D'Nealian Style Print Worksheets
All About These 15 Worksheets
D’Nealian Style Print handwriting worksheets provide a structured and effective approach for students to develop and refine their handwriting skills in this unique style. The exercises in these worksheets are designed to cater to different stages of learning, ensuring a gradual and comprehensive mastery of D’Nealian handwriting. The benefits of practicing with these worksheets extend beyond improved handwriting, impacting fine motor skills, cognitive development, and ease of transition to cursive writing. For students and educators alike, these worksheets are valuable tools in the journey towards achieving excellent penmanship.
This technique is named after its creator Donald Neal Thurber, it is a unique style of writing and a popular teaching method introduced in the 1970s. This style is known for its distinct slanted letters and smooth transitions to cursive writing. These worksheets are specifically designed to teach this style. These worksheets offer a variety of exercises aimed at developing the handwriting skills of students, particularly those in the early stages of their writing education. The D’Nealian method bridges the gap between print writing and cursive, making the transition easier for students.
Types of Exercises
Basic Stroke Practice – The foundation of D’Nealian handwriting is mastering its unique strokes. These include slanted lines, curves, and hooks. Worksheets often begin with exercises where students practice these basic strokes, essential for forming D’Nealian characters. Although this print does not connect letters as in cursive, it introduces elements that make the transition to cursive smoother. Worksheets include exercises that practice slight connections or proximity between letters.
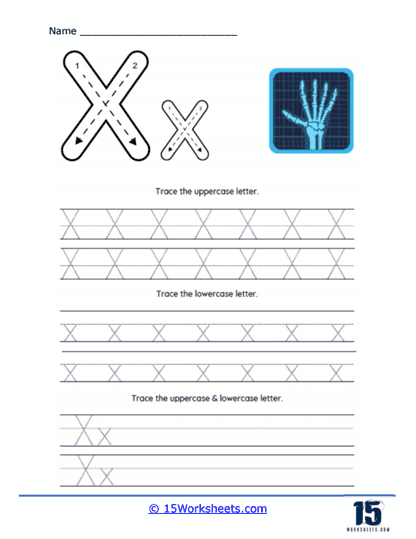
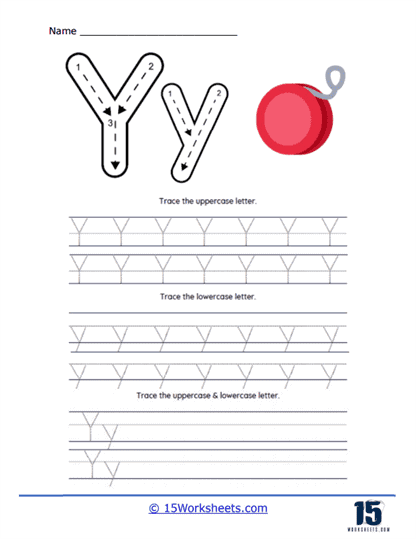
Letter and Word Formation – D’Nealian handwriting worksheets provide exercises for writing each letter of the alphabet. These exercises focus on the specific slant and shape of the letters, both uppercase and lowercase. They usually start with tracing exercises, followed by independent writing. After mastering individual letters, students practice forming words. This practice is crucial as it teaches consistent letter size, spacing, and the unique slant of D’Nealian handwriting within words.
Sentence Writing – Writing sentences in D’Nealian style helps students apply their skills in a more practical context. It also teaches them to maintain consistency in letter size and spacing across longer text formats. These exercises involve copying a text written in D’Nealian style. This practice reinforces the letter shapes and the overall style of D’Nealian handwriting.
Transition to Cursive – As students become proficient in D’Nealian print, worksheets often introduce elements of D’Nealian cursive. This gradual introduction helps ease the transition to fully cursive writing. Besides letters, worksheets include exercises for writing numerals and punctuation marks in the D’Nealian style, ensuring a comprehensive understanding of the font. Proper spacing between letters and words is crucial for legibility. Worksheets include exercises focusing on maintaining uniform spacing and alignment.
The Benefits
Easier Transition to Cursive
The primary advantage of the D’Nealian style is its seamless transition to cursive writing. The unique slants and shapes of the letters are designed to evolve naturally into cursive forms. Regular practice with D’Nealian worksheets leads to more legible and aesthetically pleasing handwriting. The distinct characteristics of the D’Nealian style, such as its slant and letter formation, contribute to this clarity. The practice of D’Nealian handwriting aids in the development of fine motor skills. The unique strokes and connections require precise hand movements, strengthening the muscles in the hands and fingers.
Consistency in Writing
Over time, students accustomed to the D’Nealian style often find that their writing speed improves. The slightly connected letters facilitate a smoother, faster writing motion. D’Nealian handwriting worksheets emphasize consistent letter size, shape, and spacing, leading to a more uniform style of writing. As students improve their handwriting and find it easier to transition to cursive, their confidence in their writing abilities increases.
Connections to Improved Reading Skills
Better handwriting and penmanship can play a crucial role in enhancing a child’s reading abilities. Firstly, practicing good handwriting helps children become more acquainted with the shapes and forms of individual letters. This familiarity with letters aids in their ability to identify and distinguish between letters when reading, reducing the chances of confusing similar-looking characters and ultimately improving reading accuracy.
As children engage in handwriting practice, they naturally develop visual discrimination skills. Paying close attention to the nuances of each letter allows them to better differentiate between various letters and recognize subtle differences in font styles and handwriting variations while reading text. This skill is particularly valuable in the context of reading comprehension.
Improved handwriting is also closely linked to the development of fine motor skills. As children gain better control over their hand movements, they can manipulate a pencil or pen more efficiently. This increased manual dexterity leads to smoother and faster writing, ultimately enhancing reading fluency by allowing children to focus more on understanding the text rather than grappling with the mechanics of writing.
The hand-eye coordination required for handwriting transfers seamlessly to reading. Children with better handwriting skills tend to have improved abilities to track words and sentences on a page, follow lines of text, and maintain their place while reading without losing their position. This coordination simplifies the reading process, making it less challenging for young readers.
Improved handwriting fosters confidence and engagement with written materials. Children who feel confident in their ability to write neatly and legibly are more likely to approach reading with enthusiasm. This boost in confidence can translate into increased motivation to practice and develop their reading skills.