Earth Day Worksheets
What is Earth Day?
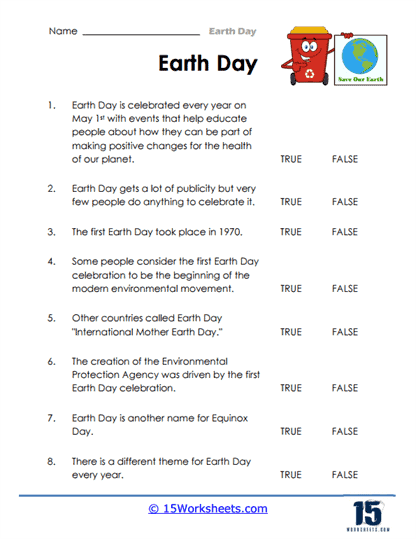
Earth Day is an annual event observed worldwide to demonstrate and promote environmental awareness and calls for the protection of our planet. It is celebrated on April 22nd each year.
The idea for Earth Day was first proposed by Gaylord Nelson, a U.S. Senator from Wisconsin, after witnessing the damages caused by an enormous oil spill in Santa Barbara, California, in 1969. He was inspired by the student anti-war movement and hoped that he could infuse that energy with an emerging public consciousness about air and water pollution, which would force environmental protection onto the national political agenda. Senator Nelson announced the idea for a “national teach-in on the environment” and recruited Denis Hayes, a young activist, to organize the event.
The first Earth Day was held on April 22, 1970, when approximately 20 million Americans took part in rallies, marches, and educational programs across the country. The event was successful in bringing environmental issues to the forefront of public consciousness. In fact, the United States Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) was created and several significant environmental acts, such as the Clean Air Act, Clean Water Act, and Endangered Species Act, were passed in the years following the first Earth Day.
In 1990, Earth Day became a global event, with 200 million people in over 140 nations participating according to Earth Day Network. This global observance helped pave the way for the 1992 United Nations Earth Summit in Rio de Janeiro.
By the turn of the millennium, Earth Day focused on global warming and clean energy. The Earth Day Network used the internet as its principal organizing tool and it was reported that 5,000 environmental groups in 184 countries held events for the 30th Anniversary of Earth Day.
Today, Earth Day is the largest secular observance in the world, celebrated by more than a billion people every year. Events are coordinated globally by the Earth Day Network in more than 193 countries. The day is marked by activities aimed at raising awareness about the need for environmental protection and sustainability, including marches, petitions, tree planting, clean-ups, and teaching sessions.
As we face global challenges like climate change, deforestation, water scarcity, and pollution, Earth Day serves as a reminder of the need for continued commitment and action to protect our planet.
Earth Day Tips For Teachers
Create an Earth Day Pledge: Have your students write pledges about what they will do to help the environment, such as recycling, using less water, or turning off lights when they’re not in use.
Start a Recycling Program: If your school doesn’t already have one, Earth Day is a great time to start a recycling program. Teach your students about what can be recycled and have them take responsibility for recycling in the classroom.
Plant a Tree or Start a Garden: If you have outdoor space, consider planting a tree or starting a garden with your students. This can teach them about how plants grow and why they’re important for the environment.
Make Art from Recycled Materials: Organize an art project where students can create something beautiful out of materials that would otherwise be thrown away.
Guest Speaker: If possible, invite a local environmental scientist or activist to speak to your class about their work.
Environmental Reading: Read a book or story about the environment. There are many children’s books that teach about the importance of taking care of our planet.
Nature Walk: Take your students on a walk around the school grounds or a local park. Use this time to point out different plants and animals, and talk about the role they play in our ecosystem.
Write Letters to Local Representatives: Have students write letters to local government representatives about an environmental issue they care about.
Virtual Field Trips: Technology allows for virtual field trips to museums, zoos, or historical sites. This can be a great way to bring a subject to life, especially if physical trips are not possible.