Elements of Drama Worksheets
All About These 15 Worksheets
The world of drama is a vibrant tapestry woven with emotions, conflicts, and human experiences. Behind the curtains lies a realm of creativity and expression that transcends time and culture.
This collection of 15 worksheets dedicated to the Elements of Drama serves as a gateway to this captivating world. These meticulously crafted worksheets invite students to explore the foundational components that bring stories to life on stage, enriching their understanding of literature, human behavior, and the art of storytelling.
The Elements of Drama form the backbone of theatrical productions, encompassing everything from character development to plot progression, setting, and more.
Understanding these elements is not solely the domain of aspiring actors or directors; it is a skill that enhances students’ appreciation of literature, sharpens their critical thinking, and equips them with tools to deconstruct narratives across various mediums.
This collection of worksheets is designed to illuminate the pivotal role of these elements and their far-reaching applications in literature, arts, and even personal communication.
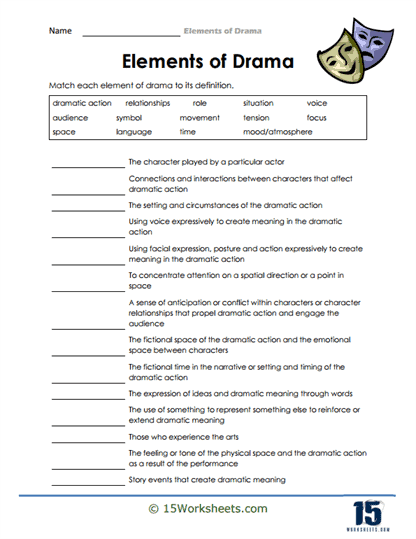
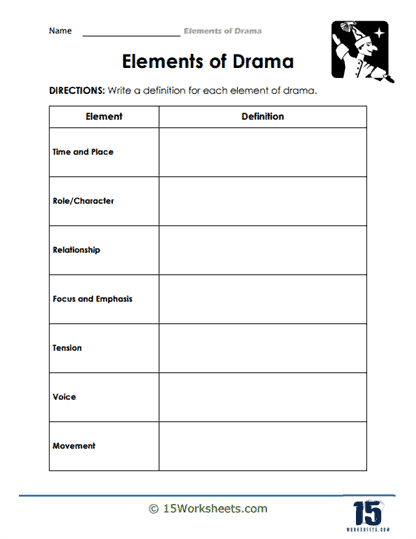
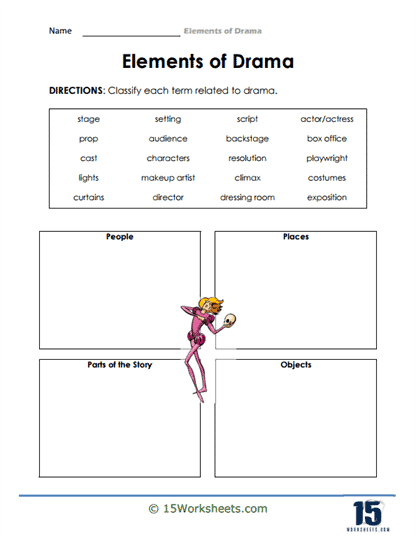
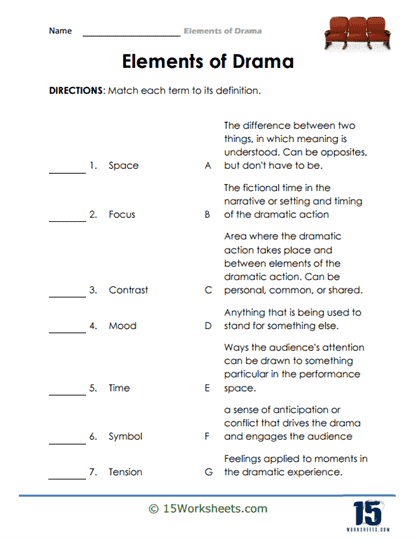
What are the Elements of Written Drama?
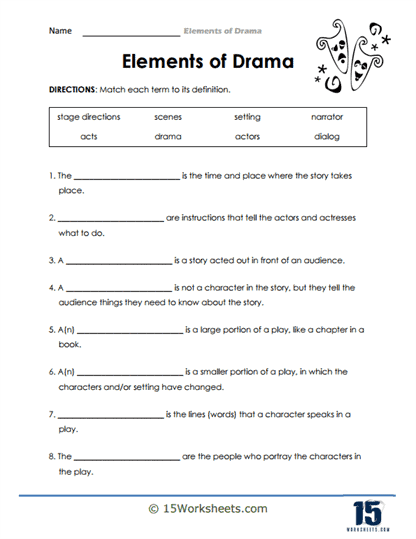
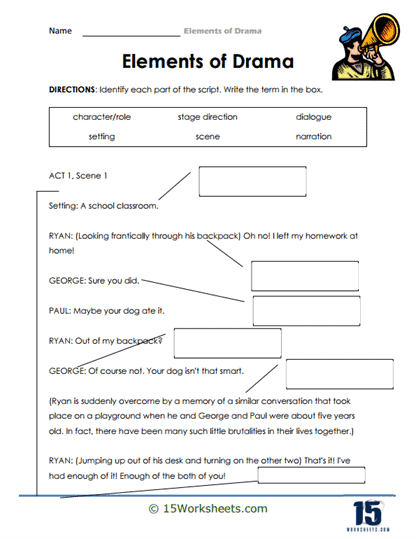
Written drama, also known as a play or theatrical script, contains specific elements that work together to create a compelling and engaging performance. These elements include:
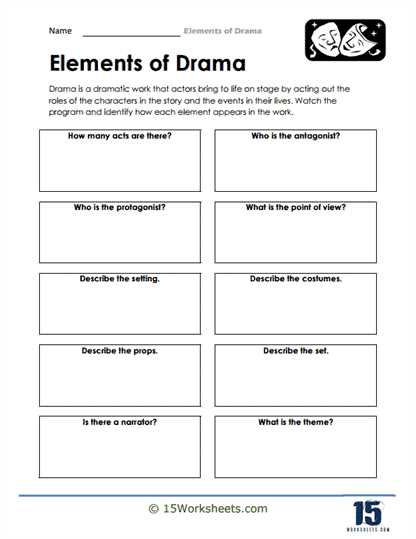
Plot: The plot is the sequence of events that make up the story in the drama. It provides the framework for the action and conflict that drives the play, often following a structure with an exposition, rising action, climax, falling action, and resolution.
Characters: Characters are the individuals who appear in the drama, each with their own personality, motivations, and relationships. Character development is essential in a drama, as it allows the audience to connect with the characters and become invested in their stories.
Dialogue: Dialogue is the spoken lines exchanged between characters in the play. It is crucial for revealing character traits, relationships, and motivations, as well as advancing the plot and creating tension or conflict.
Stage directions: Stage directions are written instructions in the script that guide the actors, director, and technical crew on how to perform the play. They include information about character movement, gestures, facial expressions, and other non-verbal elements that convey meaning and emotion.
Setting: The setting refers to the time and place where the drama occurs. It helps establish the context and atmosphere of the play, providing a backdrop for the characters and their actions.
Theme: The theme is the underlying message or central idea explored in the drama. It can encompass moral, social, or philosophical issues, and often reflects the playwright’s perspective on the human condition.
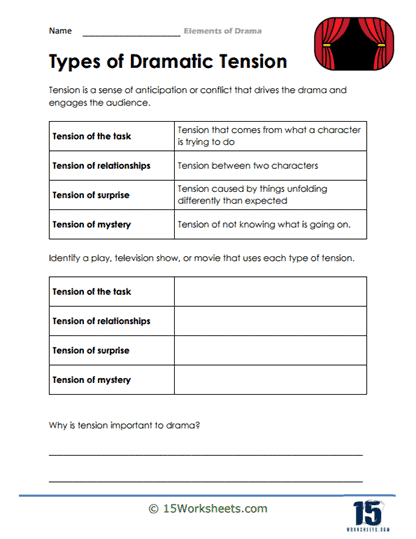
Conflict: Conflict is a crucial element in drama, as it creates tension, drives the plot, and shapes character development. It can be internal (within a character’s mind) or external (between characters or forces), and often involves opposing desires, goals, or values.
Structure: The structure of a play is its organization into acts and scenes, which can vary depending on the playwright’s intent and the needs of the story. Traditional plays often follow a three- or five-act structure, while modern plays may have more fluid, experimental structures.
Tone and mood: Tone refers to the playwright’s attitude toward the subject matter or characters, while mood is the emotional atmosphere created for the audience. Both elements contribute to the overall impact and emotional resonance of the drama.
By incorporating and balancing these elements, playwrights can create engaging and thought-provoking dramas that resonate with audiences and provide a compelling theatrical experience.