2 Digit Place Value Worksheets
About These 15 Worksheets
Have you ever thought about why we use different places to represent numbers? For instance, in the number 47, why is the ‘4’ in the tens place and the ‘7’ in the ones place? Or how do we know that 50 is more significant than 5? To understand all of these concepts, we use something known as place value, and one of the best ways to learn and practice place value is by using 2 Digit Place Value Worksheets.
These worksheets were developed to help students like you understand the value each digit holds in a two-digit number. For instance, in the number ’25,’ the ‘2’ stands for two tens (or 20), and the ‘5’ stands for five ones (or 5). So, the total is 20+5, which equals 25!
Understanding place value is like learning the foundation of a building. Just as a building needs a sturdy base to stand strong, your math skills need a solid understanding of place value to flourish. By practicing with 2 Digit Place Value Worksheets, you will understand the value each digit has depending on its position in the number. This understanding is important for your math journey because it will help you to solve more complex problems in addition, subtraction, multiplication, and division.
Here are some common types of activities found in two-digit place value worksheets:
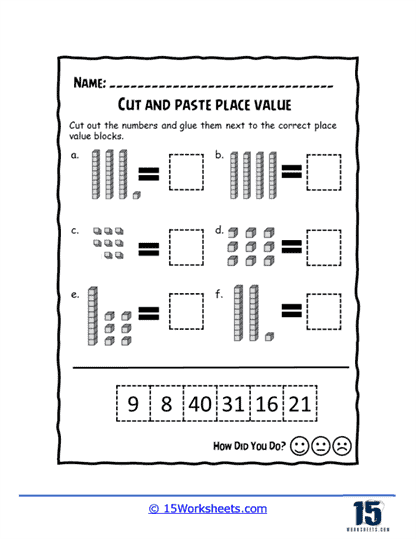
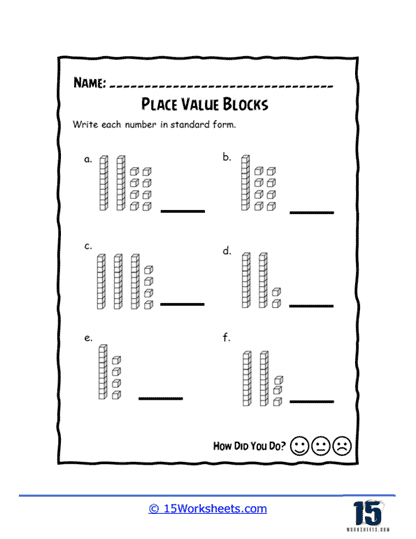
Identifying the value of each digit – Students are presented with two-digit numbers and are required to identify the value of each digit (e.g., tens place and ones place) by writing it down or circling the correct answer.
Writing numbers in expanded form – Students learn to express two-digit numbers in expanded form, which involves breaking down the number into its component parts (e.g., tens and ones) and writing them as an addition expression (e.g., 20 + 5).
Comparing and ordering numbers – Students compare two-digit numbers and determine which one is greater or smaller. They may be asked to use the symbols >, <, or = to indicate the relationship between the numbers. Additionally, students practice arranging numbers in ascending or descending order.
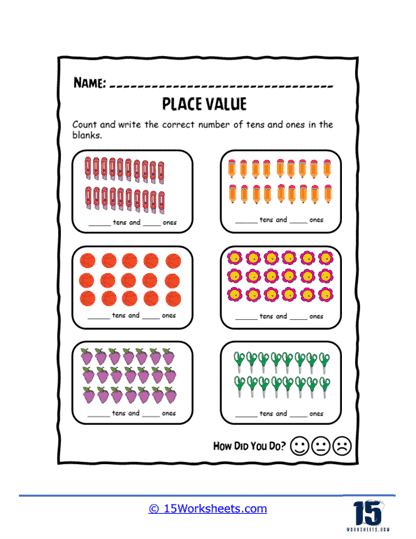
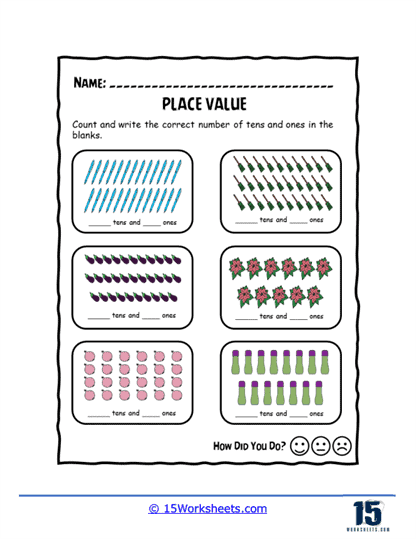
Counting and skip counting – Students practice counting forwards and backward by specific increments, such as counting by tens or counting by fives. This helps reinforce the concept of place value and the patterns observed when counting in different intervals.
Adding and subtracting two-digit numbers – Students solve addition and subtraction problems involving two-digit numbers. These exercises focus on aligning digits in the correct place value positions and carrying or borrowing when necessary.
Place value charts – Students are provided with place value charts and asked to fill in missing digits or write the number represented by a given chart.
What is 2-Digit Place Value?
Place value is a fundamental concept in mathematics that helps us understand the relative worth of digits within a number. It refers to the position or location of a digit within a numeral, which determines its value. When we talk about 2-digit place value, we are specifically discussing the value and significance of the digits in numbers that have two digits, i.e., numbers ranging from 10 to 99.
In a 2-digit number, there are two places:
Tens Place – This is the leftmost position in a 2-digit number. It represents the number of tens in the number. For example, in the number 45, the digit 4 is in the tens place, which means there are 4 tens or 40 in the number.
Ones Place – This is the rightmost position in a 2-digit number. It represents the number of ones in the number. For example, in the number 45, the digit 5 is in the ones place, which means there are 5 ones in the number.
Why Place Values Matter
Place values matter significantly in mathematics for various reasons. They aid in understanding the magnitude or size of numbers. In the context of 2-digit numbers, the digit in the tens place carries much more weight in determining the overall value than the digit in the ones place. For instance, in the number 36, the 3 in the tens place signifies 30, while the 6 in the ones place represents merely 6. Without comprehending place value, it would be challenging to grasp this distinction in magnitude.
Place value plays a pivotal role in arithmetic operations such as addition, subtraction, multiplication, and division. When working with 2-digit numbers, aligning the digits correctly based on their place values is essential to obtain accurate results. Similarly, in multiplication and division, a solid grasp of place value helps position the digits correctly, ensuring the correct outcome.
Place value serves as the foundation for representing numbers in various numeral systems, with the decimal system being the most common. In this system, each digit’s position signifies a power of 10, enabling the concise and precise representation of large numbers. Place value is fundamental for understanding more advanced mathematical concepts such as decimals, fractions, percentages, and powers of ten. Without a firm understanding of place value, grasping these concepts becomes considerably more challenging.
In practical terms, place value is indispensable for problem-solving involving numbers in real-world scenarios. It is essential for financial calculations, measurements, and data analysis, enabling us to interpret and manipulate numerical information accurately.
Place value serves as a critical building block in a student’s mathematical education, typically introduced in early elementary school. A strong grasp of place value is necessary as students progress to more advanced mathematical topics, ensuring a solid foundation for their mathematical skills development. Therefore, the significance of place value cannot be overstated in the realm of mathematics and its practical applications.
How Do These Worksheets Help Students?
Understanding Number Magnitudes – Place value helps us understand how big or small a number is. When you use these worksheets, you’re not just learning to count from one to a hundred; you’re learning that ’50’ means five tens and zero ones, which is more than ’15,’ which is one ten and five ones.
Basic Math Operations – Understanding place value is crucial when you’re adding or subtracting numbers. For example, when adding 37 + 24, we need to know that we’re adding three tens (30) and seven ones (7) to two tens (20) and four ones (4). This becomes much easier once you have mastered place value.
Better Number Sense – With practice, you’ll develop a sense of numbers, which means you’ll instinctively understand what numbers mean and how they relate to each other. For example, you will quickly realize that 45 is smaller than 54, even though they have the same digits.
Preparation for Higher Math – As you grow, you will encounter larger numbers and more complex math problems. Mastery of place value in two-digit numbers prepares you to understand three-digit numbers, four-digit numbers, and so on.
Error Detection – Understanding place value can also help you spot errors in your calculations. If you know the value of each digit in a number, you are less likely to make mistakes when doing math operations.