Receptive Language Worksheets
About These 15 Worksheets
Receptive language refers to the ability to understand information. It involves understanding the words, sentences, and meaning of what others say or what is read. Receptive language is integral to communication, as it enables an individual to comprehend instructions, follow conversations, and grasp the essence of stories or texts.
These worksheets are geared towards enhancing an individual’s ability to process and comprehend spoken or written information. The exercises challenge and expand various facets of receptive language, ensuring a holistic approach to improving comprehension, memory, attention to detail, and logical reasoning. Such worksheets are invaluable in educational settings, speech therapy, and language learning environments.
Types of Exercises
Listening Comprehension – Often, a short story or scenario is narrated or read out loud, after which the individual answers questions related to what they heard. This tests their ability to understand and retain the spoken content.
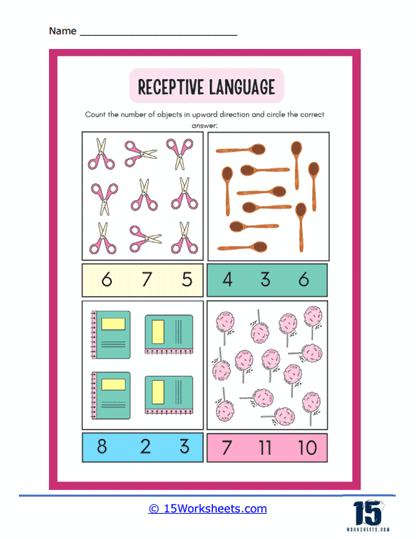
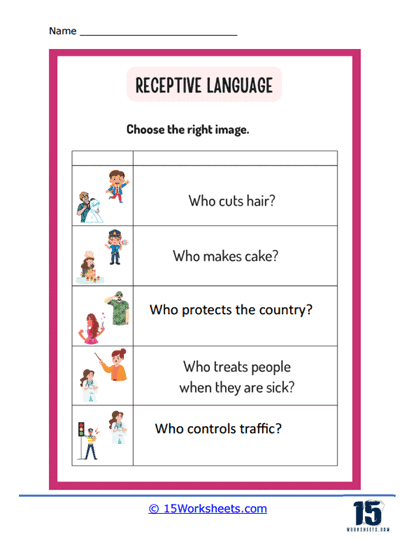
Picture Matching – In this exercise, the individual might hear a description or a name of an object, emotion, action, etc., and they would need to match it to the correct picture among several options.
Following Directions – Here, a series of verbal instructions are given, and the individual must perform actions or tasks based on what they hear. For example, “Circle the largest apple” or “Draw a line under the blue square.”
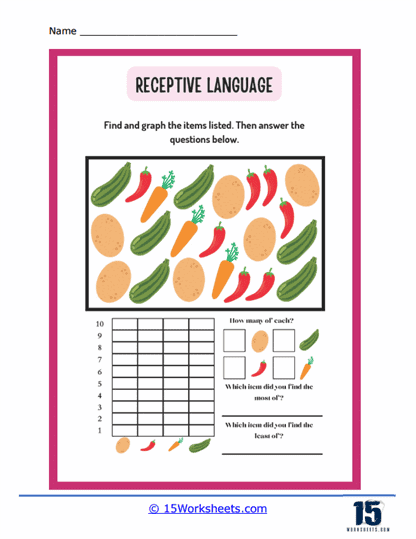
Sequencing Activities – After hearing a story or a list of events, the individual is asked to arrange pictures or statements in the order they occurred.
Vocabulary Recognition – This might involve hearing a word and choosing the correct definition or matching it to a corresponding image. It tests word comprehension and vocabulary breadth.
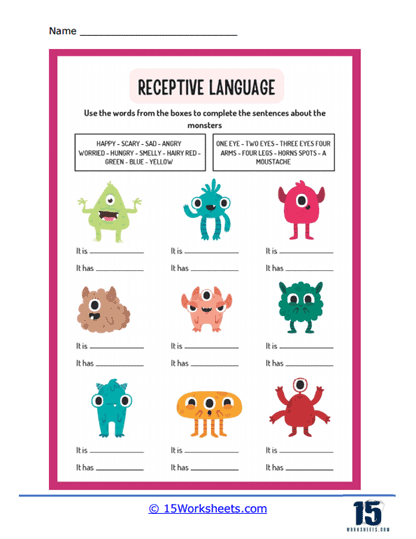
Sentence Completion – Based on the context provided, the individual would need to choose the correct word or phrase to complete a sentence, ensuring it makes logical and grammatical sense.
Identifying Emotions – This might involve listening to a scenario and identifying the emotion a character might be feeling, aiding in the comprehension of emotional cues in language.
Wh- Questions – Exercises that focus on answering who, what, when, where, and why questions related to a heard passage or story.
Categorization – Listening to a list of items or words and then categorizing them based on certain criteria, like “things you can eat” or “animals.”
What is the Difference Between Expressive and Receptive Language?
Expressive and receptive language serve as the fundamental pillars of communication.
Receptive language is about understanding words and what people say. It’s like when you listen to a story or read a book and understand what it means. Sometimes, if people have trouble with receptive language, they might not understand instructions or get confused by big words.
Expressive language is about talking and sharing our thoughts. It’s when you tell a story, write something down, or chat with friends. If someone has problems with expressive language, they might use the wrong words, speak in short sentences, or find it hard to tell a story in the right order.
To put it simply, receptive language is about understanding words, and expressive language is about using words. Both are important for talking to people and understanding what’s going on around us.