Decimals on a Number Line Worksheets
About These 15 Worksheets
Decimals on a Number Line worksheets are an instructional tool used to help students visualize and understand the concept of decimal numbers and their relative positions to one another. They use a number line, a visual representation of numbers placed in order on a horizontal line, to graphically demonstrate where decimal numbers fit in relation to whole numbers and other decimal numbers.
The skills gained from using Decimals on a Number Line worksheets are applicable in various real-life scenarios. For instance, understanding decimals can help when dealing with money, as most currencies are divided into a decimal system with 100 smaller units making up the main unit. In measurements too, for instance, when determining distances or quantities in recipes, understanding decimals is crucial. The number line representation also develops a visual understanding of math, which can be helpful in many professions like engineering, architecture, data analysis, and more.
A Look At Individual Worksheets
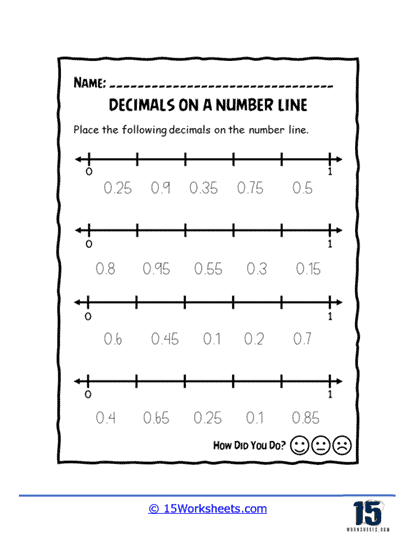
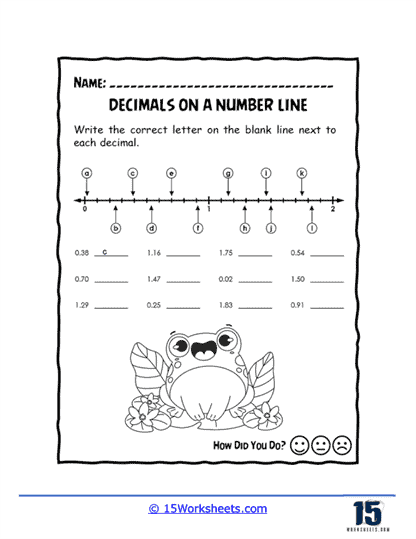
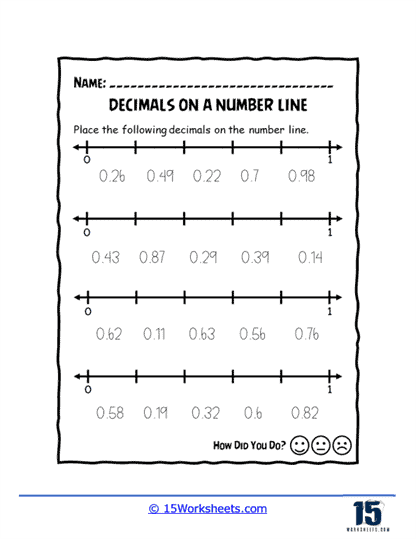
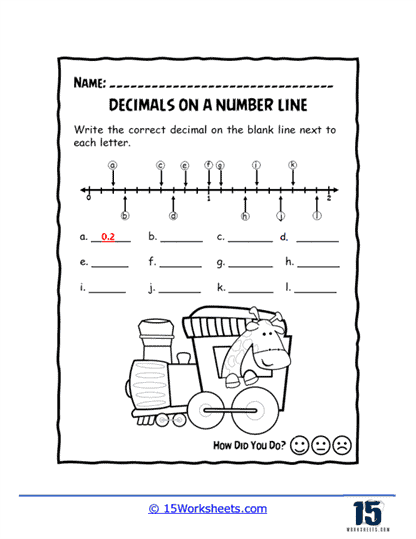
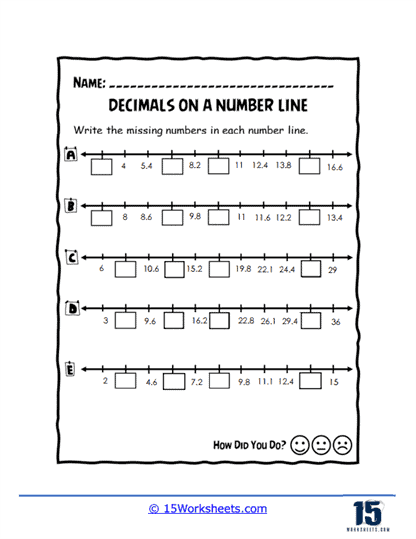
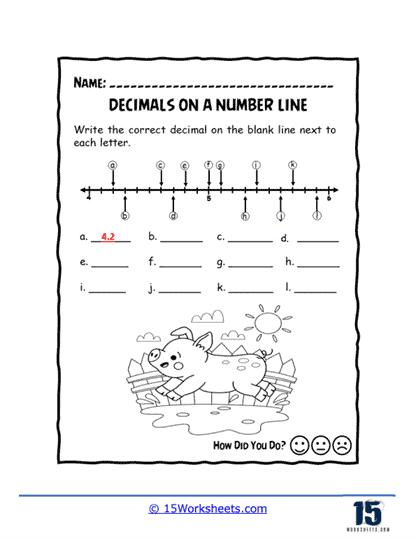
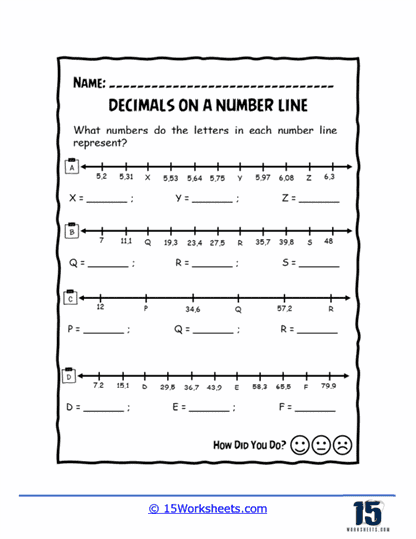
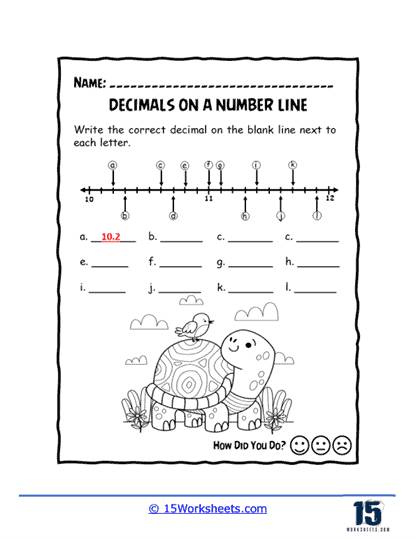
Worksheets like Pointing on the Line, Missing Values, and Values of Points introduce students to the basics of plotting decimals on a number line. These exercises help learners visualize where decimals fit between whole numbers, enhancing their number sense. Correct Letter and Number Line Letters add a twist by associating letters with decimal points, turning the activity into a fun decoding challenge.
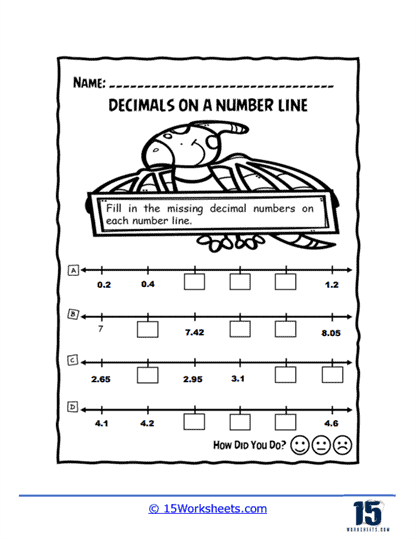
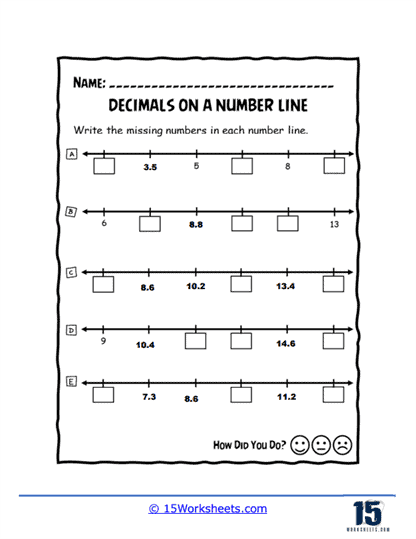
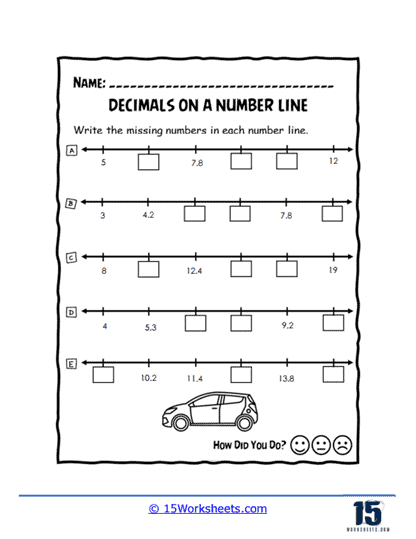
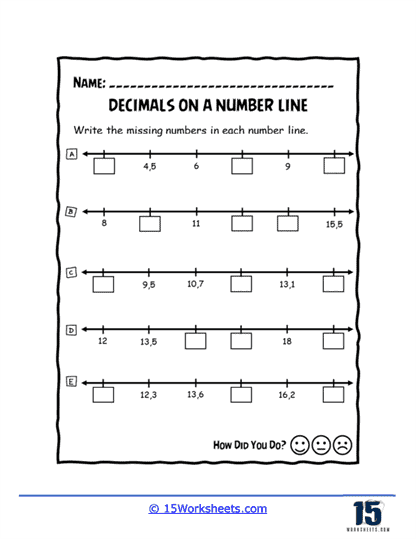
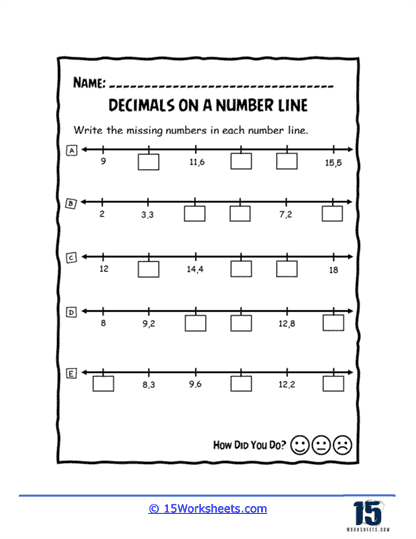
To grasp the relative sizes of decimals, worksheets such as Order and Flow, Sequencing Up, and Decimal Train guide students through ordering and sequencing tasks. These activities often use engaging themes, like trains or ascending sequences, to make the learning experience enjoyable. Boxed Decimals and Number Line Holes present puzzles where students fill in missing decimals, reinforcing their understanding of decimal intervals.
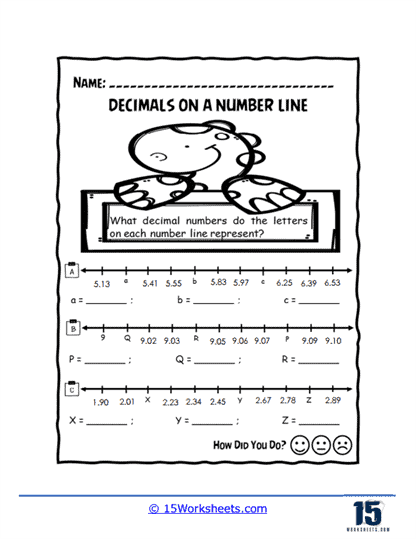
Worksheets like Represent Decimals, Naming Values, and Commas as Decimals bridge the gap between abstract concepts and real-world applications. By interpreting decimals in various contexts, students learn to apply their knowledge to situations like reading prices or measuring lengths. Forming Spaces challenges learners to identify specific decimal values, honing their precision and attention to detail.
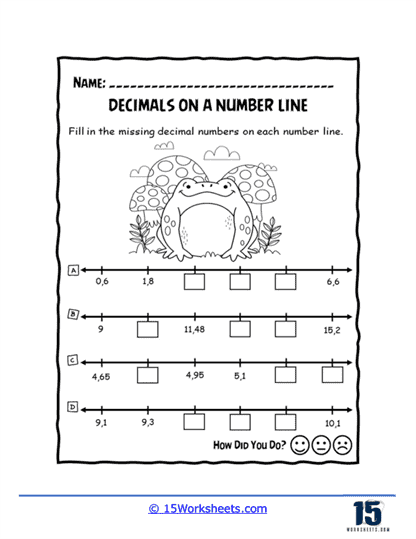
Froggy Decimals introduces a playful element, where students help a frog leap to the correct decimal points. This imaginative approach not only captures students’ interest but also reinforces their ability to locate and understand decimals on a number line.
How Do You Plot a Decimal Value on a Number Line?
Plotting a decimal value on a number line can be a great way to visualize the value of the number and its relation to other numbers. Here’s a step-by-step guide on how to do it:
Draw a Number Line – Start by drawing a horizontal line. This represents your number line.
Mark the Number Line – Decide on the range of numbers that your number line will represent. For example, if you are plotting decimals between 0 and 1, you would place a small mark or line at each end of your number line to represent these numbers. Write “0” below the line on the left side and “1” below the line on the right side.
Divide the Number Line – Divide the space between 0 and 1 into 10 equal parts, each part represents one-tenth (0.1). This is the typical setup when dealing with decimals, but you could divide into more sections if you’re dealing with hundredths (0.01), thousandths (0.001), and so forth.
![]()
Identify the Decimal – Identify the decimal number that you are trying to plot. Let’s say the number is 0.4.
Plot the Decimal – To plot a decimal like 0.4, count four-tenths (or four of the equal parts you divided your line into) from 0 and make a mark. That’s where 0.4 would be located on the number line.
Label the Point – Finally, label the point with the decimal number, in this case, 0.4.
Remember, the steps may vary slightly depending on the decimal you’re plotting. If you’re plotting a number like 1.4, your number line would need to extend from 0 to at least 2 and then you’d count one whole and four-tenths to find where to plot your decimal.
Using a number line to understand decimals is an excellent way to visualize them, which can be especially helpful when learning about these types of numbers for the first time. It’s also a useful tool when it comes to comparing decimals or when you’re learning to round decimals.