BODMAS Worksheets
All About These 15 Worksheets
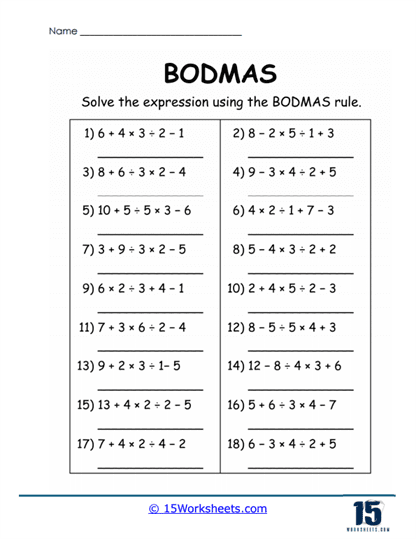
BODMAS is an acronym that stands for Brackets, Orders, Division and Multiplication, Addition and Subtraction. This set of rules dictates the sequence in which mathematical operations are performed to ensure consistent and correct results. BODMAS is a vital concept in mathematics, as it prevents ambiguity in calculations, especially when dealing with complex expressions.
BODMAS Operations worksheets are educational tools designed to help students practice and master the principles of this rule. These worksheets are typically organized to include problems of varying difficulty, from basic to advanced, to accommodate learners at different stages of their mathematical journey.
Components of BODMAS
To understand the essence of BODMAS worksheets, it’s important to break down the acronym and its components:
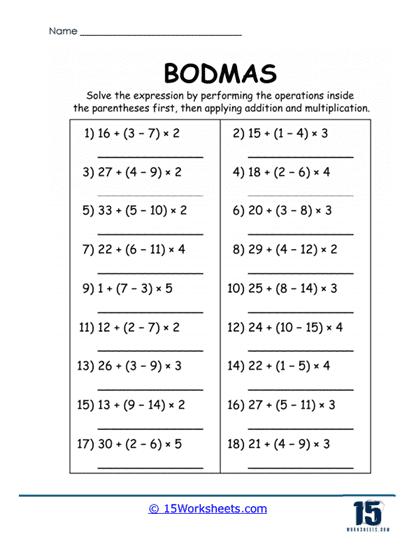
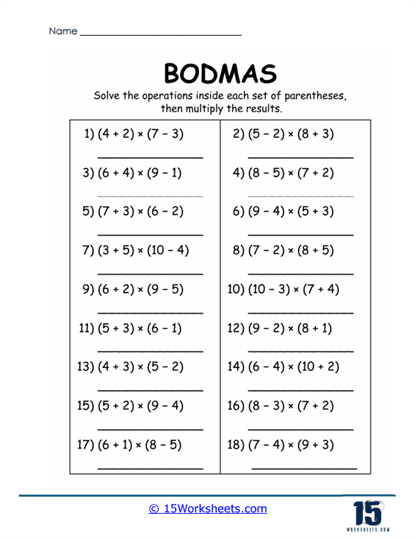
Brackets (B) – These include parentheses (), square brackets [], and curly braces {}. Operations within brackets are completed first, regardless of the operations outside.
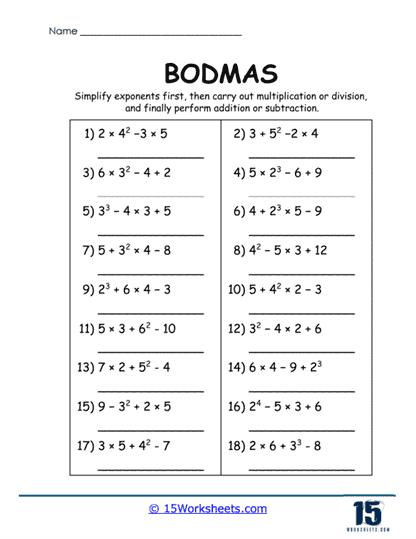
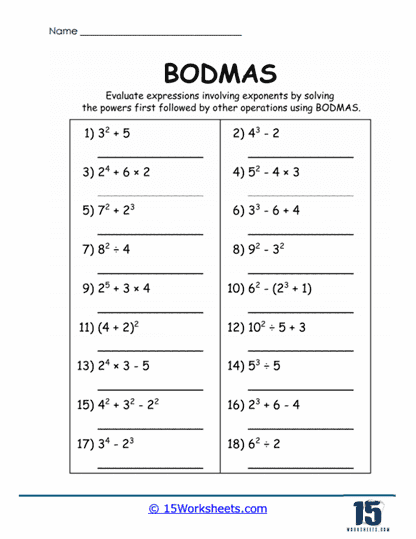
Orders (O) – This refers to exponents and roots, such as 23 or √16. These are solved after brackets but before other operations.
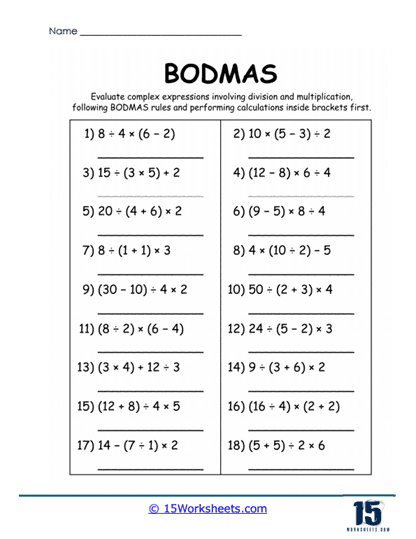
Division and Multiplication (DM) – These are solved from left to right. Division and multiplication hold equal priority.
Addition and Subtraction (AS) – Similarly, addition and subtraction are solved from left to right and are of equal precedence.
By following this order, learners can solve expressions systematically and avoid errors.
Skills Learned Through BODMAS Worksheets
By completing BODMAS Operations worksheets, students develop several critical mathematical skills. These skills are not only essential for academic success but also for solving real-world problems.
1. Understanding the Order of Operations
The primary skill acquired is a firm grasp of the sequence in which operations must be performed. Students learn that following BODMAS ensures consistency, regardless of who solves the problem. For instance:
Problem: 8 + 2 x 3
Without BODMAS: Adding first yields 10 x 3 = 30, which is incorrect.
With BODMAS: Multiplying first gives 8 + 6 = 14, the correct answer.
This foundational skill is crucial for advanced mathematics and fields requiring precise computations.
2. Accuracy in Calculations
BODMAS worksheets emphasize precision. Students must carefully analyze each part of an expression, minimizing careless mistakes. Repeated practice fosters a habit of double-checking work and maintaining focus, which is essential for solving both academic and practical problems.
3. Problem-Solving and Critical Thinking
Many BODMAS worksheets incorporate complex, multi-step problems that require logical thinking and strategic planning. Students must evaluate which operation to perform first and anticipate the consequences of each step. This enhances their ability to:
Break down problems into manageable parts.
Use critical thinking to decide the best approach.
Persevere through challenging problems.
4. Working with Exponents and Roots
A significant aspect of “Orders” in BODMAS is understanding powers and roots. Worksheets introduce students to operations like
23 or √25, enabling them to:
Grasp the concept of repeated multiplication.
Develop familiarity with square roots and higher-level powers.
Transition smoothly to advanced topics like logarithms and algebra.
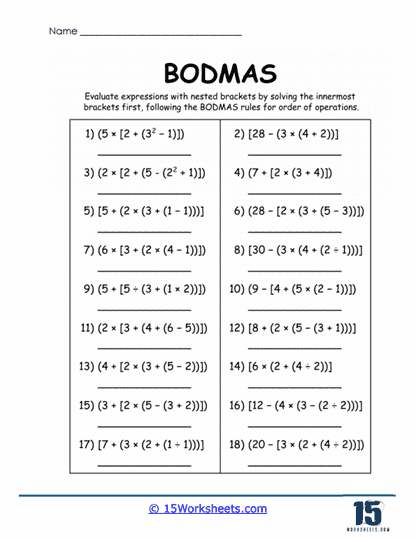
5. Mastery of Brackets and Nested Expressions
Brackets are essential for organizing operations, especially in complex problems. Worksheets train students to:
Solve expressions with different types of brackets, such as [(3 + 4) x 2] – 5.
Handle nested brackets, where operations must be completed from the innermost to the outermost level.
This skill is invaluable in algebra, calculus, and programming, where similar hierarchical rules apply.
6. Left-to-Right Processing
BODMAS teaches that some operations, like division and multiplication, or addition and subtraction, are processed left to right when they appear together. Worksheets reinforce this concept, sharpening students’ directional thinking and attention to detail.
PEMDAS vs. BODMAS
PEMDAS and BODMAS are acronyms used to represent the order of operations in mathematics, which is the sequence in which calculations should be performed to ensure consistent results. Although they serve the same purpose, they differ slightly in terminology due to regional variations in mathematical education.
The use of PEMDAS and BODMAS in different regions stems from variations in educational systems and historical influences. Mathematics education has evolved differently across countries due to the legacy of colonialism, language differences, and local educational standards. For instance, the British educational system emphasized “brackets” and “orders,” leading to the use of BODMAS in countries influenced by British traditions, such as India and the UK. Meanwhile, the United States, with its own distinct educational approach, adopted PEMDAS, using terms like “parentheses” and “exponents” that align with American English. These terminological differences became entrenched over time as textbooks, curricula, and teacher training adapted to their respective systems.
A universal standard has not emerged because these regional differences have no impact on the mathematical principles themselves-both acronyms lead to the same correct order of operations. Educational authorities in different countries have not prioritized unification of these terminologies, as the primary goal is consistency within a given system. Furthermore, local contexts and linguistic preferences influence the choice of terms, making it unlikely for a single acronym to gain universal acceptance. Instead, educators focus on ensuring that students understand the underlying concept of the order of operations, which transcends the specific acronyms used.
PEMDAS (used in the United States and some other countries):
P: Parentheses
E: Exponents
MD: Multiplication and Division (from left to right)
AS: Addition and Subtraction (from left to right)
BODMAS (used in the UK, India, and other countries):
B: Brackets (inclusive of all types: (), {}, [])
O: Orders (refers to powers, roots, and other indices)
DM: Division and Multiplication (from left to right)
AS: Addition and Subtraction (from left to right)