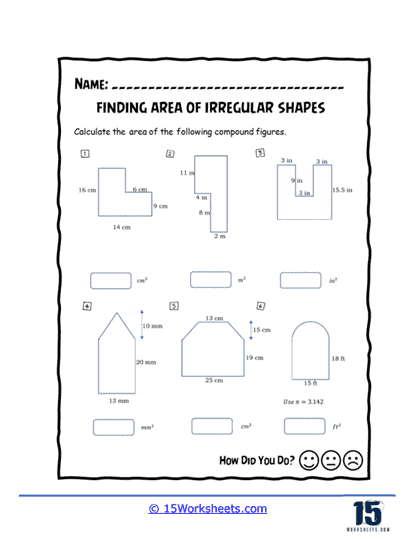
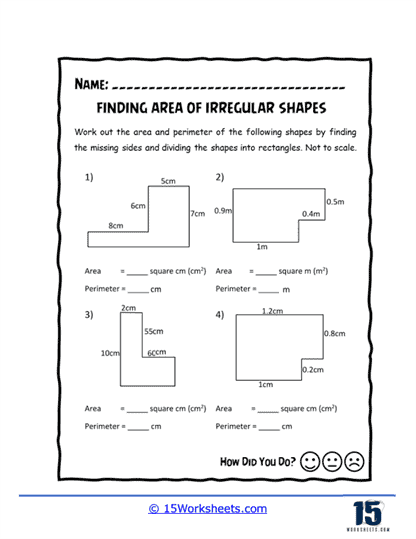
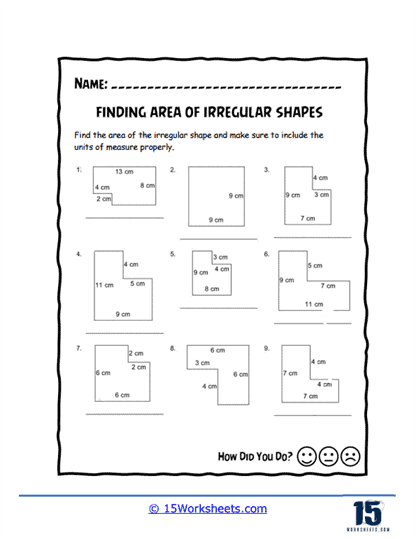
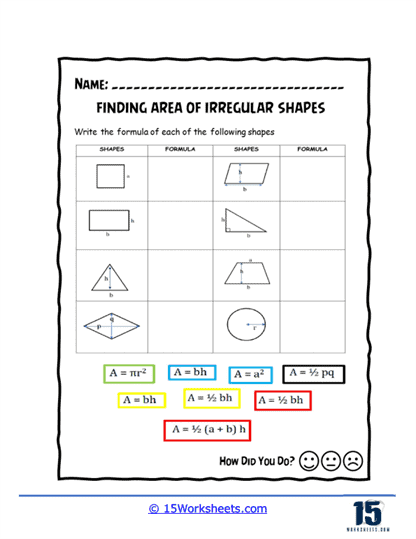
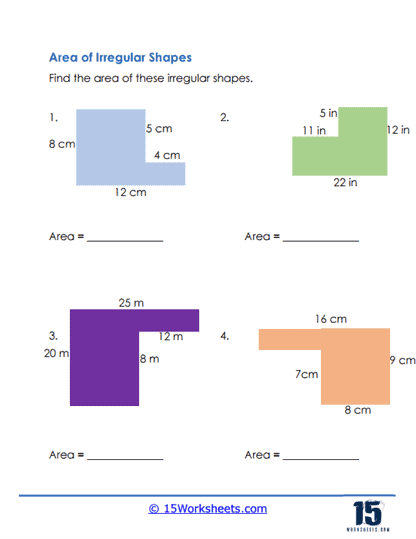Area of Irregular Shapes Worksheets
About Area of Irregular Shapes Worksheets
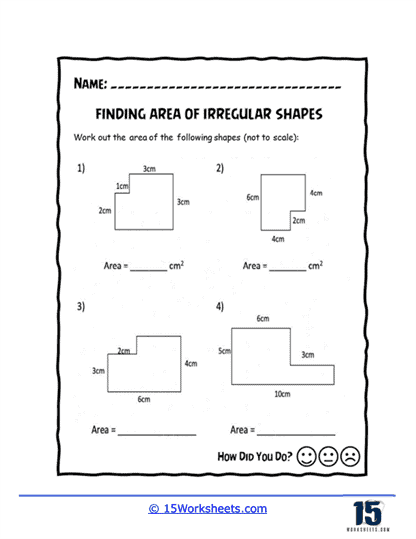
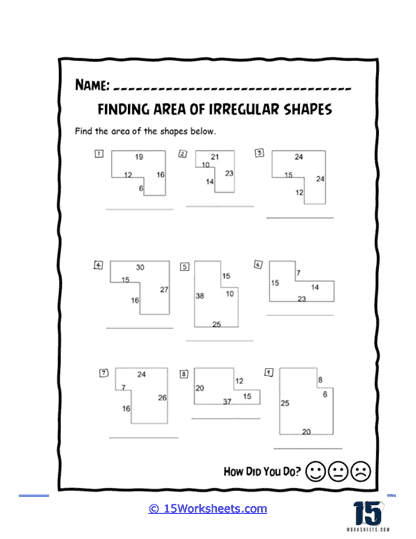
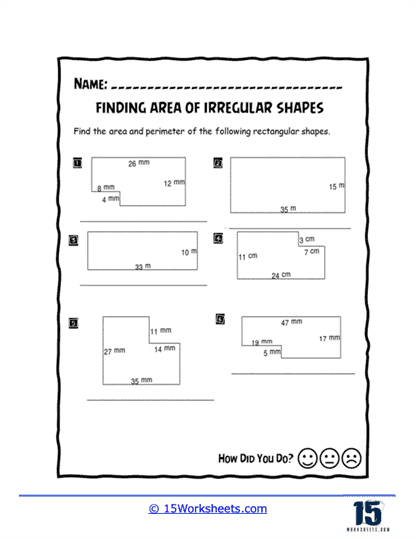
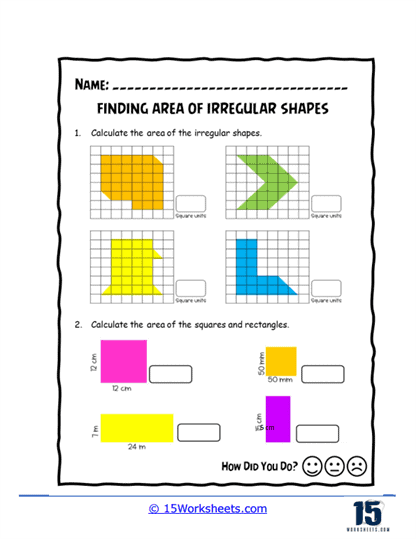
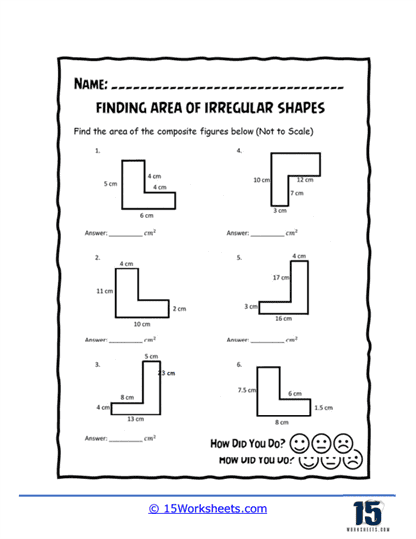
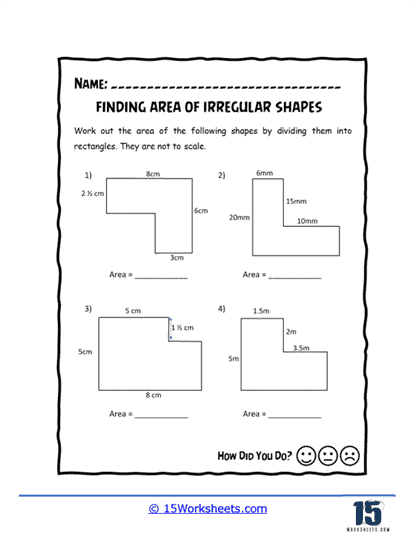
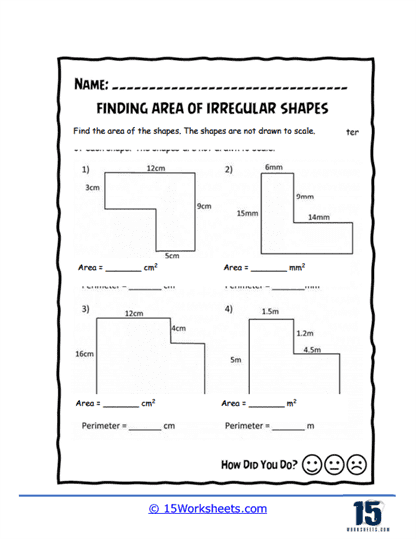
Area of irregular shapes worksheets are designed to help students understand and calculate the area of shapes that do not conform to standard geometric figures. These worksheets guide students through various methods to determine the area of these irregular shapes, often by decomposing them into simpler shapes. By working through these worksheets, students develop a deeper understanding of geometric principles and enhance their problem-solving skills.
Mathematical Skills Explored
Area of irregular shapes worksheets cover a range of mathematical skills, including:
Geometry and Spatial Reasoning – Students learn to visualize and understand the dimensions and shapes of irregular figures. They practice identifying how these shapes can be decomposed into simpler shapes like rectangles, triangles, and squares.
Measurement – These worksheets require students to measure the dimensions of various shapes accurately. They practice using different units of measurement and converting between them as needed.
Algebraic Manipulation – Calculating the area of irregular shapes involves applying multiple algebraic formulas. Students learn to substitute values into these formulas and simplify expressions to find the total area.
Problem-Solving – Working through these exercises enhances students’ problem-solving abilities. They learn to approach complex problems systematically, breaking them down into manageable steps and combining their knowledge of simple shapes to solve for irregular figures.
Exercises and Practice Problems
The worksheets on the area of irregular shapes typically include a variety of exercises and practice problems, such as:
Identification and Labeling – Students begin by identifying the different parts of irregular shapes and the simple shapes they are composed of, such as rectangles, triangles, and squares. They label these dimensions, which are essential for calculating area.
Decomposition into Simple Shapes – The worksheets guide students through the process of breaking down irregular shapes into simpler shapes. Students then use the area formulas for these simple shapes and sum the areas to find the total area of the irregular figure.
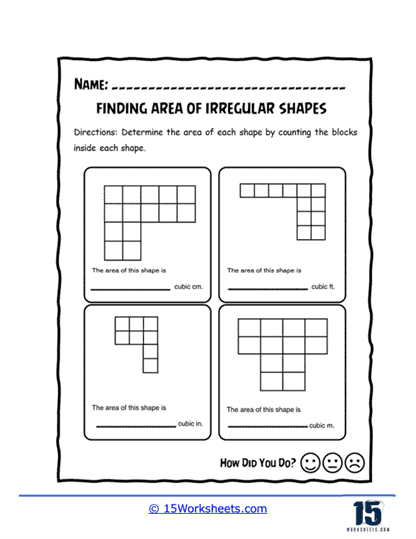
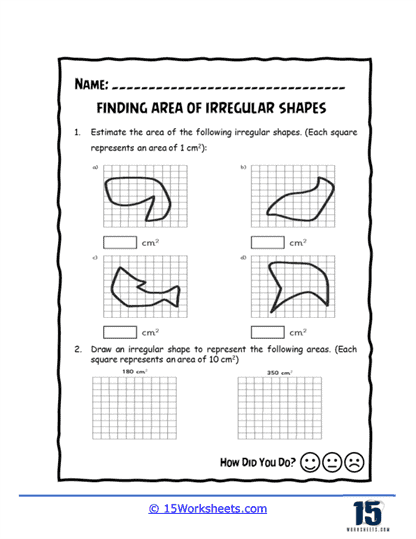
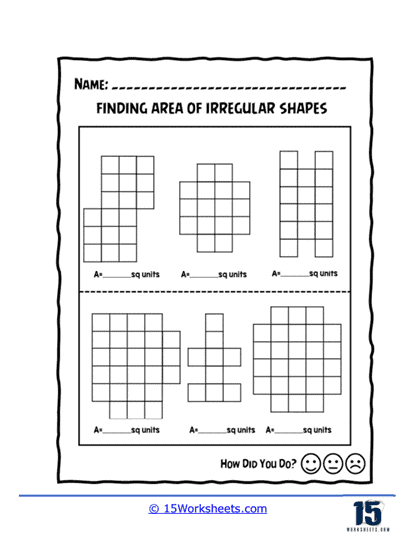
Counting Blocks Method – Some worksheets use a grid system where students count the number of unit squares that make up the irregular shape. This method is particularly useful for younger students or for shapes that can be easily placed on a grid.
Worked Examples – These worksheets include worked examples that demonstrate how to apply the formulas to specific problems. Students follow step-by-step solutions to understand the process of calculating the area of irregular shapes.
Practice Problems – The main component of these worksheets is a series of practice problems. These problems vary in difficulty and complexity, ensuring that students of all skill levels can benefit. Problems may involve calculating the area of a single irregular shape or comparing the areas of multiple figures.
Real-World Applications – Some worksheets incorporate real-world scenarios where students must calculate the area of irregular shapes. These problems help students understand the practical significance of area calculations in everyday life.
Benefits of These Worksheets
Area of irregular shapes worksheets offer several benefits to students:
Enhanced Understanding of Geometry – These worksheets provide a solid foundation in geometry, helping students understand the properties and dimensions of irregular figures.
Improved Mathematical Skills – Students develop a range of mathematical skills, including measurement, algebraic manipulation, and problem-solving, which are essential for success in higher-level math courses.
Practical Applications – By working on real-world problems, students see the relevance of geometry in everyday life and various careers, such as architecture, engineering, and landscaping.
Increased Confidence – Regular practice with these worksheets builds students’ confidence in their mathematical abilities, encouraging them to tackle more challenging problems.
Real-World Examples and Careers
Understanding the area of irregular shapes is crucial in many careers. Here are some real-world examples:
Architecture – Architects need to calculate the area of irregularly shaped plots of land or components of buildings to determine the amount of materials required for construction.
Engineering – Engineers use area calculations to design and build structures with irregular shapes, ensuring efficiency and functionality.
Landscaping – Landscape designers calculate the area of irregular garden beds or lawns to plan planting layouts and estimate the amount of soil or mulch needed.
Example Problem: A garden is shaped like an L. The longer section of the L is 8 meters long and 4 meters wide. The shorter section of the L is 5 meters long and 3 meters wide. Calculate the total area of the garden.
Step-by-Step Solution
1. Identify the dimensions of the two rectangles:
a. Longer section – Length = 8 meters, Width = 4 meters
b. Shorter section – Length = 5 meters, Width = 3 meters
2. Calculate the area of the longer section:
Area Longer = Length x Width = 8 meters x 4 meters = 32 square meters
3. Calculate the area of the shorter section:
Area Shorter = Length x Width = 5meters x 3 meters = 15 square meters
4. Add the areas of the two sections to find the total area:
Total Area = Area Longer + Area Shorter =32 square meters + 15 square meters = 47 square meters
5. Final Answer: The total area of the garden is 47 square meters.