Circles Worksheets
All About These 15 Worksheets
Preschool is one of the most formative stages in a child’s life. It’s a time when curiosity is at its peak, when every experience and interaction helps shape the developing mind, and when children are naturally inclined to explore the world around them. During these early years, learning is not confined to facts and figures-it’s about building foundational skills that set the stage for future academic success and cognitive development. Among the many concepts introduced during this period, understanding shapes is crucial, and one of the most essential shapes in a child’s early education is the circle.
Circles are everywhere-in the wheels of a bike, the sun in the sky, the rim of a cup, or even the face of a clock. They are among the first shapes children learn to identify because of their simplicity and prevalence in everyday life. Yet, the significance of teaching circles goes far beyond just recognition. The circle, as a shape, plays a profound role in helping children develop spatial awareness, early math skills, and even creativity. This is where the “Circles Worksheets” come in, offering an invaluable resource for caregivers, parents, and educators who are looking to enhance a child’s learning experience in a fun, engaging, and educational way.
Teaching shapes, particularly circles, isn’t just about showing children how to recognize a form-it’s about fostering a deeper understanding of the world. Shapes are the building blocks of geometry, a branch of mathematics that young children will continue to explore throughout their academic journey. When children first learn about shapes like circles, they begin to grasp the concept of geometry at a very basic level. This understanding later expands into more complex ideas such as symmetry, patterns, and even abstract problem-solving.
But why focus on circles? Circles hold a special place in a child’s cognitive development. For one, they are symmetrical, which helps children begin to understand the idea of balance and uniformity. Moreover, circles are continuous; they have no edges or corners, making them unique compared to squares, triangles, or rectangles. This uniqueness captures children’s attention and helps them differentiate shapes more effectively. As children practice recognizing, tracing, drawing, and counting circles, they are not just learning about geometry-they are also developing critical motor skills, spatial reasoning, and even their ability to focus.
This collection of worksheets for preschoolers is designed to offer a dynamic, multi-faceted approach to learning about this essential shape. These worksheets provide more than just shape recognition; they create opportunities for young learners to strengthen fine motor skills, deepen their understanding of math concepts, and ignite their imaginations through artistic expression. By using these worksheets, children can explore circles in a hands-on way, which is critical at this stage of learning, as preschoolers learn best through active, tactile experiences.
Ah, the noble circle-nature’s way of saying, “I have no corners, but I’m still cool.” The circles collection takes this humble shape and turns it into a full-blown preschool party. Kids start their circular journey with activities like Write And Color and Tracing And Coloring, where they trace circles with the precision of a tiny Picasso and color them in with the enthusiasm of someone discovering crayons for the first time. Then there’s Circle Hunt, a thrilling adventure where children identify circles hidden among other shapes-think of it as “Where’s Waldo?” but with fewer striped shirts and more geometry.
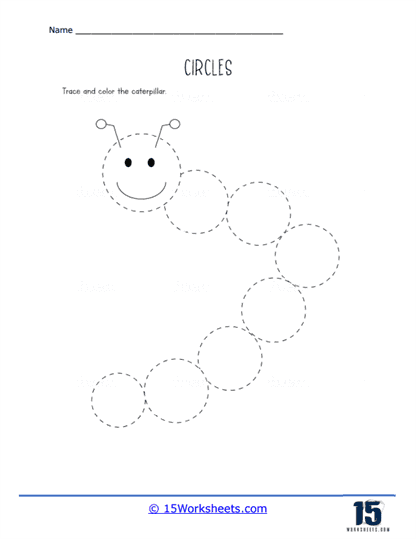
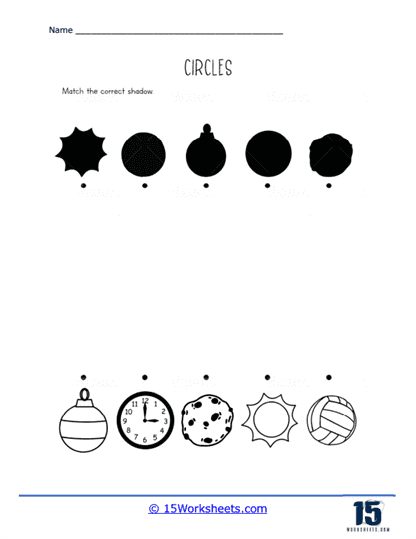
But the fun doesn’t stop there! Enter the whimsical world of the Circling Caterpillar, where each segment is a circle waiting to be traced, turning a simple shape into a delightful insect friend. In Matching Shadows, kids play detective, pairing objects with their shadowy counterparts-because even circles have a dark side. Draw A Snowman lets children stack circles to create their own frosty friend, proving that with enough circles, you can build a winter wonderland. And let’s not forget Ladybug Spots, where counting and coloring converge as kids add spots to ladybugs, combining math skills with artistic flair.
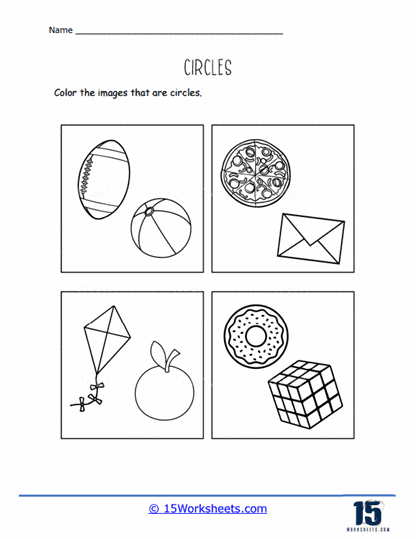
For those seeking a challenge, Color Maze offers a pathfinding puzzle where only the circular route leads to victory. Complete It dares kids to finish partially drawn circles, testing their spatial awareness and imagination. Colorful Flowers transforms circles into blooming masterpieces, while Trace Them All is a marathon of circular tracing that would make even the most seasoned doodler proud. Shapes Bonanza and Circular Objects mix and match various shapes, helping kids distinguish circles from the rest. Find In Each Row sharpens their scanning skills, and The Other Half challenges them to draw the missing halves of shapes, completing the circle-literally. It’s a whirlwind tour of roundness that’s as educational as it is entertaining.
Impact on Child Development
Early childhood education is a critical stage in a child’s cognitive and physical development. During this period, children are naturally curious and eager to learn, making it the perfect time to introduce foundational concepts that will benefit them for years to come. One of the most effective tools educators and parents can use are circle worksheets.
These worksheets might appear simple at first glance, but the range of activities they offer can make a profound impact on a child’s developmental journey. From fine motor skills to early mathematical understanding, circle worksheets provide a versatile platform for growth. Let’s explore the variety of activities they include and dive deeper into how each of them uniquely supports a child’s learning process.
Building Precision and Creativity
The act of tracing shapes, particularly circles, is one of the earliest activities that children engage in during their preschool years. While it may seem like a basic exercise, tracing circles plays a pivotal role in developing a child’s fine motor skills, which are essential for tasks such as writing, drawing, and other manual tasks. Tracing demands a certain level of control over hand movements as children follow the shape’s curvature with a pencil or crayon. This hand-eye coordination is fundamental as it lays the groundwork for more complex tasks, including letter formation and writing sentences in the future.
Once the circles are traced, children often get the opportunity to color them. Here, the simplicity of a circle becomes a blank canvas for a child’s creativity to blossom. The act of choosing colors is more than just fun-it’s a form of self-expression. As children select which colors to use, they are also practicing decision-making and honing their ability to visualize and create something unique. In this small but significant way, children learn to associate creativity with learning, fostering a positive attitude toward education.
Identifying Circles Among Other Shapes
The next step in a child’s journey with circle worksheets is learning how to identify circles amidst a mix of other shapes. This activity may seem straightforward, but it serves a deeper purpose. Distinguishing circles from squares, triangles, and other polygons challenges children to pay close attention to details. This skill is fundamental not only for visual recognition but also for sharpening a child’s focus and attention span.
By practicing shape identification, children are also developing their visual discrimination skills, a critical component of early reading. When a child learns to differentiate between a circle and a square, they are exercising the same cognitive skills required to distinguish between letters, such as “b” and “d,” which are essential for literacy. Beyond reading, this ability to focus on subtle differences primes a child for success in tasks that require pattern recognition, problem-solving, and critical thinking-all of which are necessary for their academic and personal growth.
Strengthening Motor Coordination and Spatial Awareness
Drawing circles, whether freehand or with the assistance of a template, is another essential activity offered by these worksheets. This task might seem simple, but it engages a child’s motor coordination and visual-spatial reasoning in significant ways. When children attempt to draw a circle without the help of a guide, they begin to develop a more refined sense of hand-eye coordination. They are tasked with controlling the movement of their hands while simultaneously visualizing the desired shape, an effort that promotes precision and patience.
Drawing circles helps children grasp the concepts of proportion and symmetry, skills that are essential not only in art but in mathematics and science as well. Over time, children learn how to balance their drawings, create equal shapes, and understand the idea of spatial relationships between different objects. Successfully drawing a circle is a rewarding experience, instilling a sense of accomplishment and encouraging persistence-valuable traits that will serve children well as they tackle increasingly difficult challenges in their learning.
Circle worksheets also provide an excellent opportunity to introduce foundational math skills. Activities that ask children to count how many circles appear on a page combine the benefits of shape recognition with early counting practice. This dual approach reinforces two key areas of learning-math and geometry-while engaging children in an enjoyable and interactive way.
Counting circles is not just about rote learning; it requires children to focus, observe, and count with accuracy. These skills translate into broader mathematical concepts, such as one-to-one correspondence, which is vital for understanding numbers. Additionally, this activity builds on their concentration and cognitive endurance, preparing them for more advanced arithmetic as they grow.
Understanding Circle Properties
As children become more familiar with the concept of circles, more advanced worksheets can introduce them to the basic properties of this shape. Understanding terms such as “circumference,” “diameter,” and “radius” might seem too complex for young learners, but these concepts are often presented in simple, visual ways that children can grasp. By learning about these properties early on, children are setting the stage for future geometry lessons.
Introducing these ideas fosters logical thinking and helps children see how shapes interact with the world around them. For example, they may begin to notice the circular wheels of a bicycle or the round face of a clock. This broader awareness helps them understand that shapes are more than just abstract ideas-they are part of everyday life. As children explore how circles function and compare them to other shapes, they are engaging in a form of analytical thinking that will aid them in subjects like science, technology, and engineering in the future.
What is a Circle?
A circle is a fundamental geometric shape that is defined as a closed curve consisting of all points in a plane that are equidistant from a fixed center point. In simpler terms, a circle is a perfectly round shape.
Here are some key characteristics and properties of a circle:
Center – A circle is defined by its center point, which is the point equidistant from all points on the circle’s boundary. It is often denoted by the letter “O” or “C.”
Radius – The radius of a circle is the distance from the center of the circle to any point on its boundary. It is represented by the symbol “r.” All radii of a circle are equal in length since they all connect the center to points on the circle’s circumference.
Diameter – The diameter of a circle is a straight line segment passing through the center and connecting two points on the circle’s boundary. It is the longest chord in a circle and is equal to twice the length of the radius.
Circumference – The circumference of a circle is the distance around its outer boundary. It can be calculated using the formula C = 2πr, where “C” represents the circumference, “r” represents the radius, and π (pi) is a mathematical constant approximately equal to 3.14159. The circumference is proportional to the circle’s diameter, and the ratio of the circumference to the diameter is always π.
Area – The area of a circle is the amount of space enclosed by its boundary. It can be calculated using the formula A = πr^2, where “A” represents the area and “r” represents the radius. The area is proportional to the square of the radius.
Chord – A chord is a line segment connecting two points on the circle’s boundary. Unlike the diameter, a chord does not necessarily pass through the center of the circle.
Tangent – A tangent is a line that touches the circle at only one point, known as the point of tangency. At the point of tangency, the tangent is perpendicular to the radius that intersects it.
Circles have various applications and are found in numerous fields, including mathematics, physics, engineering, and art. They possess symmetry, and their properties play a fundamental role in trigonometry, geometry, and calculus. They are used to model natural phenomena, such as planetary orbits and the shape of wheels, as well as in architectural designs, computer graphics, and many other practical applications.