Fact or Opinion Worksheets
All About These 15 Worksheets
These are tools that help you understand the difference between facts and opinions, which is super important in your daily life and as you continue with your education. Your job is to read each statement and identify whether it is a fact (something that can be proven true or false) or an opinion (someone’s belief or feeling that can’t be proven right or wrong). For example, a worksheet might have a statement like, “Ice cream is cold.” You would identify this as a fact because we can prove that ice cream is, indeed, cold.
These worksheets can be a lot of fun and are great for developing critical thinking skills. That means they help you think more deeply and carefully about things. Understanding the difference between fact and opinion is super important, especially in today’s world where we get a lot of information from different sources like the internet, books, and even chats with friends.
A Look At These Individual Worksheets
1. Everyday Life and Silly Scenarios
The journey begins in the whimsical world of Doggy Discernment, Deciphering Donuts, and Gorilla Verdicts, where students tackle the difference between facts like “Dogs bark” and opinions like “Poodles are the most elegant breed.” In Deciphering Donuts, things get deliciously murky-is “Glazed is best” a universal truth or just a sticky opinion? And in Gorilla Verdicts, learners swing between zoological facts and the wild assumption that gorillas would make great courtroom judges. These worksheets ground critical thinking in silly, relatable contexts that keep students laughing while they learn.
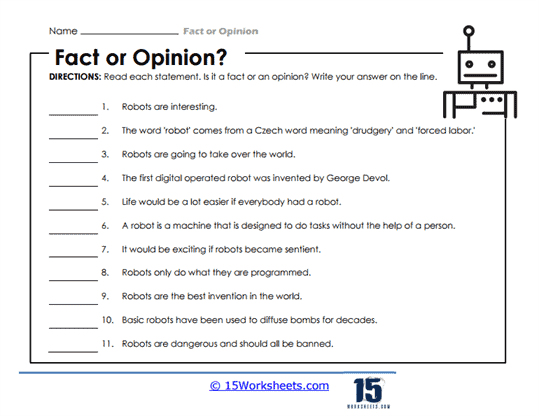
2. Tech, AI & Robot Realities
In the brave new world of AI Realities, Navigating Robo‑Claims, and Proven or Personal?, students learn that not everything high-tech is high-truth. They weigh statements like “AI writes essays” (fact) against “AI essays are better than human ones” (a very arguable opinion). Navigating Robo-Claims explores sensational tech headlines and robot drama, while Proven or Personal? challenges students to reflect on whether their beliefs are backed by evidence or emotion. These worksheets are great for fostering skepticism, discernment, and maybe even a healthy distrust of toasters that talk back.
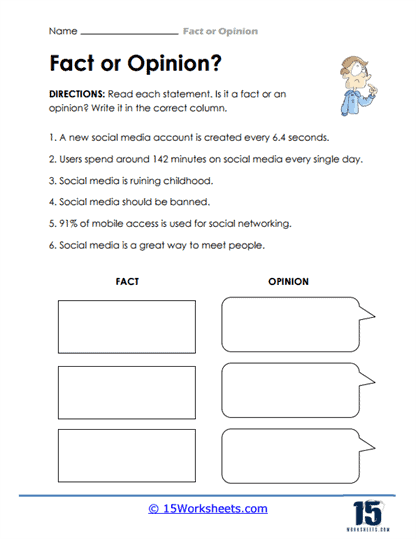
3. Fact-Check & Media Mysteries
With The Social Media Maze, Fact‑Checking Challenge, Lights, Camera, Judgment, and Factuality and Subjectivity, students are thrown into the information battleground of modern life. Is that viral post true? Is that movie review fair? In The Social Media Maze, they navigate real vs fake online claims. Lights, Camera, Judgment brings the drama of opinion-packed entertainment reviews, and Fact‑Checking Challenge gives students the Sherlock Holmes treatment-can they verify a claim, or is it just influencer fluff? This group of worksheets builds strong media literacy and the ability to spot spin in a scroll-heavy world.
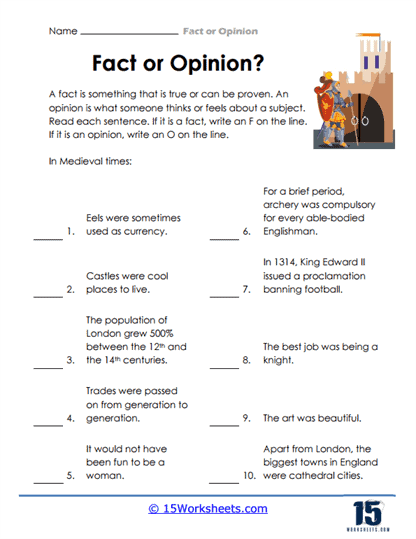
4. Historical & Curious Contexts
Step into the past (and some pretty random trivia) with Evaluating Medieval Statements, Exploring Diverse Topics, Wheeling It, and Verifiable or Not. In Evaluating Medieval Statements, knights and dragons ride into the conversation-can students sort historical truth from medieval myth? Wheeling It rolls through transportation facts, while Exploring Diverse Topics offers a mixed bag of fun and factual brain teasers. Verifiable or Not is the big philosophical one: can this claim actually be checked? These worksheets promote nuanced thinking and a touch of skepticism-even if you’re talking about jousting or unicycles.
5. The Grand Synthesis
Facts and Opinions Galore ties everything together in a glorious mashup. This is the capstone experience-a chance for students to show off everything they’ve learned by evaluating a wide range of mixed statements. It’s part logic test, part opinion rodeo, and part reflection session. By this point, students aren’t just identifying facts and opinions-they’re explaining why they think something qualifies as one or the other. It’s the grand finale of critical thinking, dressed up as a fun activity.
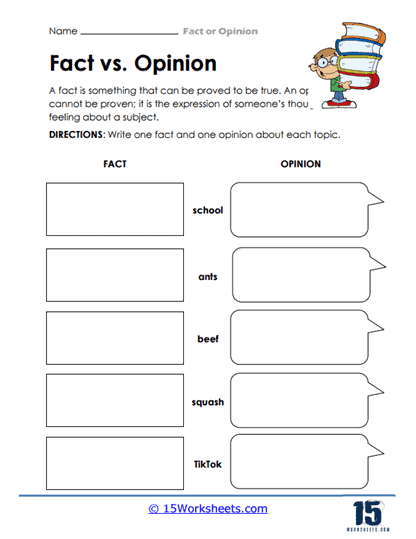
What is the Difference Between Fact And Opinion?
Facts and opinions are two different types of information that people encounter in various forms of communication. It is important to understand and explain the difference between the two, as it helps in evaluating the credibility, accuracy, and usefulness of the information presented. Here’s an explanation of the differences between facts and opinions:
Facts
Objective: Facts are objective statements or pieces of information that can be verified through evidence, observation, or research. They are based on reality and independent of personal feelings or beliefs.
Verifiable: Facts can be proven or disproven, which means they can be tested, observed, or confirmed using reliable sources or methods.
Consistency: Facts remain consistent and true across different situations, contexts, and perspectives. They don’t change based on personal beliefs, emotions, or biases.
Examples: “Water boils at 100 degrees Celsius at sea level,” “The Earth revolves around the Sun,” or “Barack Obama was the 44th president of the United States.”
The Opinions
Subjective: Opinions are subjective statements that reflect personal beliefs, feelings, thoughts, or preferences. They are based on individual perspectives and can vary from person to person.
Not verifiable: Opinions cannot be proven or disproven in the same way facts can be. While they may be based on factual information, they are ultimately a matter of personal judgment or interpretation.
Variability: Opinions can change over time and differ among individuals, as they are influenced by personal experiences, emotions, values, and cultural backgrounds.
Examples: “Chocolate ice cream is the best flavor,” “The latest superhero movie is boring,” or “Public transportation should be free for everyone.”
To explain the difference between facts and opinions, emphasize that facts are objective, verifiable, and consistent pieces of information, while opinions are subjective, not directly verifiable, and can vary among individuals based on their personal beliefs, feelings, and experiences. Understanding these differences is crucial for evaluating and interpreting information, especially when making decisions, forming arguments, or engaging in critical thinking.