Bill of Rights Worksheets
About These 15 Worksheets
Think the Bill of Rights is just a bunch of old-timey rules written by guys in powdered wigs? Think again! Our Bill of Rights worksheets take this cornerstone of American freedom and give it a much-needed classroom makeover. We’ve broken down the big, bold ideas of the first ten amendments into bite-sized, brain-friendly activities that students can actually understand (and maybe even enjoy). Whether they’re matching amendments to real-life situations or decoding who gets to say what without being tackled by the government, kids won’t just memorize the Bill of Rights-they’ll get it.
Now, let’s be real: the language of the Constitution wasn’t exactly written with 8th graders in mind. Terms like “due process,” “quartering soldiers,” and “unreasonable searches” can make students’ eyes glaze over faster than a history lecture after lunch. But our worksheets cut through the legal mumbo jumbo and serve up the good stuff-like what it actually means to have freedom of speech or why your backpack can’t be searched just because it looks “suspiciously full of snacks.” Every amendment is unpacked in a way that’s relevant, relatable, and occasionally hilarious (because who doesn’t want to argue a fake court case about a kid who got arrested for tweeting a meme?).
But we don’t stop at reading and matching. These worksheets pull students right into the action with role-playing scenarios, debate prompts, and “what if?” questions that bring the Bill of Rights into the 21st century. What if the Founding Fathers had to deal with TikTok bans? What does “cruel and unusual punishment” look like in a school cafeteria? Students are challenged to think critically, debate respectfully, and connect these 200-year-old ideas to their own digital-age lives. So if you’re looking to make the Constitution less snooze-worthy and more “aha!”-you’ve come to the right place.
Types of Exercises
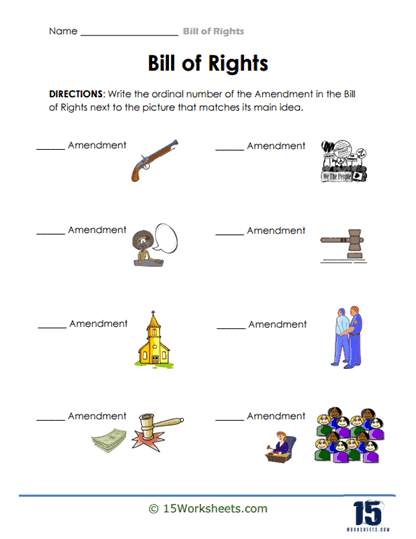
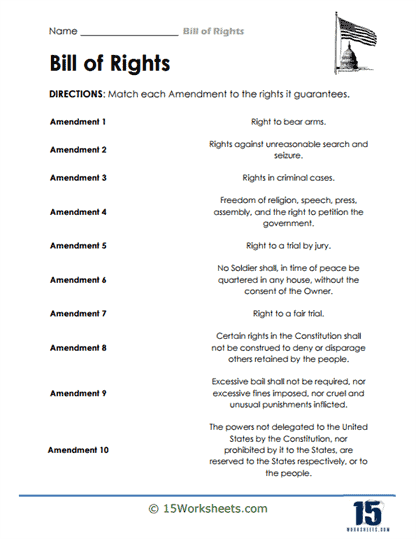
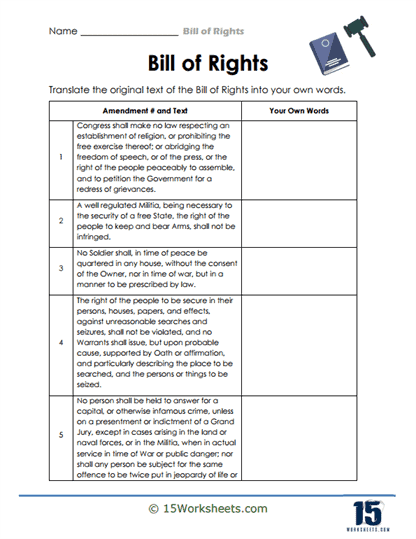
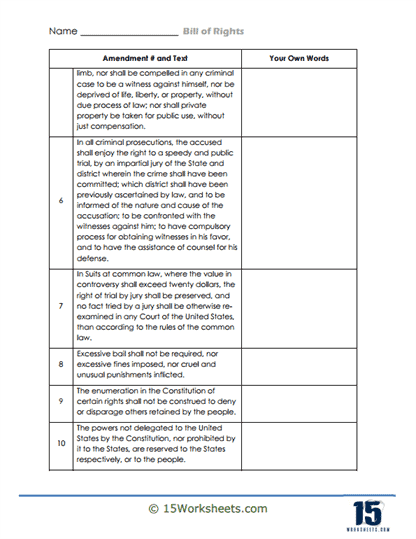
These worksheets are packed with activities that make constitutional amendments more digestible than a slice of apple pie at a Fourth of July picnic. Students will engage in matching exercises, pairing each amendment with its corresponding rights—like matching the First Amendment with freedom of speech, religion, and the press. It’s like a game of constitutional memory, but with higher stakes and fewer snacks.
These worksheets also include multiple-choice questions that challenge students to identify which amendment protects against unreasonable searches and seizures (hint: it’s the Fourth). True or false statements keep students on their toes, such as “The Eighth Amendment allows for cruel and unusual punishment” (spoiler alert: false). And for those who love a good fill-in-the-blank, there are exercises that require students to recall specific terms and concepts related to the Bill of Rights. It’s like Mad Libs, but with more legal jargon and fewer talking animals.
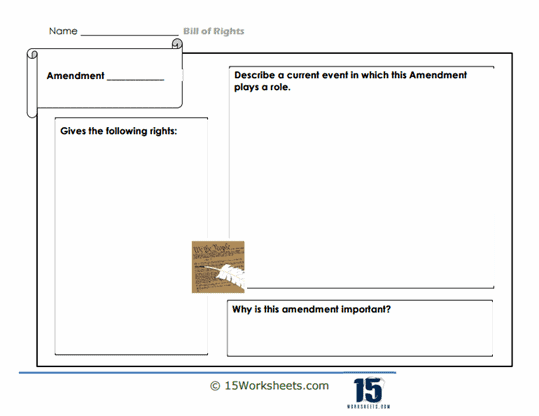
The real showstopper, however, is the scenario analysis. Students are presented with hypothetical situations-like a journalist being arrested for criticizing the government-and must identify which amendment is being violated. It’s a chance for them to apply their knowledge in real-world contexts, turning abstract concepts into tangible understanding. Plus, it gives them the opportunity to channel their inner legal eagle and argue cases with the passion of a Supreme Court justice.
What is the Bill of Rights?
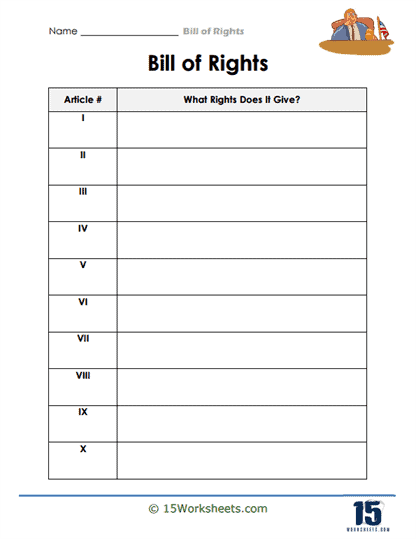
The Bill of Rights is the first ten amendments to the United States Constitution, designed to protect the individual freedoms of American citizens. Created in 1789 and ratified in 1791, the Bill of Rights was born from the need to ensure that the government wouldn’t overstep its bounds and infringe upon personal liberties. Many of the Founding Fathers, especially those known as Anti-Federalists, worried that the newly formed government could become too powerful, so they pushed for clear safeguards to prevent tyranny. This set of amendments guarantees fundamental rights, like freedom of speech, religion, and the press, which still serve as the backbone of American democracy today.
Each amendment in the Bill of Rights addresses a specific area of protection for the people. For instance, the First Amendment guards freedoms related to expression, ensuring people can speak their minds, worship as they choose, and gather peacefully. Other amendments deal with issues like the right to bear arms (Second Amendment), protection against unreasonable searches and seizures (Fourth Amendment), and the right to a fair trial (Sixth Amendment). Together, these ten amendments work to ensure that individuals have a buffer against government intrusion, allowing them to live freely under the rule of law.
The Bill of Rights remains as vital today as it was when it was created, continuing to shape how laws are interpreted and applied. Over time, the protections it outlines have been expanded to include all citizens, strengthening the country’s foundation of equality and justice. From the courtroom to the streets, the principles enshrined in the Bill of Rights guide Americans’ understanding of their freedoms and responsibilities, serving as a living document that adapts with the nation while preserving its core values.