Letter Recognition Worksheets
About These 15 Worksheets
Letter recognition is a foundational skill in early childhood education, playing a critical role in a child’s journey toward becoming a confident reader and writer. The collection of letter recognition worksheets presented here provides a dynamic array of activities designed to build and strengthen this essential skill set. With a focus on both uppercase and lowercase letters, phonemic awareness, and visual discrimination, these worksheets cater to the diverse learning needs of young students, offering engaging and interactive ways to reinforce their understanding of the alphabet.
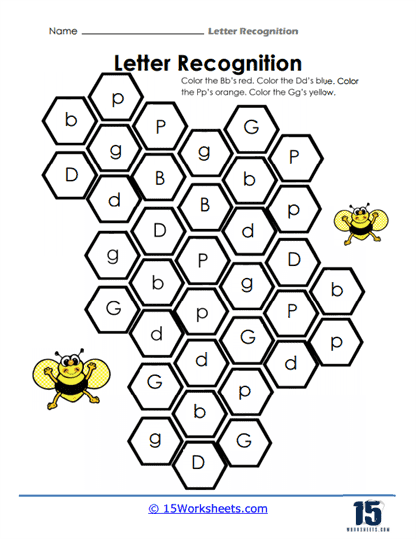
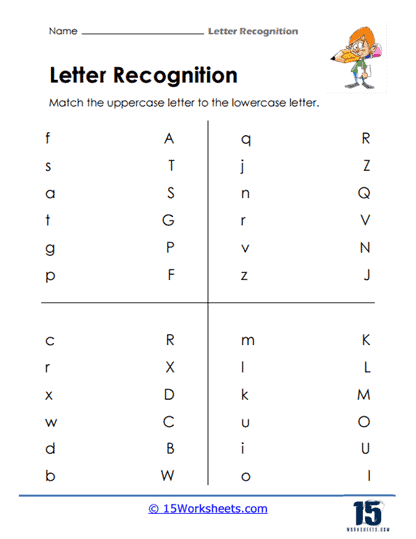
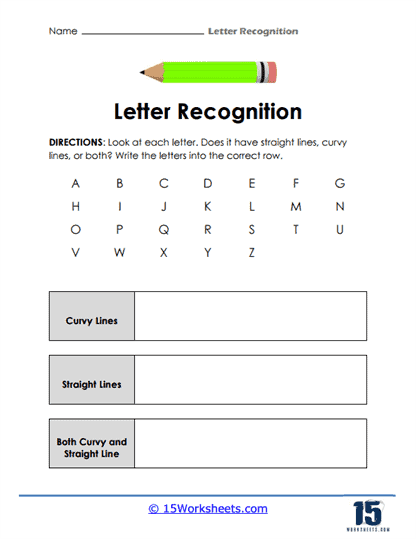
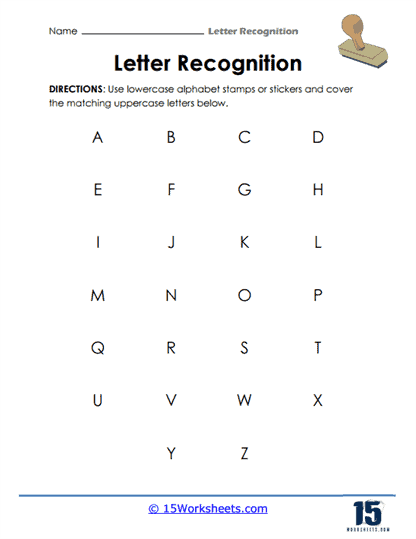
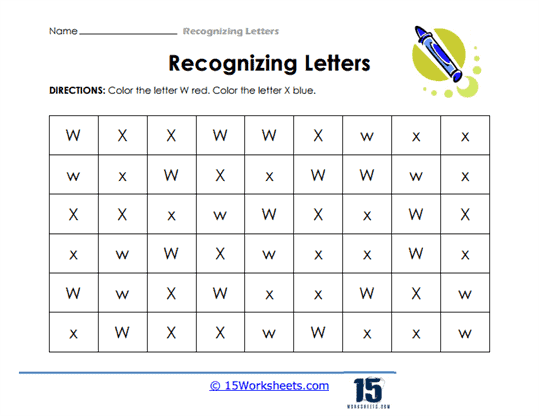
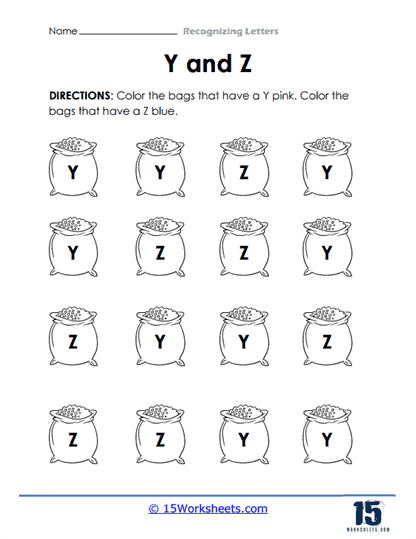
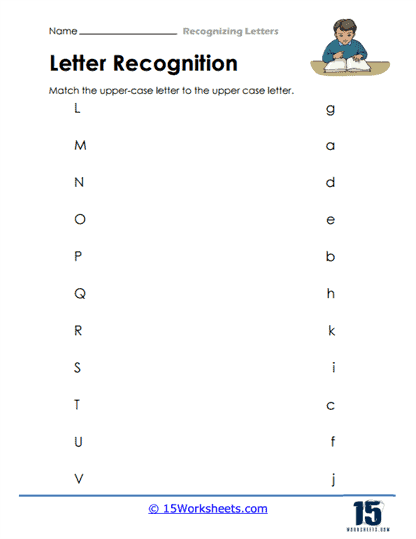
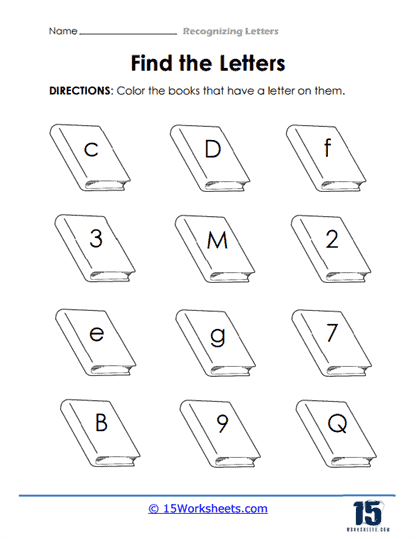
One of the most fundamental skills that these worksheets aim to develop is the ability to differentiate between letters. For children just beginning to explore the world of written language, understanding that each letter has a distinct form-and that this form can vary between uppercase and lowercase-is an important milestone. These worksheets often include activities where students are presented with a mix of letters and are asked to identify, color, or circle a specific one. This practice helps to hone their visual discrimination, which is crucial for both reading fluency and writing accuracy.
Take, for example, the worksheets that ask students to circle all instances of a particular letter within a jumble of others. This seemingly simple task goes far beyond just identifying a letter. It requires the child to actively engage their cognitive abilities, such as attention to detail, focus, and concentration, all while reinforcing their understanding that letters are unique symbols. Additionally, by including both uppercase and lowercase forms in these exercises, the worksheets emphasize the concept that these variations represent the same sound, a realization that is fundamental to early literacy development.
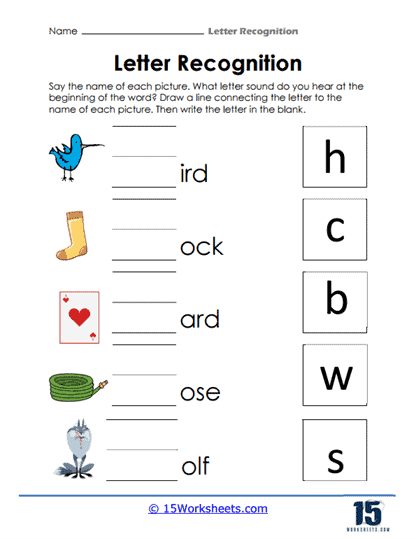
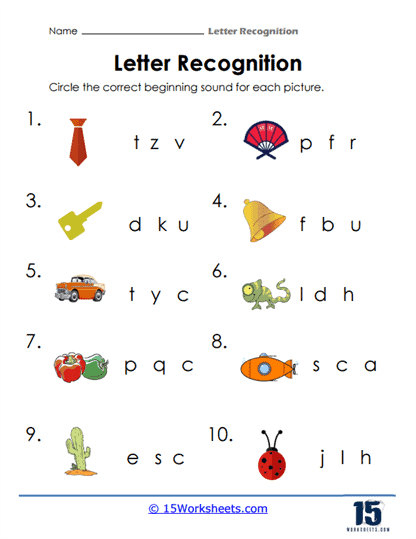
In addition to visual recognition, these worksheets place a strong emphasis on sound-letter correspondence, an integral part of phonemic awareness. Many activities focus on beginning sounds, asking students to match letters with the initial sounds of words or images. This connection between the visual representation of a letter and the sound it makes is a critical early reading skill. Phonemic awareness lays the groundwork for decoding words, which is the ability to translate written language into spoken words, an essential skill for fluent reading.
For instance, a worksheet might feature pictures of a cat, a sun, and a ball, with students tasked to identify which picture starts with the letter “C.” This exercise reinforces the concept that letters represent specific sounds in language, helping children move beyond rote memorization of the alphabet to a deeper understanding of how letters function within words. By continually linking letters to sounds, these worksheets help students build a strong foundation for decoding, which will serve them well as they progress to more complex reading tasks.
Another engaging feature of these worksheets is their incorporation of categorization exercises. In these activities, students may be asked to group letters or words based on their starting letter, fostering their ability to categorize and organize information. Categorization is not only a valuable cognitive skill but also an important aspect of literacy. It teaches children to identify patterns and relationships between letters and sounds, enhancing both their reading comprehension and their overall understanding of language structure.
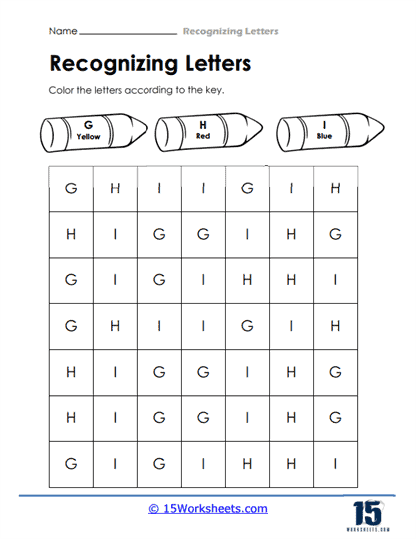
Some of the worksheets take a more creative approach by incorporating mazes, puzzles, and color-by-letter activities. These types of exercises not only make learning fun but also provide students with additional ways to engage with the material. For example, a maze worksheet might ask students to follow the path of a specific letter through a winding trail, helping to solidify the shape of the letter in their minds. This visual and kinesthetic approach to learning helps to reinforce letter recognition in a more playful and less structured way, catering to students who may thrive with hands-on activities.
The inclusion of tracing exercises is another crucial element found in these worksheets. Tracing both uppercase and lowercase letters helps students develop the fine motor skills necessary for writing. As children trace over the dotted lines of a letter, they are not only learning its shape but also building muscle memory that will later enable them to write the letters independently. Once the tracing portion of the worksheet is complete, students are often given the opportunity to practice writing the letter on their own, further solidifying their mastery of the letter’s form.
Independent writing practice is where students begin to take ownership of their learning. After tracing, they move on to writing the letters freehand, which requires them to apply the knowledge and skills they have acquired. This shift from guided practice to independent work is a critical step in the learning process, as it encourages students to internalize the information and develop confidence in their abilities.
Many worksheets incorporate basic vocabulary alongside letter recognition activities. By including words that start with the letters being practiced, these worksheets provide a dual benefit. Not only are students reinforcing their letter recognition skills, but they are also expanding their vocabulary and improving language comprehension. For example, a worksheet focusing on the letter “S” might include images of a snake, sun, and sandwich, helping students to associate the letter with familiar words and concepts.
How These Worksheets Can Help
Practicing with letter recognition worksheets can significantly improve student reading and phonics skills in several ways:
Familiarization – Continuous exposure to letters through these worksheets helps students become familiar with the shapes and names of letters, which is the first step in learning to read.
By engaging in activities that connect letters with sounds, students develop phonemic awareness, which is the ability to hear, identify, and manipulate individual sounds-phonemes-in spoken words. This is a critical skill for reading and spelling. Phonics-based activities on these worksheets support decoding, which is the ability to apply knowledge of letter-sound relationships, including knowledge of letter patterns, to correctly pronounce written words.
Fine Motor Skills – Tracing and writing exercises improve the fine motor skills necessary for writing. Good handwriting is closely linked to reading skills, as it reinforces the visual recognition of letters.
Visual Discrimination – Activities that require students to distinguish between different letters help develop visual discrimination. This skill is essential for reading, as it allows students to recognize words quickly and accurately. Understanding the relationship between letters and their sounds is fundamental for phonics instruction, which teaches students to use these relationships to read and spell words.
Vocabulary Building – Worksheets often include pictures or words that help students build vocabulary. Recognizing that a picture of an apple starts with the letter ‘A’ links the letter with a word and its meaning, making reading a more comprehensive skill. As students become more proficient in letter recognition, their confidence grows. This confidence encourages them to engage more with text, further improving their reading skills.
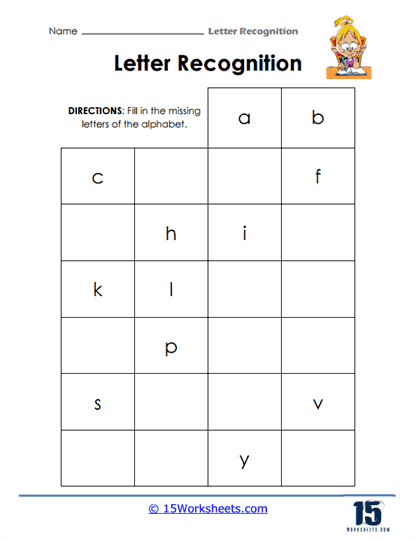
Repetitive tracing and letter-writing activities improve memory retention of letter shapes and the sequence of letters in the alphabet, which is beneficial for reading development. By systematically working through the alphabet, worksheets help students understand the sequential order of letters, which is important for dictionary skills and understanding alphabetical order in various contexts.
How Do You Teach Identification of Letters?
Teaching the identification of letters is a crucial step in early literacy, and it’s important to approach this task with a structured, engaging method. Begin by focusing on letter recognition, introducing the alphabet letters one at a time, starting with uppercase letters which are generally easier to distinguish. Use flashcards, alphabet books, or magnetic letters for this purpose, ensuring that each letter is shown clearly while its name is pronounced. Once the student becomes familiar with these, introduce the corresponding lowercase letters, highlighting the similarities and differences between the pairs.
Moving forward, incorporate phonics into the lessons by teaching the sound each letter makes, starting with the most common sound for each. Use objects or pictures that start with that letter’s sound to create a strong association. Engaging the child in interactive activities like puzzles, matching games, or letter-finding activities can make the learning process more enjoyable and effective.
As you progress, introduce letter formation through writing exercises, using large, easy-to-grip writing tools and wide-lined paper. Demonstrate how each letter is written and guide the student’s hand in the beginning, gradually moving towards independent writing. Regular reading sessions where books are read aloud can further reinforce letter recognition. Point to each letter as you read and ask the child to identify letters to help them see these characters in context.
Technology, when used wisely, can be a beneficial tool. Educational apps and online resources that focus on letter identification can complement traditional learning methods, provided they are age-appropriate. It’s essential to regularly review and reinforce the letters already learned to ensure long-term retention, celebrating progress and gently correcting mistakes as you go.
Personalize the learning experience based on the child’s interests and encourage their curiosity and questions. Creating an environment where the child feels comfortable asking questions can lead to a deeper understanding and a greater interest in learning more about letters and words. Remember, patience and positive reinforcement are key, as each child learns at their own pace.
How Can Students Improve Their Letter Naming Fluency?
Improving letter naming fluency in students is an essential part of their early literacy development. This process involves several strategies that focus on recognition, repetition, and engagement.
Students should regularly practice naming letters in a variety of settings and contexts. This could involve using flashcards, alphabet charts, or digital apps. Consistent practice helps reinforce their memory and familiarity with each letter. During these practice sessions, encourage students to name both uppercase and lowercase letters, enhancing their ability to recognize each letter in any form.
Incorporating games and activities can significantly boost letter naming fluency. Games like alphabet bingo, memory matching with letter cards, or letter scavenger hunts make learning fun and interactive. These activities not only reinforce letter recognition but also keep students engaged and motivated.
Reading plays a vital role in improving letter naming fluency. Teachers and parents should read aloud to students regularly, pointing out letters and asking students to name them. This activity helps students see letters in various fonts and contexts, improving their ability to recognize and name letters quickly.
Another effective method is to integrate letter naming in daily routines. Labeling objects around the classroom or home with their corresponding starting letters helps students make real-world connections with the alphabet. For example, labeling a door with ‘D’ and a window with ‘W’ reinforces letter recognition in a practical and meaningful way.
Peer learning can be very beneficial. Pairing students together or in small groups, where they can quiz each other on letter names, creates a collaborative learning environment. This peer interaction can boost confidence and provide a supportive space for practicing letter naming.
Using music and songs that emphasize the alphabet can also enhance letter naming fluency. Songs like the classic “Alphabet Song” or other creative variations help students remember the letters and their sequence, making it easier for them to recall and name each letter.
It’s important to track progress and provide regular feedback. Teachers and parents can monitor students’ letter naming fluency through informal assessments or games. Positive reinforcement and constructive feedback help build confidence and encourage continued practice.
Tailoring the learning experience to each student’s needs and learning style is crucial. Some students may benefit from visual aids, while others might find kinesthetic activities more effective. Understanding and adapting to these individual needs will ensure that each student develops letter naming fluency in the most effective way possible.