Figurative Language Worksheets
About These 15 Worksheets
Figurative Language Worksheets serve as a pivotal educational tool designed to enhance students’ understanding and use of figurative language. Figurative language, a cornerstone of expressive writing and critical reading, encompasses the use of words or phrases that deviate from their literal interpretation to convey more complex, imaginative, or nuanced meanings. Through these worksheets, students engage with various exercises that challenge them to identify, interpret, and employ figurative language, thereby bolstering their grammar, vocabulary, and reading comprehension skills.
Through identification, interpretation, creation, matching, fill-in-the-blank, and comparison exercises, these worksheets provide a robust framework for learning that significantly improves students’ grammar, vocabulary, writing creativity, reading comprehension, analytical skills, and appreciation of literature. The practice of figurative language not only equips students with the tools to excel academically but also empowers them to navigate the world with a richer, more nuanced understanding of language.
Types of Exercises
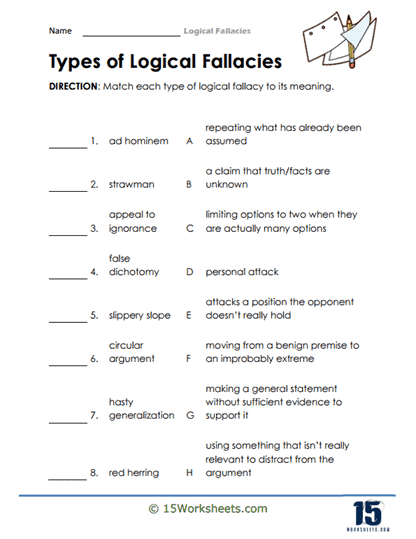
Identification – These exercises task students with pinpointing instances of figurative language within given texts. Students must discern between literal and figurative language, identifying specific types such as metaphors, similes, personification, hyperbole, idioms, and onomatopoeia. This foundational skill aids in the development of analytical reading abilities.
Interpretation – Here, students analyze the meaning behind figurative language expressions. They might explain what an idiom means within the context of a sentence or interpret the deeper significance of a metaphor in a poem. This fosters critical thinking and deepens comprehension of nuanced textual meanings.
Creation – Students get creative prompts encouraging them to craft their sentences or paragraphs using specific types of figurative language. This practice not only enhances their writing skills but also encourages them to think imaginatively and apply what they’ve learned in a practical context.
Matching – These involve connecting figurative language terms with their definitions or examples. It’s an effective way to reinforce the understanding of different figurative language types and their functions within texts.
Fill-in-the-Blank – By completing sentences with appropriate figurative language terms or phrases, students practice applying their knowledge in a controlled format, gradually building their confidence in using figurative expressions accurately.
Comparison – Tasks might include comparing and contrasting similes and metaphors, or analyzing how different types of figurative language achieve various effects in writing. This sharpens analytical skills and deepens understanding of stylistic choices in literature.
The Benefits of These Worksheets
Practicing with figurative language worksheets significantly advances students’ grammatical and reading competencies in several key ways:
Enhanced Vocabulary – Regular exposure to and practice with figurative language enrich students’ vocabularies. Learning to understand and use nuanced expressions broadens their linguistic repertoire, enabling more sophisticated communication.
Improved Writing Clarity and Creativity – By learning how to effectively employ figurative language, students can convey complex ideas more vividly and accurately. This not only improves their writing’s clarity but also injects creativity into their expressions, making their writing more engaging and compelling.
Boosted Reading Comprehension – Figurative language often encapsulates intricate ideas succinctly and evocatively. Familiarity with these expressions enables students to unpack complex meanings in literature, enhancing their interpretive skills and overall reading comprehension.
Refined Analytical Skills – The analysis of figurative language requires students to think critically about text, context, and subtext. This analytical practice extends beyond literature, equipping students with the skills to evaluate information and arguments in various subjects and real-life situations.
Greater Appreciation of Literature – Understanding figurative language opens up the layered meanings of literary texts, allowing students to appreciate the artistry and depth of writing. This fosters a lifelong engagement with literature and a deeper appreciation for the craft of writing.
Improved Grammar Understanding – Engaging with figurative language exercises reinforces grammatical structures and encourages precision in language use. Students become more adept at manipulating syntax to create impactful sentences, enhancing both their comprehension and production of complex grammatical constructions.
What Are All The Forms Of Figurative Language?
Have you heard phrases like the howling sky, dancing trees, or sleeping water while reading a novel and asked if the author was drunk while writing the book? Well, my friend, let me break it to you; this is a creative method of writing that conveys deeper meanings using non-literal sentences.
You will come across figurative language mostly in novels or creative writing pieces. Authors use it to add an edge or creativity to their writing. Let’s discuss what are all the forms of figurative language to help you grasp the concept behind them.
What Is Figurative Language?
Before discussing the forms of figurative language, let’s define this concept. Figurative language is a way of using words that focuses on expressing a complex or deeper meaning through non-literal sentences. Through figurative language, we can mention an idea in a regular sentence without clearly stating it.
For example, ‘I was drowning in a puddle of grief’ this sentence is a metaphor, indirectly stating how someone feels ample grief without clearly saying it.
There are multiple forms of figurative language; here are the eight most commonly used ones:
Simile
Similar refers to a comparison of two different things with the use of ‘as or like.’ For example, her hair was as black as coals, or the dress fit like a glove.
Alliteration
Alliteration is used to enhance the expressiveness of a text using words starting with similar sounds. Alliteration occurs when you notice two or more words beginning with the same consonant. For Example: Go grab the crab for me.
The words go, grab and crab start with similar sounds, which adds to the expressiveness and uniqueness of the sentence.
Hyperbole
Hyperbole refers to the exaggeration in a speech that helps the writer add more stress to an idea or concept. For example, ‘it was excruciatingly painful’ instead of it was painful.
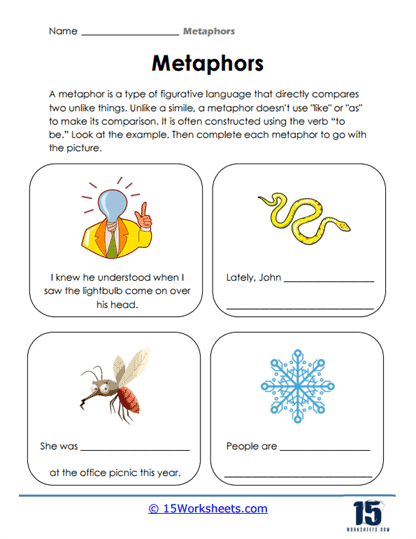
Metaphor
Opposite to a simile, a Metaphor refers to a figure of speech where we compare two different things without using ‘as or like’; for example, he had a heart of stone.
Onomatopoeia
Onomatopoeia refers to words that make similar sounds to the noise they make, for example, clap, chomp, boo, or drip.
Oxymoron
Oxymoron refers to contradicting statements or words, for example, bittersweet, deafening silence, or silent scream.
Personification
Personification refers to personifying or giving human attributes to a non-living object; for example, he looked up at the gloomy sky or the wind was roaring.
Idiom
A sentence or expression has an entirely different meaning than the words suggest. For example, a piece of cake or spill the beans.
If you have to write a story for your English class or you want to enhance your writing in general, by understanding these eight figures of speech, you can start using them in your writing. Using figurative language will help keep the readers engaged in your stories and add a form of uniqueness to your writing.