Non Sequitur Worksheets
About These 15 Worksheets
These worksheets help enhance students’ understanding and skills in language arts, particularly in areas like reading comprehension, critical thinking, vocabulary development, and the ability to understand and create logical connections within texts. The term “Non Sequitur” refers to statements, ideas, or conclusions that do not logically follow from the previous statements. These worksheets use such non-logical progressions as a basis to challenge students to identify inconsistencies, illogical progressions, or irrelevant information within a given text or series of statements. By engaging with these exercises, students learn to critically analyze text, detect nuances, and improve their overall reading skills.
Through a variety of exercises, these worksheets not only improve specific language arts and reading skills but also foster overall cognitive development. Students learn to question, analyze, and understand texts in a deeper and more nuanced way, preparing them for more advanced studies and effective communication in their daily lives. Practicing with Non Sequitur Worksheets thus represents an innovative and engaging approach to enhancing students’ language competencies, critical thinking, and logical reasoning abilities.
Types of Exercises
These worksheets comprise various exercises, each designed to target specific aspects of language arts and reading skills. These exercises include:
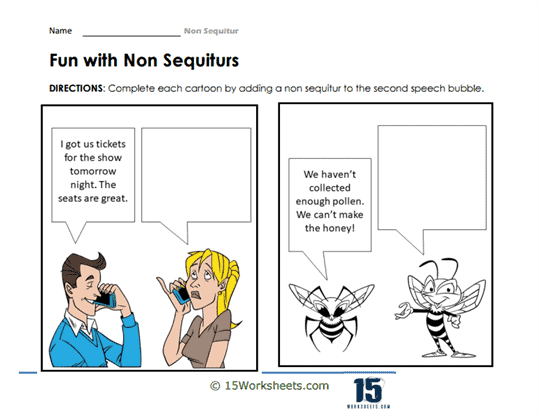
Identifying – Students are presented with a series of statements or a paragraph where they must identify the Non Sequitur(s). This exercise sharpens their ability to recognize when a conclusion does not logically follow from its premises.
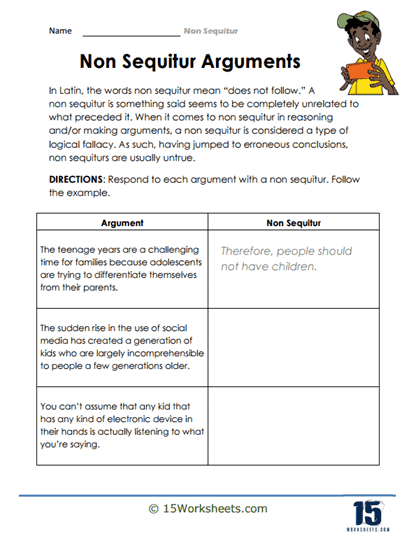
Correcting – Beyond identifying nonlogical statements, students are asked to correct them. This could involve rewriting a sentence or paragraph to ensure that all statements logically connect, enhancing their writing and logical reasoning skills.
Creating – In a more creative vein, students might be asked to create their own Non Sequiturs within a logical narrative. This encourages creativity and a deeper understanding of how logical connections in language function.
Comparing and Contrasting Statements – Exercises that ask students to compare and contrast statements to identify which is a Non Sequitur foster skills in critical analysis and attention to detail.
Logical Sequence Ordering – Students are given a list of statements or events and asked to order them logically. This exercise improves their ability to discern logical order and sequence in texts.
Inference Making – Some exercises focus on making inferences from a series of statements, with one or more being Non Sequiturs. This challenges students to rely on context and logic to fill in gaps in information.
Cause and Effect Relationships – These exercises require students to identify incorrect cause and effect relationships within a given text, promoting an understanding of logical progression and consequence.
Contextual Vocabulary Usage – Worksheets might include exercises where students must identify words or phrases used in a Non Sequitur manner, enhancing vocabulary and context skills.
The Benefits of These Worksheets
Practicing with these worksheets offers several benefits in the development of language arts and reading skills:
Improved Reading Comprehension – Regular engagement with these worksheets enhances students’ ability to understand and interpret complex texts, as they learn to identify and question illogical statements or progressions.
Enhanced Critical Thinking – Identifying, correcting, and creating Non Sequiturs require students to apply critical thinking and reasoning skills, making them more adept at analyzing texts and arguments.
Better Logical Reasoning – By focusing on the logical (or illogical) flow of ideas, students develop a stronger grasp of logical reasoning, which is essential for effective communication and argumentation.
Increased Vocabulary – Exercises involving the correction and identification of Non Sequiturs in contextual vocabulary usage can expand students’ lexicon and improve their ability to use words appropriately in various contexts.
Creative Thinking and Writing – Creating Non Sequiturs within a narrative context encourages creative thinking, allowing students to explore language in unconventional ways, thereby improving their writing skills.
Attention to Detail – These exercises require a keen eye for detail, helping students to develop a meticulous approach to reading and writing.
Improved Analytical Skills – Analyzing texts to identify Non Sequiturs or to understand the logical flow of ideas sharpens analytical skills, benefiting students across all subjects.
Enhanced Problem-Solving Skills – Correcting Non Sequiturs involves problem-solving, as students must figure out how to make a series of statements logically coherent.
What is the Literary Device of Non Sequitur?
The literary device of Non Sequitur represents an intriguing and often sophisticated element within the realm of storytelling and narrative construction. Originating from the Latin for “it does not follow,” a Non Sequitur is a statement or conclusion that does not logically follow from the previous statement or argument. This device, when skillfully employed by authors, can serve various purposes, ranging from injecting humor and surrealism to challenging readers’ perceptions and encouraging deeper engagement with the text.
The Defining Feature of a Non Sequitur
The main defining feature of a Non Sequitur is its apparent lack of logical connection to what precedes it. This can manifest in dialogue, narrative descriptions, or the actions of characters within a story. Unlike other literary devices that rely on building upon established ideas or themes, Non Sequiturs intentionally break from logical progression, creating a stark contrast and often leaving the reader puzzled, amused, or deeply contemplative.
Characteristics of a Non Sequitur
Non Sequiturs in literature can be characterized by several key features:
Unexpectedness – They catch the reader off guard with an element that seems out of place or unrelated to the context.
Disruption – Non Sequiturs disrupt the flow of thought or narrative, creating a jarring effect that demands attention.
Versatility – They can be used in various contexts, from dialogue and narrative to descriptions and character thoughts.
Multiplicity of Purpose – Authors may use Non Sequiturs for humor, to evoke surrealism, to underline a character’s mental state, or to engage readers in a deeper exploration of the text.
Ambiguity – Often, Non Sequiturs leave room for interpretation, challenging readers to find meaning or coherence where it is not immediately apparent.
Examples of Non Sequitur in Literature
“Alice’s Adventures in Wonderland” by Lewis Carroll – This classic novel is rife with Non Sequiturs, particularly in the dialogue of its characters. For instance, the Mad Hatter’s conversation during the tea party is filled with nonsensical statements that do not follow logically, such as, “Why is a raven like a writing desk?” This Non Sequitur serves to immerse the reader in the absurdity and whimsy of Wonderland, highlighting the illogical and dream-like quality of Alice’s experiences.
“Catch-22” by Joseph Heller – Heller’s novel is renowned for its use of circular reasoning and contradictory statements, epitomizing the Non Sequitur. A notable example is the catch itself – “You’re damned if you do and damned if you don’t.” This statement, among others, illustrates the absurdity of war and the bureaucratic paradoxes that trap the characters, reflecting on the illogical extremities of human institutions.
“The Hitchhiker’s Guide to the Galaxy” by Douglas Adams – Adams frequently employs Non Sequiturs to comedic effect, such as the sudden appearance of a sperm whale and a bowl of petunias falling through the sky, prompted by the transformation of two missiles into these entirely unrelated objects. This instance not only serves as a humorous interjection but also underscores the randomness and unpredictability of the universe Adams has created.
The Effect of Non Sequitur on the Reader
The use of Non Sequiturs in literature can have a profound effect on readers, engaging them in a multifaceted experience that transcends traditional narrative expectations. Some of the key impacts include:
Engagement through Curiosity – Non Sequiturs pique readers’ curiosity and encourage them to delve deeper into the text to uncover potential meanings or connections, fostering a more engaged reading experience.
Emotional and Intellectual Stimulation – By juxtaposing unrelated or illogical elements, authors can evoke a range of emotional responses, from amusement to confusion, and stimulate intellectual exploration.
Challenge to Expectations – Non Sequiturs challenge readers’ expectations of coherence and logical progression in storytelling, inviting them to embrace ambiguity and the unexpected.
Highlighting Themes or Ideas – When used purposefully, Non Sequiturs can underscore themes or ideas within a narrative, drawing attention to them in a unique and memorable way.
Creating a Distinctive Narrative Voice or Style – The use of Non Sequiturs can contribute to a distinctive narrative voice or style, setting a work apart and giving it a unique flavor that resonates with readers.
By weaving unexpected, illogical elements into their storytelling, writers can evoke a range of responses, from humor and whimsy to contemplation and critique. Non Sequiturs challenge readers to look beyond the surface, exploring the complexities and ambiguities of language and meaning. Through examples like “Alice’s Adventures in Wonderland,” “Catch-22,” and “The Hitchhiker’s Guide to the Galaxy,” we see the diverse applications and profound effects of this literary device, highlighting its enduring appeal and significance in literature.