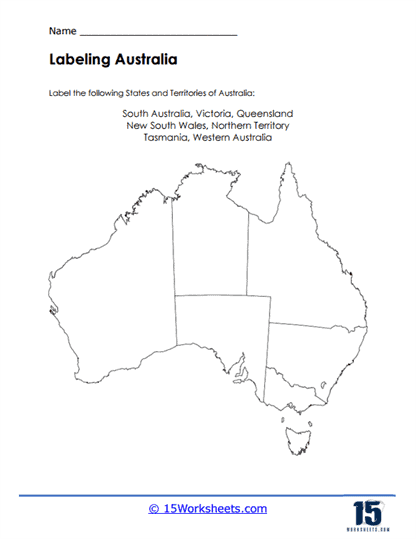
Labeling Exercises – Labeling exercises require students to label specific elements on maps, such as countries, capitals, rivers, mountain ranges, and deserts. By actively engaging with maps in this manner, students reinforce their knowledge of geographical features and their locations, facilitating a deeper understanding of each continent’s physical geography.
Matching Activities – Matching activities involve pairing geographical terms or features with their corresponding descriptions or locations. For example, students may match country names with their capitals or match mountain ranges with their respective continents. These activities promote associative learning and reinforce students’ comprehension of geographical concepts.
Research Tasks – Research tasks encourage students to conduct independent research on various aspects of different continents, such as their climates, ecosystems, cultures, languages, and historical landmarks. Students may be required to create presentations, write reports, or compile fact sheets based on their findings. These tasks foster critical thinking, information literacy, and a deeper appreciation for the diversity of cultures and environments around the world.
Crossword Puzzles and Word Searches – Crossword puzzles and word searches incorporate geographical terms, landmarks, and cultural elements related to specific continents. These activities help students expand their vocabulary, reinforce spelling, and familiarize themselves with key geographical and cultural concepts in an engaging and enjoyable manner.
Coloring and Mapping Exercises – Coloring and mapping exercises provide students with blank maps of continents that they can color and annotate according to specific criteria, such as political boundaries, physical features, climate zones, or cultural regions. These activities encourage creativity, spatial visualization, and hands-on learning while reinforcing geographical knowledge.
Comparative Analysis – Comparative analysis exercises prompt students to compare and contrast different aspects of various continents, such as their population demographics, economic activities, natural resources, and cultural practices. By examining similarities and differences between continents, students gain insights into global patterns and develop a broader perspective on the interconnectedness of world regions.
Critical Thinking Prompts – Critical thinking prompts challenge students to reflect on complex geographical issues, such as environmental sustainability, geopolitical conflicts, urbanization, and globalization. Students may analyze case studies, evaluate alternative solutions, and formulate reasoned arguments supported by evidence. These prompts stimulate higher-order thinking skills and encourage students to consider the social, economic, and environmental implications of geographic phenomena.
Benefits of These Worksheets
Geographical Literacy – Continent worksheets promote geographical literacy by providing students with structured opportunities to explore the diverse landscapes, cultures, and societies of different continents. Through map-based activities, research tasks, and comparative analysis, students develop a solid foundation of geographical knowledge that enables them to understand the complexities of the world around them.
Cultural Awareness – By engaging with continent worksheets, students gain a deeper appreciation for the rich cultural diversity present on each continent. Through research tasks, students learn about the customs, traditions, languages, and historical heritage of different regions, fostering cross-cultural understanding and empathy.
Critical Thinking Skills – Continent worksheets encourage the development of critical thinking skills by prompting students to analyze, interpret, and evaluate geographical information from multiple perspectives. By engaging with complex issues and solving challenging exercises, students hone their analytical abilities and learn to make informed judgments about geographical phenomena.
Spatial Reasoning – Map-based exercises on continent worksheets enhance students’ spatial reasoning skills, including map-reading, interpretation of scale and distance, and mental mapping. By actively engaging with maps and geographical data, students develop a spatial awareness that enables them to navigate and comprehend spatial relationships in both physical and virtual environments.
Research and Inquiry Skills – Research tasks featured on continent worksheets cultivate students’ research and inquiry skills, empowering them to gather, evaluate, and synthesize information from diverse sources. By conducting independent research on geographical topics, students learn to formulate research questions, locate relevant resources, and present their findings effectively, fostering lifelong learning habits.
Global Perspective – Continent worksheets provide students with opportunities to develop a global perspective by exploring the interconnectedness of world regions and understanding the geopolitical, economic, and environmental forces shaping our planet. Through comparative analysis exercises and critical thinking prompts, students gain insights into global issues and develop a broader awareness of their roles as global citizens.
Multidisciplinary Learning – Continent worksheets facilitate multidisciplinary learning by integrating geographical concepts with other disciplines, such as history, economics, sociology, and environmental science. By examining the intersection of geography with other fields of study, students develop a holistic understanding of the complex relationships between human societies and their environments.
What is a Continent?
A continent is a large, continuous landmass that is typically distinguished by geographic, cultural, and geological features. The Earth’s surface is divided into seven continents, each with its own unique characteristics, landscapes, and cultural diversity. Here, I’ll name each continent and provide a brief overview of its key features:
Africa
Africa is the second-largest continent, covering approximately 20% of the Earth’s land area. It is characterized by diverse ecosystems, including savannas, deserts, rainforests, and mountains. Africa is home to a rich cultural heritage, with thousands of languages spoken and a wide variety of ethnic groups. Major landmarks include the Sahara Desert, the Nile River, Mount Kilimanjaro, and the Serengeti National Park.
Antarctica
Antarctica is the southernmost continent and the fifth-largest, covering about 9% of the Earth’s land area. It is the coldest, windiest, and driest continent, largely covered by ice sheets and glaciers. Despite its harsh climate, Antarctica supports diverse wildlife, including penguins, seals, and seabirds. Antarctica is primarily used for scientific research, with numerous research stations operated by various countries.
Asia
Asia is the largest and most populous continent, spanning from the Arctic Ocean in the north to the Indian Ocean in the south. It is known for its vast landscapes, including the Himalayas, the Gobi Desert, the Siberian tundra, and the tropical rainforests of Southeast Asia. Asia is home to a multitude of cultures, languages, and religions, with significant historical and economic importance. Major landmarks include Mount Everest, the Great Wall of China, the Taj Mahal, and the cities of Tokyo, Beijing, and Mumbai.
Europe
Europe is the second-smallest continent in terms of land area but one of the most densely populated. It is known for its rich history, diverse cultures, and architectural landmarks. Europe is characterized by its varied landscapes, including mountains (e.g., the Alps), plains, rivers, and coastlines. Major landmarks include the Eiffel Tower, the Colosseum, the Acropolis, and cultural centers such as Paris, Rome, London, and Berlin.
North America
North America is the third-largest continent, bordered by the Arctic Ocean to the north, the Atlantic Ocean to the east, and the Pacific Ocean to the west. It is characterized by diverse landscapes, including mountains (e.g., the Rocky Mountains), forests, deserts, and coastlines. North America is home to a range of cultures, languages, and indigenous peoples, as well as significant urban centers. Major landmarks include the Grand Canyon, Niagara Falls, Yellowstone National Park, and cities such as New York, Los Angeles, and Toronto.
South America
South America is the fourth-largest continent, bordered by the Atlantic Ocean to the east and the Pacific Ocean to the west. It is known for its diverse ecosystems, including the Amazon rainforest, the Andes Mountains, the Atacama Desert, and the Galápagos Islands. South America is culturally rich, with a blend of indigenous, European, and African influences. Major landmarks include Machu Picchu, Christ the Redeemer, Angel Falls, and cities such as Rio de Janeiro, Buenos Aires, and Lima.
Australia (Oceania)
Australia, often considered both a continent and a country, is the smallest and driest inhabited continent. It is characterized by its unique wildlife, including marsupials such as kangaroos and koalas, and diverse ecosystems such as the Great Barrier Reef. Australia is culturally diverse, with influences from Indigenous Australian, British, Asian, and other immigrant populations. Major landmarks include Uluru (Ayers Rock), the Great Barrier Reef, the Sydney Opera House, and cities such as Sydney, Melbourne, and Brisbane.